التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط قد يتحول بسرعة لالتهاب شديد في حال عدم علاجه جيداً، لنتعرف أكثر على أعراض الزائده وكيفية علاج الالتهاب في مراحله الخفيفة.
قد يتم علاج التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط بدون الحاجة لإجراء عملية جراحية لاستئصال الزائده، وهنا تكمن فائدة كشف اعراض التهاب الزائدة مبكراً قبيل تطور الحالة وظهور حاجة ملحة لعملية إزالة الزائدة بشكل إسعافي.
الشعور المفاجئ بألم حاد في الجزء الأيمن من أسفل البطن يعتبر من أهم علامات الزائدة الملتهبة، وعلى الرغم من أن الألم هو العرض الأشيع للزائدة إلا أنه قد لا يظهر إلا بعد مراحل متأخرة من حدوث الإلتهاب، وبالنسبة لالتهاب الزائدة عند الأطفال قد يعجز الطفل عن التعبير جيداً عن شعوره بالألم، فما هي الأعراض الأخرى للالتهاب البسيط وكيف يتم العلاج؟
لمحة عن التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط
عادة ما يبدأ التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط على شكل عوارض وعلامات خفيفة تجعل تشخيصه الباكر أمراً صعباً بعض الشيء، فقد يظن مريض الزايده أن ألم بطنه هو مجرد مغص بسيط ناتج عن الإكثار من تناول الطعام.
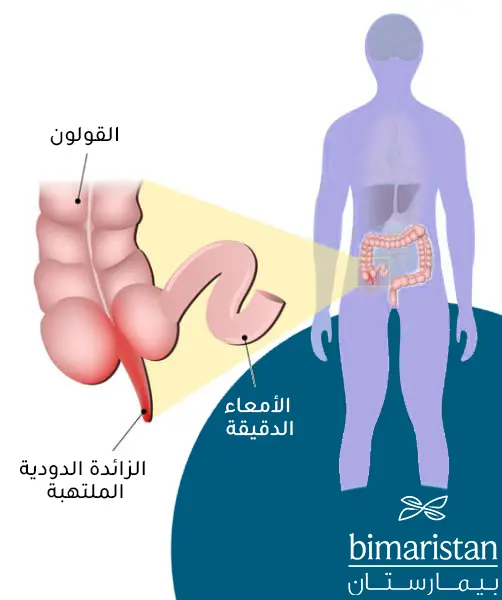
التهاب الزائدة الدوديّة هو حالة شائعة للغاية وتعتبر من الأسباب المهمة لآلام البطن التي تستدعي إجراء عمل جراحي للعلاج، إذ يصاب حوالي 5% من سكان العالم بالتهاب الزائدة، وأكثر ما يشاهد الالتهاب عند الشباب في سن العشرينات ولكنه قد يصيب الجميع باختلاف أعمارهم.
الزائدة الدودية هي عبارة عن عضو صغير الحجم له شكل الإصبع، تتصل الزائدة مع القولون على الجانب السفلي والأيمن للبطن، ما تزال وظيفة الزائده غير مفهومة جيداً ويعتقد الأطباء بأنها تشكل مخزناً للبكتيريا النافعة للجسم، إذ يمكن للإنسان عيش حياته بصورة طبيعية دون وجود الزائدة الدودية.
على الرغم من أن التهاب الزائدة البسيط قابل للعلاج وعادة ما يشفى المريض نهائياً منه إلا أن التأخير في علاجه قد يسبب بعض المضاعفات الخطيرة والمهددة لحياة الإنسان، لذا من الضروري الإحاطة بأعراض الالتهاب لكشفه أبكر ما يمكن.
ما هي أعراض التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط؟
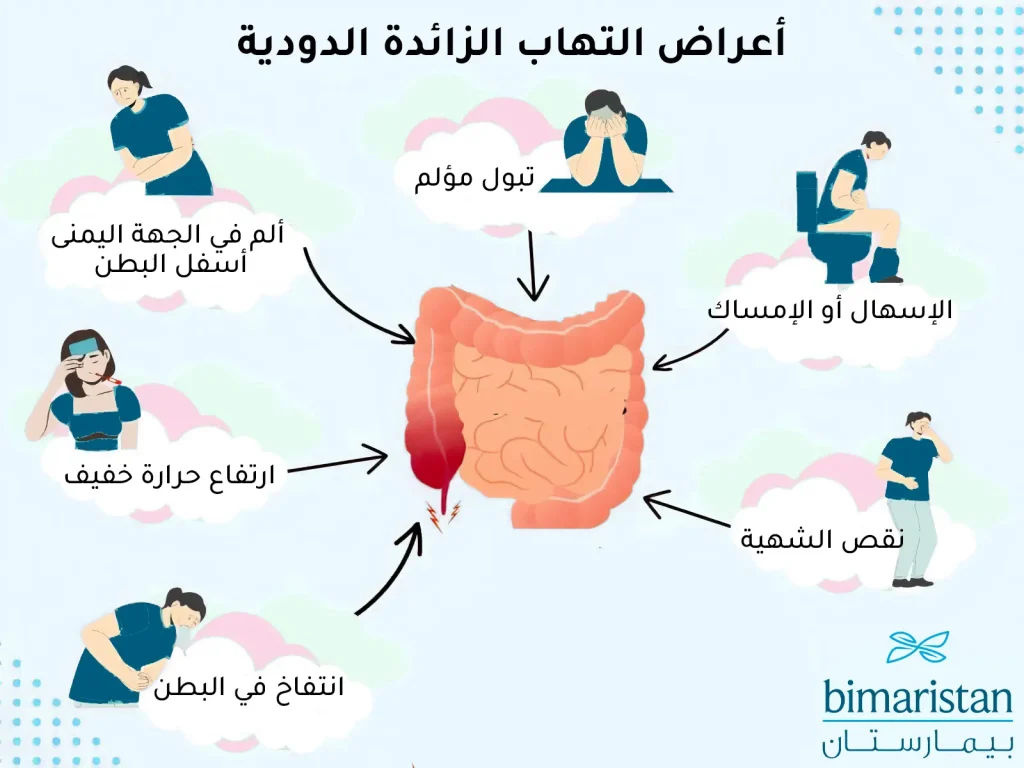
قد تختلف اعراض الزائدة من مريض لآخر بحسب شدة الالتهاب وعمر المريض، وقد تختلط في بعض الأحيان علامات التهاب الزائدة مع أمراض هضمية أخرى تسبب عوارض مشابهة.
تزداد شدة الأعراض تدريجياً عند مرضى الزائده بازدياد شدة الالتهاب، ومن أهمها ما يلي:
- ألم مفاجئ في الجهة اليمنى من البطن يشتد عند الحركة والسعال
- يصبح الألم شديد للغاية مع مرور الوقت
- الغثيان والإقياء
- نقص الشهية للطعام
- ارتفاع حرارة طفيف (حمى خفيفة)
- إسهال أو إمساك مع رغبة بالتغوط
- انتفاخ في البطن
- كثرة التبول
أسباب التهاب الزائدة الدودية
إن السبب الرئيسي لحدوث التهاب الزايدة البسيط ما يزال غير معروف تماماً، ولكن يوجد اعتقاد بأن الالتهاب يحصل نتيجة انسداد جزء من نسيج الزائدة بعائق يؤدي إلى انتفاخ الزائده والتهابها.
قد يكون العائق المسبب للالتهاب هو تجمع بقايا برازية بالزائدة أو كتلة ورمية أدت للانسداد، وفي كلتا الحالتين يتسبب الانسداد بتورم وكبر حجم الزائده وقد تنفجر الزائدة عند تأخير علاج الالتهاب.
بعض العوامل قد تساهم في زيادة خطر إصابة الفرد بالتهاب الزائدة البسيط ومن بينها:
- إصابة سابقة لأحد أفراد العائلة بالالتهاب
- المراهقين والشباب هم أكثر عرضة لالتهاب الزائدة الدودية من كبار السن
- الذكور معرضين بشكل أكبر للالتهاب من الإناث
- التهابات الجهاز الهضمي السابقة
كيفية علاج التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط
بالنسبة لحالة التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط فإن الالتهاب قد يشفى بدون جراحة عند تشخيصه ومعالجته باكراً، ولكن عندما يتطور التهاب الزائدة لمراحل شديدة تصبح عملية إزالة الزائدة الدودية خيار لا مفر منه.
التهاب الزائدة الدودية الشديد قد يسبب مضاعفات خطيرة على حياة الإنسان، لذا فإن التدبير والعلاج السريع للالتهاب قد يحمي المريض من مخاطر الزائدة الملتهبة، بالإضافة إلى أن المعالجة تكون بسيطة في المراحل الخفيفة من الالتهاب.
يتم تدبير التهاب الزائدة البسيط عبر أحد الطرق التالية:
علاج الزائدة الدودية بالمضادات الحيوية
الأدوية المضادة للبكتيريا هي العلاج الأول الذي يعطى لمرضى التهاب الزائدة عند وصولهم إلى المستشفى، تعطى هذه الادوية عبر الوريد وتفيد في محاربة البكتيريا للتقليل من شدة الالتهاب إضافةً لمنع انتشار الجراثيم إلى أعضاء مجاورة في البطن.
في بعض حالات التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط قد تكون المعالجة الدوائية كافية للشفاء من التهاب الزائده، فقد يتحسن مريض الزائدة وتخف أعراضه باستخدام المضادات الحيوية فقط ولا يحتاج إلى القيام بعملية جراحية لإزالة الزائدة.
بعض الأمثلة عن أدوية التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط ما يلي:
- سيفترياكسون Ceftriaxone
- سيفوتاكسيم Cefotaxime
- جنتاميسين Gentamicin
- الأمبيسلين Ampicillin
عملية استئصال الزائدة الدودية
يتم إزالة الزائدة الدودية الملتهبة في معظم حالات الالتهاب التي لا تتحسن باستعمال المضادات الحيوية، تجرى العملية إما بالجراحة التقليدية (فتح البطن) أو عن طريق المنظار.
يتميز المنظار بأنه طفيف التوغل وذو خطورة أقل من الجراحة المفتوحة للبطن، كما أن فترة التعافي بعده قليلة إذ يتمكن المريض من العودة لممارسة نشاطاته اليومية بسرعة أكبر.
عادةً ما تجرى العملية مباشرةً دون تأخير خوفاً من احتمال تمزق الزائدة وانفجارها المهدد للحياة، اقرأ المزيد عن عملية الزائدة الدودية بالمنظار.
مضاعفات التهاب الزائدة الدودية
قد تؤدي الزائدة الملتهبة إلى حدوث بعض المضاعفات عند إهمال علاجها جيداً، ومن أخطر الاختلاطات التي قد يسببها الالتهاب هو تمزق الزائدة وانتشار البكتيريا إلى مناطق مجاورة والتسبب بما يعرف بالتهاب البريتوان وهو حالة طبية خطيرة قد تسبب وفاة المريض.
قد يحدث أيضًا تجمع خراج قيحي داخل الزائدة مما يتطلب إجراء تصريف للخراج قبل عملية الزائدة الدودية.
وبالنهاية فإن التهاب الزائدة الدودية البسيط هو مرض كثير الشيوع بين عامة الناس وخاصة عند فئة الشباب والأطفال، قد يتظاهر بأعراض بسيطة تجعل كشفه الباكر صعباً بعض الشيء فيتحول بسرعة إلى التهاب شديد يتطلب جراحة لعلاجه، ولكن عند تشخيص المرض باكراً قد يستعاض عن الجراحة بالأدوية المضادة للبكتيريا والتي قد تكون كافية للشفاء التام من الالتهاب.
المصادر:

