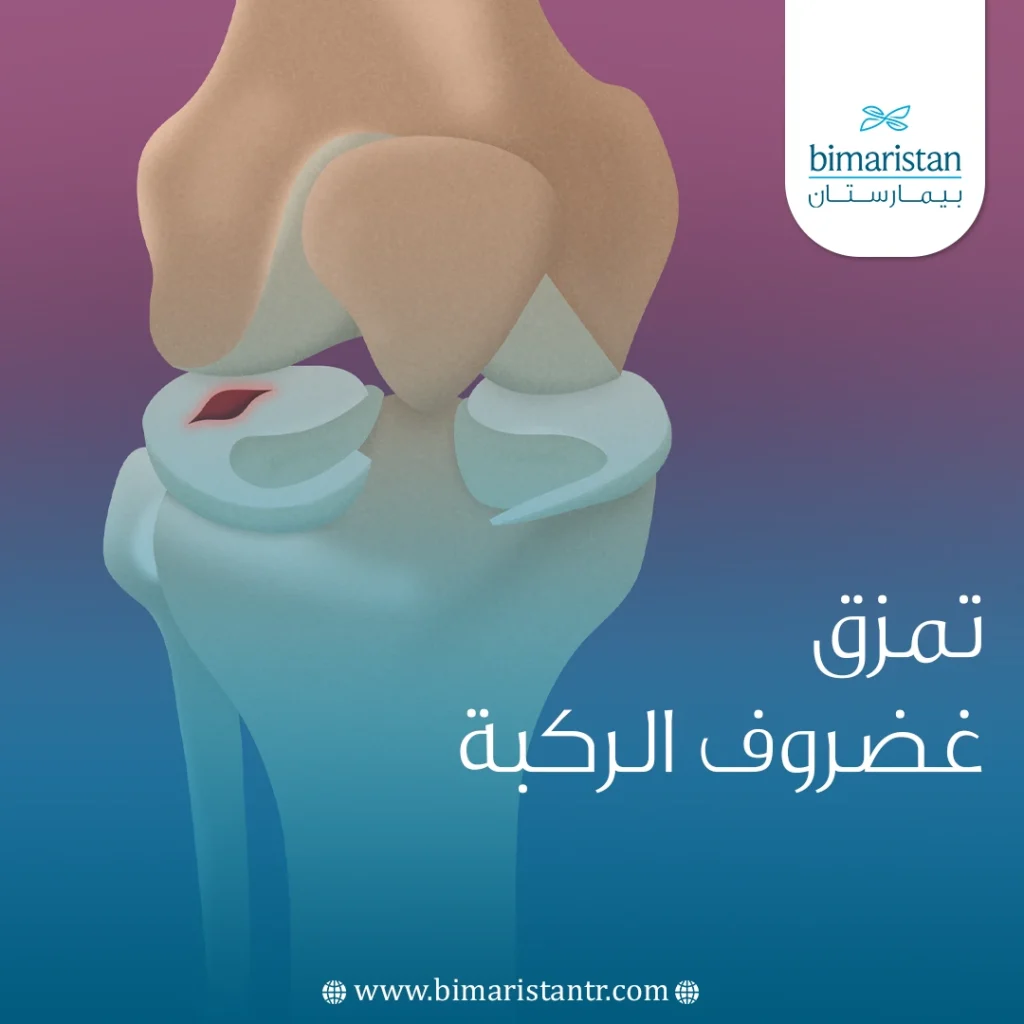
تمزق غضروف الركبة أحد أكثر الإصابات شيوعًا عند الرياضيين، يسبب قطع الغضروف المفصلي للركبة أعراض عدة، فكيف يحدث هذا التمزق وكيفية علاجه.
إن كيفية علاج تمزق غضروف الركبة يعتمد على شدة الإصابة الحاصلة بالغضروف، فقد يكون العلاج بسيطاً للغاية، وقد نحتاج في الحالات الشديدة لتداخل جراحي.
يوجد في كل ركبة من ركبتيك قطعتين من غضاريف هلالية على شكل حرف C، تأخذ هذه الغضاريف دور وسادة مزلقة لتسهيل الحركة بين عظمي الفخذ والساق، وتعمل على حماية ساقك من الضغط الناتج عن حمل وزن الجسم.
ما هو تمزق غضروف الركبة؟
يحصل تمزق غضروف الركبة Torn meniscus نتيجة القيام بحركة خاطئة تؤدي لتمزق الغضروف، مثل تغيير اتجاه الحركة المفاجئ الذي يؤدي إلى التواء بالركبة، أكثر ما يشاهد التمزق الغضروفي عند لاعبي كرة القدم والرياضيين عموماً.
بالنسبة لكبار السن فإن الأمراض التنكسية التي تصيب مفصل الركبة قد تساهم في زيادة خطر تمزق الغضروف بدون التعرض لحادث رضي شديد.
عند تمزق الغضروف المفصلي للركبة سوف تشعر بألم وقد تلاحظ احمرار وتورم في ركبتك، قد لا يكون الشعور بهذه الأعراض فوري وقد لا تظهر إلا بعد مرور 24 ساعة من التعرض للإصابة
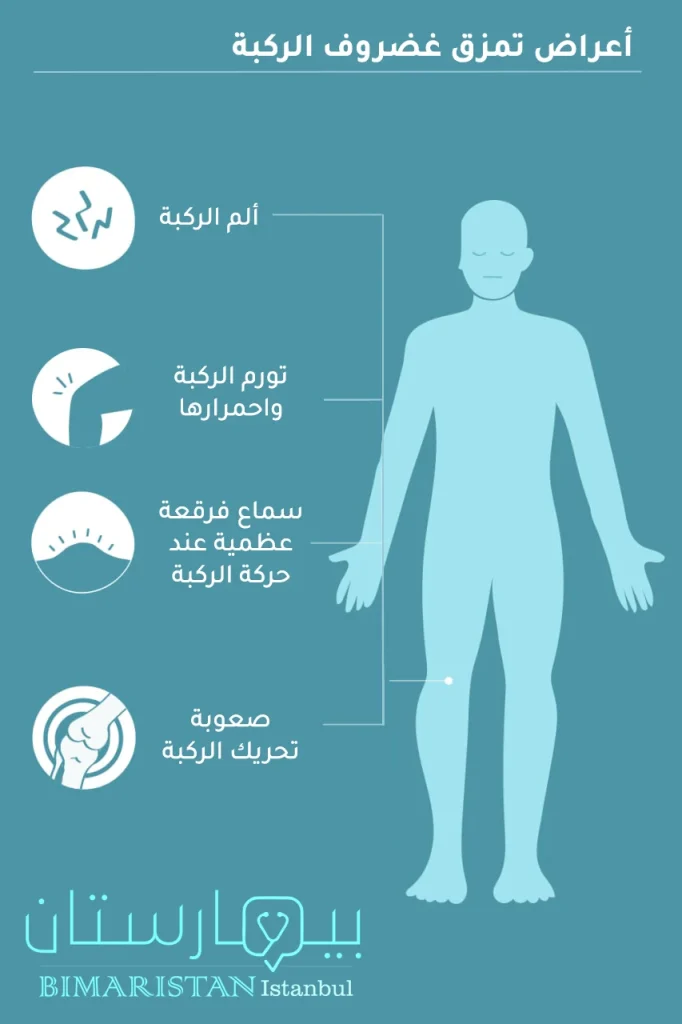
أعراض تمزق غضروف الركبة
تختلف أعراض تمزق غضروف الركبة من شخص لآخر بحسب شدة الإصابة ودرجة التمزق، ففي الدرجات الخفيفة للتمزق قد لا تكون الأعراض ظاهرة إلا بعد مرور يوم أو يومين من وقوع الإصابة.
من أهم العلامات المنذرة بتمزق غضروف الركبة ما يلي:
- الألم الذي يشتد عند محاولة تدوير الركبة
- تورم واحمرار
- صعوبة القدرة على تحريك المفصل (البسط أو الثني)
- سماع صوت فرقعة عظمية
- العرج أثناء الحركة
- تيبس بالمفصل
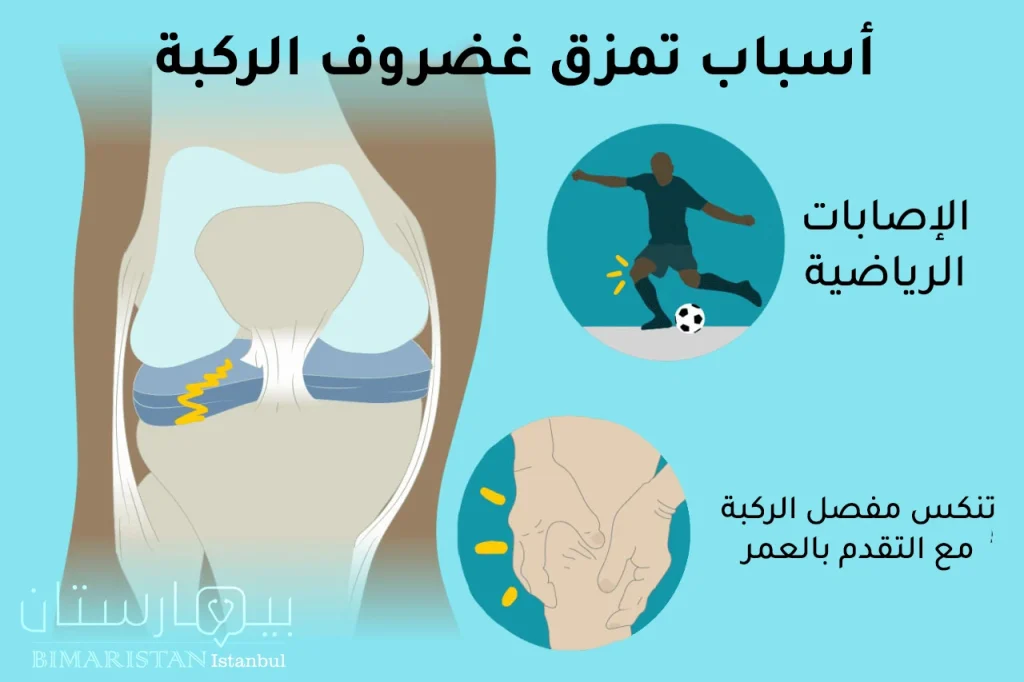
أسباب قطع غضروف الركبة
كما أسلفنا سابقاً فإن الإصابات الرياضية هي أشيع المسببات لحدوث تمزق بغضروف مفصل الركبة، ومن عوامل الخطورة التي تزيد من خطر حصول التمزق:
- التقدم بالعمر (أكبر من 60 سنة)
- التهاب المفاصل أو ما يعرف بالفصال العظمي
- إصابة سابقة بتمزق الرباط الصليبي الأمامي
- الذكور عرضة للتمزق بشكل أكثر من الإناث
- رفع الأوزان الثقيلة
- لاعبي كرة القدم
درجات تمزق غضروف الركبة
تم تصنيف تمزّق غضروف الركبة لعدة درجات تبعاً لشدة القطع الحاصل للغضروف، تساعد درجة تمزق الغضروف في تحديد طريقة العلاج الأنسب للمريض ومتى نحتاج لإجراء تداخل جراحي، فتكون الدرجات على الشكل الآتي:
الدرجة الأولى لقطع غضروف الركبة
مرحلة خفيفة لإصابة الغضروف وغالباً ما تشفى تلقائياً بالراحة بعد أسبوع أو أسبوعين ولا تستدعي الحاجة لعمل جراحي، يصبح الغضروف بهذه الدرجة طري وقد يلاحظ انتفاخ وتورم مع إحساس بالألم.
تفيد الأطعمة الغنية بفيتامين د بتسريع الشفاء، بالإضافة إلى الدور المهم للمعالجة الفيزيائية وإعادة التأهيل في التئام قطع الغضروف.
تمزق غضروف الركبة من الدرجة الثانية
التمزق هنا متوسط الشدة وقد توجد شقوق لا يزيد طولها عن 1.5 سم بالغضروف ولا يصل الشق إلى ما تحت عظم الغضروف.
بالنسبة للعلاج فقد يكتفي الأخصائي بوصف أدوية مضادة للالتهاب ومسكنة للألم مع نصح المريض بإراحة ركبته، تفيد أيضاً التمارين الخاصة بالعلاج الفيزيائي في تسريع التعافي.
تمزق الغضروف من الدرجة الثالثة
يكون التمزق هنا ذو خطورة معتبرة ويجب أن يولى اهتماماً خاصاً، يزيد الشق بالغضروف عن 1.5 سم وقد يصل للعظم ما تحت الغضروف.
تستدعي هذه الدرجة في أغلب الأحيان إجراء عمل جراحي لإصلاح تمزق غضروف الركبة.
تشخيص تمزق غضروف الركبة المفصلي
غالباً ما يشخص الطبيب تمزق غضروف الركبة عبر الفحص السريري وملاحظة علامات وأعراض الإصابة، سيسأل عن وجود قصة رض سابق بالإضافة إلى بضع أسئلة أخرى عن التاريخ المرضي.
قد يلجأ طبيب العظام إلى طلب إحدى الفحوصات التالية:
التصوير بالأشعة السينية X-rays
يعد من طرق التشخيص المستعملة لنفي وجود إصابات أخرى كوجود كسور في الركبة مسببة للألم، يتم تسليط أشعة سينية تقوم بإظهار عظام مفصل الركبه، لا يظهر الغضروف الهلالي على صورة الأشعة.
الرنين المغناطيسي MRI
هو الأكثر مقدرة على كشف تمزُّق غضروف الركبة، يعتبر من تقنيات التصوير المعتمدة على توجيه حقل مغناطيسي قوي يسمح بإظهار النسيج الرخو والصلب للركبه، حيث يمكن رؤية غضروف الركبة الهلالي بواسطة هذه التقنية.
علاج تمزق غضروف الركبة بدون جراحة
يعتمد اختيار الطريقة المناسبة في العلاج على مكان التمزق ودرجته والأسباب التي أدت لحدوثه، فالجراحة ليست دائماً مستطبة وقد يشفى التمزق الخفيف بالغضروف تلقائياً دون الحاجة لأية تداخلات علاجية.
أما في حالات تمزق غضروف الركبة ذو الدرجة المتقدمة والذي لا يمكن أن يلتئم بشكل تلقائي، يكون العمل الجراحي مستطباً وغالباً ما يجرى باستخدام منظار الركبة.
من أفضل العلاجات الغير جراحية لتدبير تمزق الهلال بالركبة ما يلي:
علاج إصابة الغضروف بالراحة
الاستلقاء وتجنب تحريك المفصل يساعد في تخفيف آلام الركبة وتسريع شفاء تمزق الغضروف، استخدام العكازات يساعد أيضاً في حالة المعاناة من ألم كبير خلال المشي.
علاج تمزق غضروف الركبة بواسطة الأدوية
إن الدور الرئيسي للأدوية هو تسكين الألم المرافق لقطع الغضروف، فمضادات الالتهاب اللاستيروئيدية كالإيبروفين أو الأسبرين تقلل من تورم الركبة والألم الذي يلي الإصابة.
تطبيق الثلج على منطقة الألم
وضع الثلج على الركبة يخفف من الاحمرار والتورم المرافق لتمزق الغضروف الهلالي، استخدم كيس بارد حاوي على ثلج أو خضروات مجمدة وقم بوضع الكيس على منطقة الإصابة لفترة تقدر بـ 20 دقيقة، أعد هذه العملية لعدة مرات باليوم.
العلاج الطبيعي للركبة
يعمل العلاج الفيزيائي على تقوية العضلات لزيادة صلابة الركبة واستقرارها، تجرى المعالجة الفيزيائية بطرق مختلفة تحت إشراف أخصائيين، يمكنك القراءة أكثر عن العلاج الطبيعي.
عملية تمزق غضروف الركبة
عندما يكون تمزق الغضروف الهلالي غير مستجيب للعلاجات الأخرى ولا تظهر أية علامات لشفاء التمزق، والألم لا يخف مع مرور الوقت، عندها تظهر الحاجة لإجراء عمل جراحي.
تعتبر عملية غضروف الركبة وسيلة فعالة لإصلاح تمزق الغضروف وخاصةً عند الأطفال والشباب، عند تعذر إصلاح التمزق يمكن استئصال الغضروف الممزق باستخدام منظار الركبة.
في الحالات المتقدمة من تمزق الغضروف المفصلي المترافق مع تنكس بمفصل الركبة تصبح الجراحة اكثر تعقيداً وقد يُنصح بإجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة الكامل.
تقسم عمليات الغضروف الهلالي إلى:
عملية إصلاح تمزق غضروف الركبة بالمنظار
من الإجراءات طفيفة التوغل قليلة الخطورة لعلاج أذية الغضروف الهلالي، وهو عبارة عن منظار أنبوبي صغير مجهز بكاميرا ومصباح، يجري إدخاله لمفصل الركبة عبر إحداث شق جراحي ضيق.
بواسطة منظار الركبة المتصل مع شاشة فيديو يتمكن جراح العظم من رؤية مفصل الركبة من الداخل، ويستطيع إصلاح التمزق بالغضروف الهلالي أو استئصاله بحسب شدة الحالة.
بعد الانتهاء من علاج القطع في الغضروف المفصلي، تستخدم الغرز الجراحية لإبقاء الغضروف ثابتاً في مكانه حتى يشفى ويلتئم التمزُق، يميل الشفاء لكونه أسرع عند الصغار بالمقارنة مع كبار العمر.
عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة
يُحتفظ بهذا الإجراء للحالات المعقدة من تمزق الغضروف بدرجة شديدة مع وجود تآكلات، غالباً ما يتم اللجوء لهذه العملية عند الكبار المصابين بالتهاب مفصل الركبة التنكسي.
يقوم الجراح باستبدال مفصل الركبة المتضرر بِشكل كامل أو جزئي، ثم يضع مفصل صناعي بديل في منطقة الاستبدال، يمكنك الاطلاع أكثر على عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة.
بالنهاية فإن تمزق غضروف الركبة هو من الأذيات الشائعة التي تحدث عند ممارسة بعض الرياضات، له درجات مختلفة ويشفى دون علاج في المراحل الخفيفة، لكن الدرجات المتقدمة للأذية قد تستدعي الحاجة للجراحة، تقوية العضلات الداعمة للركبتين عبر ممارسة التمارين يساهم في الوقاية من حدوث هذا التمزق، وتذكر بأن استشارة الطبيب عند الشعور بألم في الركبة أمر هام لبدء العلاج باكراً قبل تطور الحالة.
المصادر: