عند إصابة طفلك بالتهاب الأذن سوف تظهر عليه أعراض ارتفاع الحرارة والتعب مع آلام بالأذن، لا داعي للقلق حيث يمكن بسهولة علاج التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الأطفال في المنزل.
تعتبر التهابات الأذن الوسطى أحد أكثر الأمراض شيوعاً عند الأطفال، 80% من أطفال العالم سيصابون بعدوى الاذن الوسطى مرة واحدة على الأقل في حياتهم وفقاً للدراسات.
أكثر ما يصيب هذا المرض الرضع من عمر 6 أشهر إلى سنتين، لكن يبقى الجميع عرضة للإصابة بالعدوى فقد تحدث أيضاً عند البالغين لكنها أقل انتشاراً.
أعراض التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الأطفال
قد تظهر اعراض التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الأطفال بشكل مخاتل ولا تكون موجهة للمرض، فغالباً ما نشاهد أعراض عامة كالحمى، نقص الشهية، البكاء، التهيج مع رفض الرضاعة.
ألم الأذن وضعف السمع من الأعراض الشائعة لالتهاب الاذن الوسطى، لكن الطفل قد لا يستطيع التعبير بشكل جيد عنهم، فلن يخبرك طفلك الرضيع بأنه يعاني من ألم في الاذن، يجب عليك كأم أو أب ملاحظة أعراض عدوى الأذن الوسطى للبدء بعلاجه.
قد يحدث إلتهاب الاذن الوسطى otitis media ويشفى تلقائياً دون ملاحظة أعراضه، نذكر أهم أعراض التهاب الاذن عند الاطفال:
- أذن مؤلمة يعبر عنها من خلال شد الأذن وفركها
- التهيُّج والبكاء
- الترفع الحروري
- نقصان الشهية
- صعوبة النوم وذلك لأن الألم يشتد عند الاستلقاء على طرف الاذن الملتهبة
- ضعف السمع
- خروج السوائل من الاذن الملتهبة

أسباب التهابات الأذن الوسطى
يعود سبب الإصابة بالتهاب الأذن عند الأطفال إلى عدوى بكتيرية أو فيروسية تنتقل للأذن الوسطى من خلال قناة أستاكيوس، تصل هذه القناة بين الأذن المتوسطة والبلعوم الأنفي وتعمل على تصريف السوائل ومنع تجمعها بالأذن الوسطى.
عند انسداد قناة استاكيوس يحدث تراكم للسوائل بالأذن الوسطى، غالباً ما يؤدي التهاب الجهاز التنفسي العلوي (الرشح أو الزكام) إلى تورم بالقناة وانسدادها.
يكون مجرى استاكيوس عند حديثي الولادة صغير وذو انحدار اقل مما هو عليه عند الكبار، يزيد هذا الأمر من فرص الانسداد وحدوث التهاب أذن وسطى عند الرضع.
تشخيص عدوى الأذن عند الأطفال
يستفسر الطبيب عن القصة المرضية للطفل ويطرح بعض الاسئلة عن الحالة والأعراض والسبب الذي دفع الأهل لاستشارته.
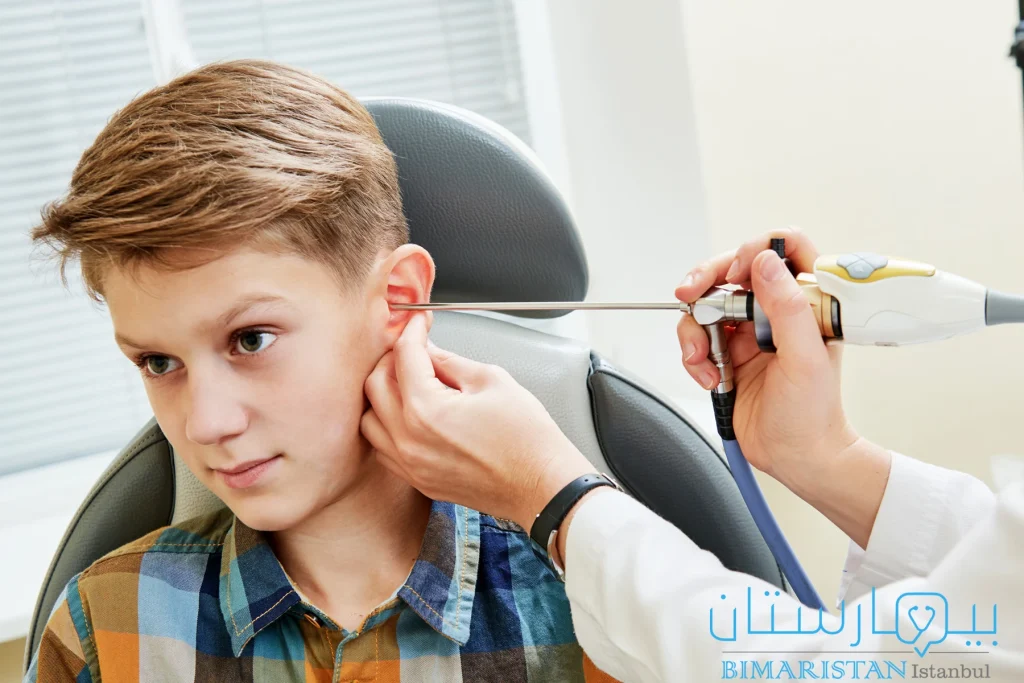
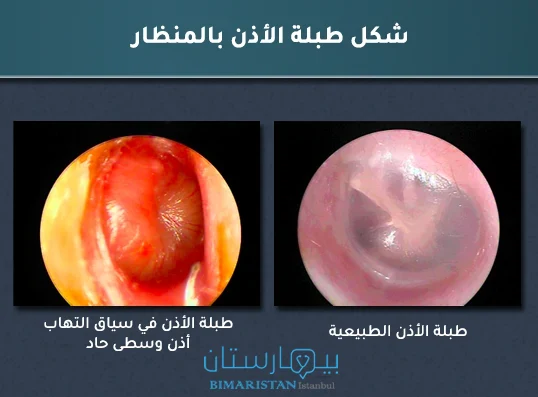
يستخدم الطبيب منظار الأذن لفحص أذن الطفل، يتم إدخال المنظار عبر مجرى السمع وصولاً إلى طبلة الأذن، يجري البحث عن علامات التهاب الطبلة كالاحمرار والتورم.
قد يجري الأخصائي بعض المناورات لتقييم قابلية غشاء الطبل على الحركة، ففي حال الالتهاب وتجمع السوائل في الأذن الوسطى تصبح الطبلة ثابتة غير قابلة للحركة.
كيفية علاج التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الأطفال
علاج التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الأطفال يشابه لحدٍ كبير التهاب الأذن عند للكبار، يعتبر العلاج ذو فعالية كبيرة وتكون نتائجه شافية في طبيعة الحال.
إن طريقة العلاج المناسبة تعتمد على عوامل عديدة منها شدة الالتهاب وطبيعته بالإضافة إلى عمر الطفل، فقد نكتفي في بعض الحالات بالمراقبة فقط.
قد يشفى التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الأطفال بشكل تلقائي دون أية معالجة، فقد يكتفي الطبيب بوصف مسكنات لعلاج الأعراض كتدبير آلام الأذن أو قد لا يصف شيئاً ويراقب الحالة.
بالنسبة للمضادات الجرثومية فإنها تعطى في الحالات الأشد والتي يكون التهاب الأذن فيها بسبب وجود البكتيريا، لا نلجأ إليها عند الإصابة بإنتان فيروسي وفي الحالات خفيفة الشدة.
تكون طرق المعالجة على الشكل الآتي:
الانتظار والمراقبة
عادةً ما تتحسن أعراض التهاب الاذن الوسطى في غضون أول يومين من الإصابة، ومعظم التهابات الأذن عند الأطفال تشفى بشكل نهائي بعد مرور أسبوع إلى أسبوعين دون تلقي أية معالجة.
توصي الجمعية الأمريكية لطب الأطفال بالانتظار والمراقبة في إحدى هذه الحالات:
- الصغار من عمر 6 شهور إلى سنتين المصابين بدرجة خفيفة من الألم بأذن واحدة منذ اقل من 48 ساعة بشرط ألا تتجاوز حرارتهم 39 درجة.
- الاطفال الأكبر من سنتين والذين يعانون من ألم خفيف بأحد الأذنين أو كلتاهما منذ اقل من يومين، ويشترط أيضاً ألا تتجاوز حرارتهم 39 درجة.
علاج ألم الاذن في المنزل
قد يسبب التهاب الأذن الوسطى آلام شديدة عند صغار السن ولا سيماً في فترات النوم، لتخفيف الألم يمكن استعمال المسكنات الفموية كالأيبوبروفين أو أسيتامينوفين، يجب توخي الحذر من استخدام الأسبرين عند الأطفال خوفاً من حدوث متلازمة خطيرة تعرف باسم متلازمة ري Reye’s syndrome.
تستخدم أيضاً قطرات الأذن في المنزل لتسكين ألم التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الأطفال، لكن يشترط عند استعمالها عدم وجود انثقاب في طبلة الأذن.
المضادات الحيوية
بعد الفحص وتحديد شدة الالتهاب، يقرر الطبيب ما إذا كان هذا المريض بحاجة لمضادات حيوية أم لا، قد يكتفي الأخصائي بمراقبة التهاب الأذن الوسطى خلال الأيام الأولى من الإصابة وملاحظة وجود أي تحسن في الأعراض.
يستخدم المضاد الحيوي بشكل مباشر بالنسبة للأطفال الرُضع الذين تقل أعمارهم عن 6 شهور والمشخص لديهم التهاب أذن وسطى حاد.
إن السبب الذي يدفع الأطباء لعدم التسرع في وصف الأدوية المضادة للالتهاب هو الخوف من تطور مقاومة للجراثيم، فالاستخدام المفرط لهم يسبب نشوء بكتيريا مقاومة للأدوية.
لا يوجد فائدة لاستخدام مضادات الجراثيم في معالجة التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الأطفال المسبب بواسطة الفيروسات، في حال عدم تحسن الطفل والشك بأن سبب التهاب الأذن الوسطى بكتيري يمكن بهذه الحالة وصف مضاد حيوي.
المضاعفات
إن التهابات الأذن التي تصيب الأطفال هي عادة غير خطيرة وتشفى بعد فترة دون أية مضاعفات، في حالات نادرة جدا قد يحدث نتيجة العدوى بعض الاختلاطات ومنها:
- انثقاب غشاء الطبل
- التهاب أذن وسطى قيحي مزمن
- تشكل ورم كولسترولي بالأذن
- نقص أو فقدان السمع
- التهاب الخشاء الحاد
- التهاب عظم الصخرة
- انتقال الالتهاب للأذن الداخلية
- التهاب السحايا
- خراج دماغي (أكثر الاختلاطات خطورة)
الوقاية من التهاب الاذن عند الأطفال
للوقاية من التهابات الاذن الوسطى عند الاطفال يجب الابتعاد عن الأسباب المؤهبة لحدوث الالتهاب وتقوية مناعة الطفل، ويتم ذلك عن طريق ما يلي:
- الإرضاع الطبيعي لدوره في تقوية المناعة
- تأمين اللقاحات اللازمة
- تجنب التدخين بجانب الطفل
- احرص على حماية طفلك من الإصابة بنزلات البرد
- غسل أيدي الأطفال والطعام بصورة جيد
- وقاية الطفل من نوبات التحسس في حال معاناته من تحسس اتجاه مادة معينة
وبالنهاية لا بد من التأكيد على ضرورة استشارة الطبيب بشكل دوري، فعلى الرغم من أن العلاج بسيط في أغلب حالات التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الأطفال إلا أن الالتهابات الشديدة قد تسبب أعراض خطيرة على الطفل وقد تترك عقابيل دائمة كفقدان السمع، وتذكر دائماً بأن درهم وقاية خير من قنطار علاج.
المصادر: