يعد التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء من أكثر أمراض الجهاز البولي شيوعاً لدى النسوة، تابعي معنا لتتعرفي على أعراض التهابات مجرى البول وطرق علاج الالتهاب بسهولة.
النساء هم أكثر عرضة للإصابة بالتهابات المجاري البولية من الرجال، حيث تصاب أكثر من نصف نساء العالم بعدوى المسالك البولية لمرة واحدة على الأقل خلال فترة حياتهن، ويعزى السبب الأهم في ذلك لكون الإحليل الأنثوي قصير وأقرب للمستقيم بالمقارنة مما هو عليه عند الرجال وبالتالي فإن البكتيريا تتمكن من دخول مجرى البول بشكل أسهل وتتكاثر لتحدث عدوى بكتيرية في أحد أقسام الجهاز البولي عند الإناث.
أعراض التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء
عادةً ما يتظاهر التهاب المسالك البولية بأعراض وعلامات عدة، فعند إصابة السيدة بالتهاب في السبيل البولي سوف تشعر بالعديد من الأعراض البولية المزعجة كالحرقة وغيرها من الاعراض الأخرى، وعلى الرغم من أن هذا الأمر قد يبدو مزعجاً بعض الشيء إلا أنه يسمح للنساء بكشف الالتهاب مبكراً لكي تبدأ بعلاجه بسرعة.
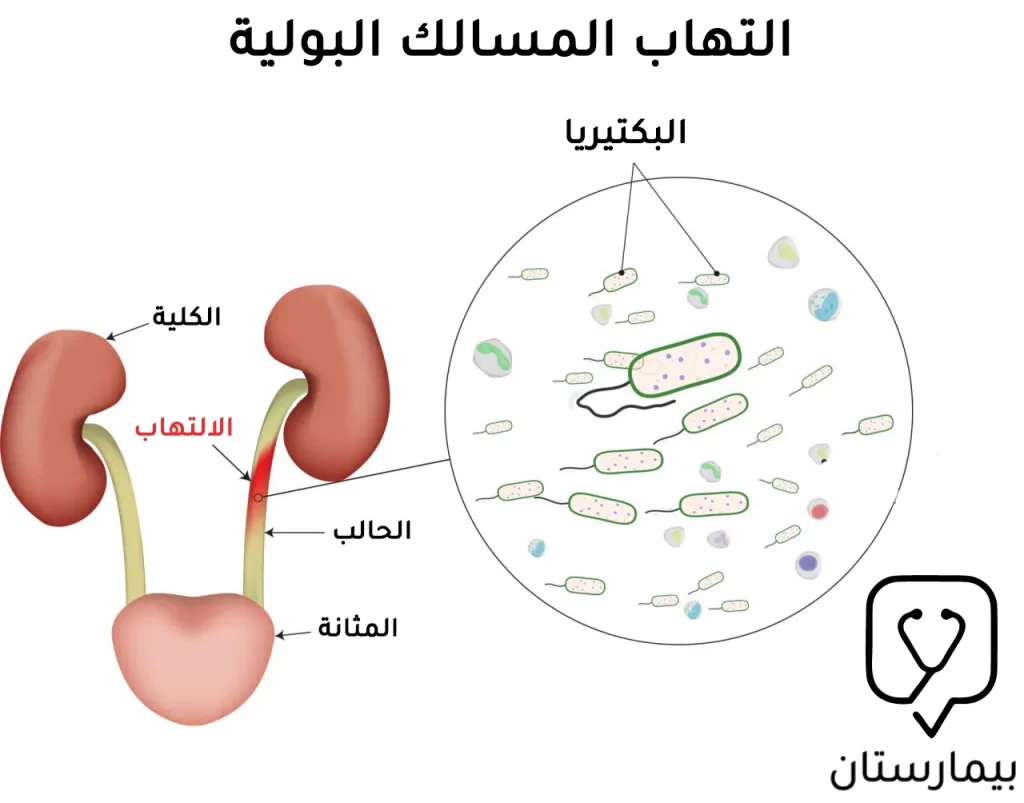
تختلف اعراض التهاب المجاري البولية من امرأة لأخرى بحسب شدة الالتهاب والمكان الذي أصابته العدوى على مسار الطريق البولي، إذ يتألف جهاز البول عند الإناث من الكلى التي تتصل مع الحالب ومن ثم المثانة التي تنتهي بالإحليل، قد يصيب الالتهاب أي جزء من هذه الأجزاء وغالباً ما تحدث معظم الالتهابات عند النساء على مستوى المثانة، عادة ما يقتصر التهاب المثانة على أعراض مزعجة ومؤلمة فقط ويكون علاجه سهلاً بالمقارنة مع التهاب الكلى الذي يعتبر النوع الأكثر خطورة من التهابات المسلك البولي وقد يترافق مع مضاعفات خطيرة مهددة لحياة المريضة عند إهمال علاجه.
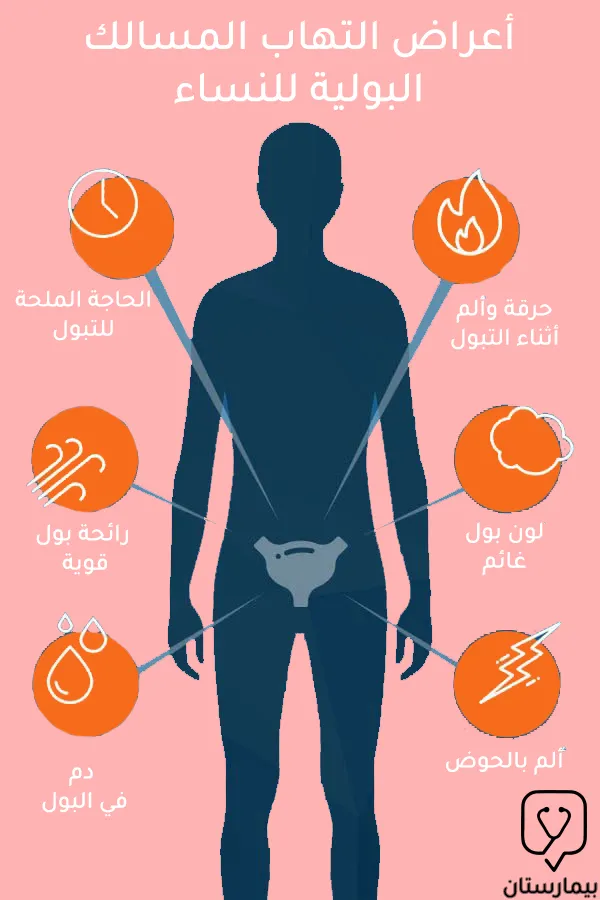
لنذكر معاً أهم وأشيع اعراض التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء:
- الشعور بألم أو حرقة أثناء التبول
- الإحساس برغبة ملحة للتبول مع عدم وجود كمية كبيرة من البول في المثانة
- رائحة كريهة للبول مع لون مائل للغائم
- التبول المتكرر والذي قد يوقظ السيدة من نومها
- نزول دم مع البول (يجب في هذه الحالة استشارة الطبيب على الفور)
- شعور بضغط أو عدم ارتياح في منطقة الحوض أو أسفل الظهر حول البطن
- قد يحصل عند انتقال العدوى إلى الكلية تعب عام مع حمى (ترفع حروري)
- ألم وعسرة الجماع عند النساء المتزوجات
في حال شعرتِ بأحد هذه الأعراض فمن الأفضل مراجعة طبيبك المتخصص لكشف المسببات التي أدت لظهور هذه العلامات ولكي يقوم بوصف علاج مناسب لحالتك.
أسباب التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء
يحدث التهاب المسالك البولية Urinary tract infection عندما تدخل أحد البكتيريا الممرضة إلى داخل جهازك البولي لتقوم بعدها هذه البكتيريا بالتكاثر ضمن أحد أجزاء مجرى البول حتى يزداد عددها وتصبح أكثر قوة، تقوم مناعة جسمك بمحاولة التصدي والقضاء على هذه الجراثيم عبر إحداث عملية التهابية مما يؤدي لظهور أعراض التهاب المسالك البولية.
غالباً ما تتمكن الجراثيم من الدخول للمسالك البولية عن طريق الإحليل والذي يشكل القسم السفلي والأخير من مسار عبور البول إلى خارج الجسم، وكما ذكرنا سابقاً فإن الاحليل عند النساء يكون أقصر من إحليل الرجال وكنتيجة لذلك تستطيع الجراثيم العبور والصعود لداخل المسالك البولية بِسهولة أكبر، لذا فإن التهاب المسالك البولية هو شائع أكثر عند النساء.
كثيراً ما يكون مصدر البكتيريا التي سببت التهاب مجرى البول عند السيدات هي بكتيريا وصلت للإحليل من البراز، فنجد أيضاً أن المستقيم عند النساء يتوضع بالقرب من الإحليل وبالتالي لا تحتاج جراثيم البراز لقطع مسافات طويلة حتى تصل للمسالك البولية وتحدث التهاب بولي.
إن أشيع الجراثيم التي تسبب التهاب المثانة هي جرثومة الإشريكية القولونية E.coli، لنتعرف أكثر على الأسباب والعوامل التي تزيد من خطر تعرض النساء لالتهاب المسالك البولية (UTI):
- عدم الاهتمام بالنظافة الشخصية
- المسح من الخلف للأمام بعد التبرز (قد يؤدي ذلك لانتقال جراثيم البراز للإحليل)
- ضعف المناعة (الداء السكري، سوء التغذية)
- الحمل (بسبب كبر حجم الرحم وضغطه على المثانة مما قد يؤدي لاحتباس وعودة البول باتجاه عكسي)
- زيادة الوزن والسمنة
- عائق يقود لانسداد المسالك البولية (كوجود حصيات كلوية)
- التقدم في العمر وبلوغ فترة انقطاع الطمث (سن اليأس)
- شرب كميات قليلة من الماء
- عدوى سابقة بالمسالك البولية
- استخدام القساطر البولية لفترات طويلة
- تعدد الشركاء الجنسيين
ما تم ذكره سابقاً هو عبارة عن أسباب وعوامل من شأنها أن تزيد من احتمال وفرص الاصابة بالتهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء، إلا أنه ليس بالضرورة أن يقتصر التهاب مجرى البول على النسوة اللواتي لديهن عامل خطورة من هذه العوامل فيمكن أن يُصيب الالتهاب جميع السيدات بلا استثناء، وبشكل عام فإن النساء المتزوجات هم عرضة بشكل أكبر للإصابة بالتهابات المجاري البولية من العازبات وذلك بسبب بعض الممارسات الخاطئة كاستخدام موانع الحمل الملوثة أو الجماع الغير آمن والذي قد يسبب أيضًا التهاب المهبل للمتزوجات.

كيفية علاج التهاب المجاري البولية عند النساء
بالنسبة لكيفية علاج التهاب المسالك البولية فهي تختلف من حالة لأخرى بحسب شدة الإلتهاب والحالة الصحية العامة للمريضة ونوع الجراثيم المهاجمة، فقد يكون العلاج بسيطاً للغاية وتشفى السيدة من الالتهاب خلال فترة وجيزة، بينما قد تصبح المعالجة أكثر تعقيداً في الحالات الشديدة لالتهاب الجهاز البولي وخاصة عندما يصاب الجزء العلوي وتحديداً إحدى الكليتين بالعدوى، نذكر أشيع الطرق المستخدمة لعلاج التهابات المسالك البولية عند النساء:
علاج التهاب المسالك البولية في المنزل للنساء
يلجأ الأطباء في معظم حالات العدوى التي تصيب مجرى البول عند السيدات إلى وصف المضادات الحيوية Antibiotics، تعمل هذه الأدوية على قتل البكتيريا المهاجمة وتثبيط تكاثرها مما يساهم بالتخلص من اعراض التهاب المسالك البولية والشفاء من هذا المرض.
يعتمد اختيار أفضل مضاد حيوي لعلاج التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء على نوع الجراثيم المسببة للالتهاب والتي يتم تحديدها من قبل الطبيب عبر إجراء فحص لعينة بول للمريضة، ولكن غالباً ما يعد الأموكسيسيلين Amoxicillin هو الدواء الأكثر استخداماً لمعالجة التهاب المسالك البولية للسيدات إلا أنه ليس بالضرورة أن يكون مناسباً لجميع النساء، فمن الادوية الأخرى المستخدمة للعلاج ما يلي:
- سيفترياكسون Ceftriaxone
- سيبروفلوكساسين Ciprofloxacin
- ليفوفلوكساسين levofloxacin
- سلفاميثوكسازول Sulfamethoxazole
تتشابه هذه الأدوية مع تلك المستخدمة في علاج التهاب المسالك البولية عند الرجال، وتذكري بأن نوع الدواء الأفضل والجرعة اللازمة سيتم تحديدها من قبل الطبيب، فمن الأخطاء الشائعة التي يقع بها الكثير من الرجال والنساء هو أخد أدوية مضادة للالتهاب بِشكل عشوائي دون استشارة طبيب متخصص وهذا من شأنه أن يؤدي لمشاكل عديدة كتشكل مقاومة بكتيرية للأدوية المضادة للجراثيم.
علاج التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء بالأعشاب الطبيعية
إن الهدف الرئيسي لاستخدام الأعشاب هو التخفيف من حدة الأعراض التي تعاني منها النساء اللواتي أصبن بالتهاب المسالك البولية، فلا يمكن الاعتماد على الاعشاب لعلاج التهاب البول عند النساء بل هو مجرد وسيلة مساعدة بالعلاج إلى جانب المضادات الحيوية.
يتميز الثوم بخصائصه المضادة للالتهاب والأكسدة وكذلك عشبة التوت البري المفيدة في تخفيف الالتهابات بالجسم، ومن الاعشاب المستخدمة أيضًا نبتة عنب الدب وذيل الحصان.
علاج التهابات المسالك البولية عند الحوامل
إن الاختلاف الذي يجعل علاج إلتهاب المسالك البولية لدى الحوامل مختلف قليلاً عن علاج الالتهاب للنساء الأخريات هو كيفية اختيار الأدوية المناسبة، وذلك لأن بعض الأدوية قد تسبب تأثيرات مشوهة تضر بالجنين لذا تختار الأدوية بعناية من قبل الطبيب.
غالباً ما يستخدم دواء الأموكسيسلين أو السيفاليكسين Cephalexin لعلاج التهابات المسالك البولية للحوامل.
مضاعفات التهاب المسالك البولية للنساء
لا يترافق التهاب المسالك البولية في معظم الأحيان مع مضاعفات خطيرة تستدعي القلق وعادةً ما يشفى الالتهاب بعد فترة من بدء المعالجة، إلا أنه قد يحصل في بعض الحالات الشديدة من التهابات المسالك البولية الغير معالجة جيداً اختلاطات قد تكون مهددة لوظيفة الجهاز البولي عند السيدة وحتى على حياتها ومن بين هذه المضاعفات:
- تكرار التهاب المسالك البولية عدة مرات بالسنة الواحدة
- انتشار العدوى إلى الكلى وحدوث فشل كلوي
- إجهاض أو ولادة مبكرة لدى الحوامل
- تشكل خراجات في المسالك البولية
- قد تنتشر البكتيريا إلى الدم ويحدث إنتان دموي Sepsis مهدد للحياة
الوقاية من التهابات المسالك البولية لدى النساء
يمكنكِ التقليل من فرص إصابتك بالتهاب المسالك البولية عن طريق اتباع النصائح التالية:
- تجنب المسح من الخلف للأمام بعد التبول أو التغوط (لمنع انتقال الجراثيم للإحليل)
- شرب كمية وافرة من الماء
- تجنب احتباس البول لفترة طويلة بالمثانة
- غسل الأعضاء التناسلية والمحافظة على النظافة الشخصية
- التبول مباشرة بعد العلاقة الزوجية (لطرح البكتيريا في حال انتقالها للسبيل البولي)
التهاب المسالك البولية والحمل
يولى التهاب المسالك البولية الذي يصيب المرأة الحامل أهمية خاصة خوفاً من تداعيات الالتهاب وتأثيره المحتمل على الجنين في بطن أمه.
يزداد احتمال الإصابة بالتهاب المجاري البولية عند النساء الحوامل وذلك بسبب التغيرات الهرمونية التي تحصل لدى الحامل وكذلك نتيجة تضخم الرحم الذي يضغط على المثانة مما يعيق جريان البول ويؤدي إلى احتباس بولي.
إهمال معالجة التهاب مجرى البول عند الحوامل قد يؤدي إلى تطور مضاعفات مثيرة للقلق كحدوث إجهاض باكر أو ولادة طفل غير مكتمل النمو وغيرها من الاختلاطات الأخرى، لذا يجب على السيدة خلال حملها مراجعة الطبيب عند شعورها بظهور علامات وأعراض التهاب المسالك البولية حتى يصف لها الأدوية المناسبة ويراقب حالتها الصحية وحالة جنينها.
وفي الختام فإن التهاب المسالك البولية عند النساء هو من أكثر الأمراض الالتهابية انتشاراً بين الإناث، يتظاهر الالتهاب البولي بالعديد من الأعراض المزعجة كصعوبة التبول والحرقان وأعراض أخرى عدة، تساهم بعض الأسباب برفع خطورة التعرض للالتهاب عند النساء حيث يمكن عبر تجنب هذه الأسباب الوقاية من خطر حدوث الالتهاب، غالبًا ما يعالج التهاب مجرى البول باستخدام المضادات الحيوية التي يصفها الطبيب وقد يتطور عند عدم معالجته جيداً ليسبب مضاعفات خطيرة كالأذية الكلوية.
المصادر:
