خناق لودفيغ هو إصابة إنتانية خطيرة سريعة الانتشار تسبب تورم في العنق، مما قد يؤدي إلى اختناق المريض، وتعد الجراحة في تركيا هي الحل الأمثل في الحالات الشديدة.
لمحة عن خناق لودفيغ
تعدّ منطقة العنق من المناطق الهامة لوجود العقد اللمفاوية ومسافات للأنسجة الضامة المعرّضة للإصابة بالحالات الإنتانية كونها على اتصال وثيق مع الجهاز التنفسي العلوي والجهاز الهضمي.
ويعتبر تجويف الفم أحد أكثر المناطق شيوعاً لإيواء الخمج نتيجة التعرض لعوامل كثيرة كمشاكل المناطق حول الذروية للأسنان وصحة الفم السيئة، لذا من المهم إجراء فحوصات لتجويف الفم بالكامل من تسوس الأسنان إلى أرضية الفم لتحرّي وجود الوذمة التي قد تشكل تهديداً للمجرى التنفسي العلوي.
ذُبَاح لودفيغ (أو خُنَّاق لودفيغ) ludwig’s angina هو إصابة بكتيرية نادرة تظهر على شكل خراج شديد مهدد للحياة يصيب منطقة الفم والفك و كذلك الرقبة، يعتبر هذا الخناق حالة خطيرة تكون أكثر شيوعاً عند الرجال والبالغين مع تنوع في عمر الإصابة كما أظهرت الدراسات.
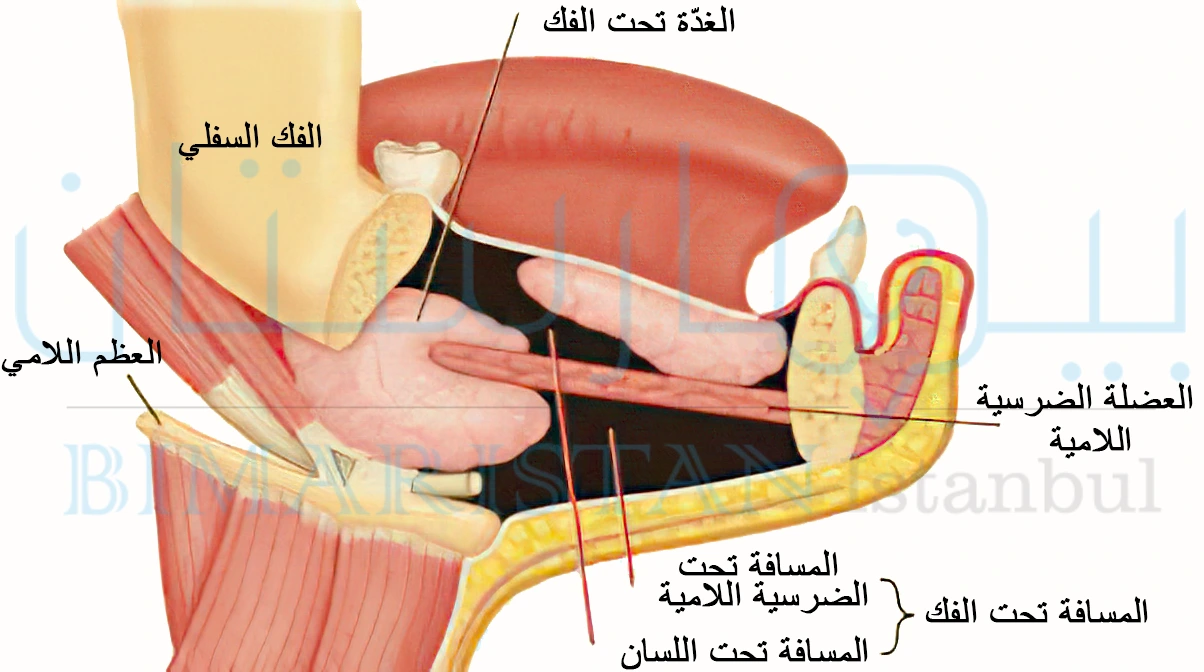
ويعتبر خناق لودفيغ نوعاً من التهاب النسيج الخلوي يحدث في المسافات تحت الفك السفلي وتحت اللسان وتحت الذقنية، يتميز بسرعة انتشاره الى الانسجة، ويتظاهر بتورم في المنطقة تحت الفك السفلي مع ارتفاع في قاع الفم واللسان مما قد يؤدي إلى صعوبات في التنفس أو حتى إعاقته تماماْ إذا ترك دون علاج.
أسباب خناق لودفيغ
سوء نظافة الفم والبكتيريا الناتجة عن التهابات الأسنان؛ حيث يمكن أن تحدث الاصابة بخناق لودفيغ في حال وجود النخور أو خراجات الأسنان (غالباً في منطقة الأضراس الثانية والثالثة) أو عند وجود التهاب في اللثة او الأنسجة الداعمة للأسنان.
تعد بكتيريا المكورات العقدية والمكورات العنقودية أشيع أنواع البكتيريا التي تؤدي إلى خناق لودفيغ، خاصةً العقديات المخضرة Streptococcus viridans والعنقوديات البشروية Staphylococcus epidermidis والعنقوديات الذهبية Staphylococcus aureus.
ما الذي يزيد من خطر الإصابة بخناق لودفيغ؟
قد تكون معرضاً لخطر الإصابة بذبحة أو خناق لودفيج إذا كان لديك أي مما يلي:
- كسر عظم الفك
- ثقب اللسان
- إنتان عظم الفك
- إنتانات الفم
- خراجات اللوزتين
- إنتانات الغدد اللعابية
- كيس الغدة الدرقية
علامات وأعراض خناق لودفيغ
غالباً تشمل أعراض خناق لودفيغ بشكل أساسي الحمى وآلام الفم وتورم الرقبة وتورم اللسان، بالإضافة الى أعراض أخرى قد تظهر تتضمن القشعريرة وآلام الرقبة وتيبسها والتهاب الحلق وألم وصعوبة بالبلع وسيلان اللعاب وتحدّد فتح الفك وصعوبة في الكلام وألم الأذن.
أما في الحالات الشديدة من خناق لودفيغ، أو عندما يُترك دون علاج، يمكن أن تظهر أعراض مثل:
- ألم الصدر
- صعوبة كبيرة بالتنفس
- ارتباك وصعوبة في التركيز
- الجفاف الشديد
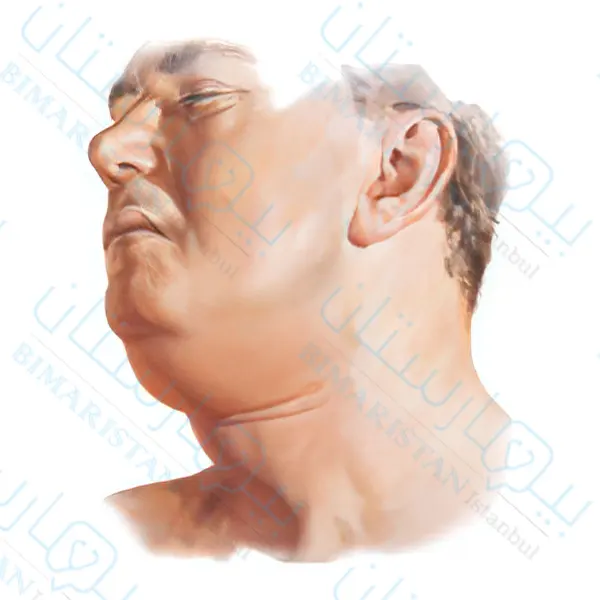
كيف يتم تشخيص خناق لودفيغ في تركيا؟
عن طريق فحص بدني يجريه الطبيب لكل من الرقبة والفك والعقد اللمفاوية وفحص داخل الفم والصدر والرئتين، في معظم الحالات يُظهر هذا الفحص البدني أعراضاً كافية لتشخيص خناق لودفيغ.
وفي حال لم يتم حسم التشخيص فقد يتم طلب إجراء زرع للدم واللعاب للتحقق من وجود البكتيريا، يمكن أيضاً القيام بالتصوير المقطعي المحوسب CT أو التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي MRI باستخدام صبغة التباين حيث يتم عن طريق هذه الإجراءات فحص الفم والعنق والفك للبحث عن تورم أو غاز أو صديد (قيح) أو التهاب.
ما هي مضاعفات الإصابة بخناق لودفيغ
عند العلاج الفوري لخناق لودفيغ، يمكن توقّع تعافي جيد مع آثار قليلة أو معدومة، أما في حال تُرك دون علاج، فهناك العديد من المضاعفات الخطيرة المصاحبة لخناق لودفيغ والتي قد تكون مهددة للحياة، مثل:
- الصدمة الإنتانية
- إنتان الرئة بالقيح
- الاختناق
- التهاب أو إصابة في القلب
- جلطة دموية في الرقبة
- انتفاخ وتمدد الأوعية الدموية في الشريان السباتي
- التهاب الصدر
قد تؤدي هذه المضاعفات إلى الوفاة المبكرة بسبب سرعة انتشار الإنتان ومنع مرور الهواء للتنفس، لذا يعد العلاج الفوري لخناق لودفيغ هو أفضل مسار للعلاج.
طريقة علاج مرض خناق لودفيغ في تركيا
يجب علاج مرض خناق لودفيغ بشكل فوري باعتباره إصابة إنتانية خطيرة سريعة الانتشار قد تؤثر على مجرى التنفس، لذا يتم التأكد أولاً من أن المريض يستطيع التنفس بشكل صحيح.
تنظيف مجرى الهواء
إذا كان التورم يتداخل مع التنفس فإن الهدف الأول من العلاج هو تنظيف مجرى الهواء.
إذا كان التنفس مقيداً جزئياً قد يتم وضع أنبوب للتنفس من خلال الفم أو الأنف، وإذا كان التنفس مقيداً بشدة فقد يخضع المريض لعملية جراحية لبضع القصبة الهوائية وإدخال أنبوب التنفس فيها.، هذا الإجراء يسمى شق القصبة الهوائية.
تصريف السوائل الزائدة
يسبب خناق لودفيغ تراكم السوائل في منطقة الرقبة والفك لذلك من المهم تصريف هذه السوائل عن طريق قيام الطبيب بشق جراحي في المنطقة وبالتالي يتمكن المريض من التنفس بشكل أسهل.
السيطرة على العدوى
من المحتمل أنك ستحتاج إلى مضادات حيوية عن طريق الوريد حتى تختفي الأعراض. بعد ذلك ستستمر في تناول المضادات الحيوية عن طريق الفم حتى تظهر الاختبارات أن البكتيريا قد اختفت لضمان عدم عودة الأعراض.
ستحتاج أيضاً إلى الحصول على علاج لأي عدوى أسنان إضافية.
العلاجات الضافية
قد تحتاج إلى علاج الأسنان التي تسببت إصابتها في حدوث ذبحة لودفيغ، وإذا كنت لا تزال تعاني من التورم فقد تحتاج لتصريف السوائل التي تسببت بتورم المنطقة.
الوقاية من حدوث خناق لودفيغ
في معظم الحالات يمكنك المساعدة في منع حدوث هذه العدوى الجلدية النادرة والخطيرة.
- حاول تجنب ثقب اللسان أو الفم لأن هذه الثقوب قد تسمح للبكتيريا بغزو عظم الفك والأنسجة الرخوة، وإذا كنت تعاني من أي ألم في الأسنان أو التهاب اللثة أو تخلخل في الأسنان حدّد موعداً مع طبيب الأسنان في أسرع وقت ممكن.
- كما يجب أن تكون العناية الجيدة بالنظافة الفموية من أولى التدابير الوقائية، تأكد من تنظيف أسنانك بالفرشاة والخيط كل يوم.
- قم بالزيارة الدورية لطبيب الأسنان للتحقق من وجود نخور الأسنان أو الخراجات أو تراكم اللويحة.
فمع العناية الجيدة واتباع نظام غذائي صحي، يمكنك تقليل خطر الإصابة بخناق لودفيغ.
