الحول هو فقدان التوازي بين العينين و عدم التناظر في حركة العينين عند النظر نحو نقطة معينة، يعتبر الحول أحد أكثر الأمراض العينية شيوعاً وتشير الإحصائيات أن 4% من الأشخاص يصاب بالحول.
قد يكون الحَوَل أو حول العيون squint دائم أو مؤقت.
تعرف على أسباب حول العينين لدى الكبار والصغار والأنواع واضطرابات الرؤية المرافقة له وأحدث طرق علاج الحول في تركيا بإشراف كادر من أفضل اختصاصيي جراحة العين وملحقاتها.
تطور طب العيون في تركيا بالسنوات الأخيرة بشكل كبير، وأصبحت من البلدان الرائدة في مجال طب العيون.
يعد الحول هو فشل العينين في الحفاظ على المحاذاة الصحيحة والعمل معاً كفريق ، قد يؤثر الحول دائماً على نفس العين أو قد يتناوب على العينين ( الحول بالتناوب) ، لمنع الرؤية المزدوجة بحالات الحول الخلقي يتجاهل الدماغ الإشارات القادمة من العين المنحرفة مما يسبب الغمش.
تعريف الحول strabismus وأنواعه
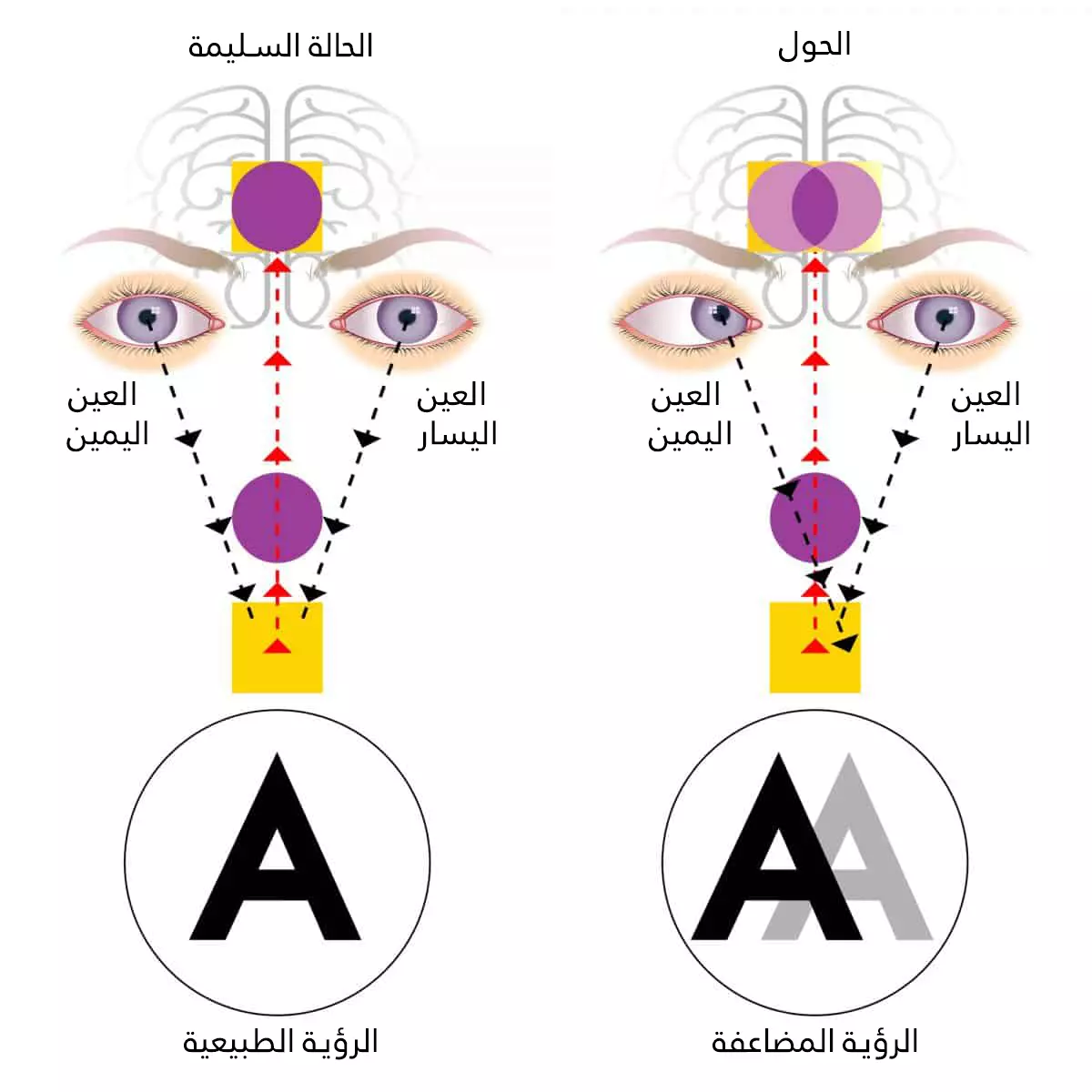
الحول هو عيب بصري يجعل العينين يتحركان بطريقة غير متوازية وغير متوازنة فلا تلتقي المحاور البصرية بنقطة وحدة، مما يسبب شفع ورؤية مزدوجة للمريض.
للعين ستة عضلات مسؤولة عن تحريكها بالاتجاهات المختلفة ، تعمل عضلات العينين بالحالة الطبيعية بطريقة متناظرة لتحافظ على توازن وتناظر الحركات بكلتا العينين، إذ تنظر العينان معاً نحو الجسم المراد رؤيته و يلتقي محورا الرؤيه بنقطة واحدة وبمساعدة الدماغ تدمج الصورتين القادمتين من العينين على شكل صورة وحدة ثلاثية الأبعاد وهذه عملية معقدة تجرى بتنسيق دقيق من الدماغ.
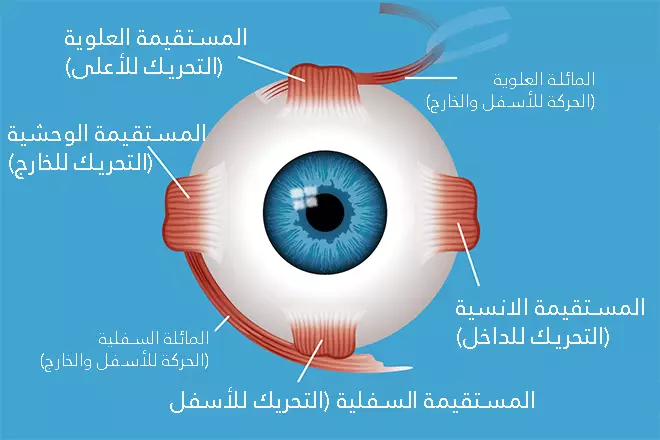
والحول من الأمراض الشائعة، إذ تشير التقديرات أن حوالي 13 million شخص مصاب بالحول بالولايات المتحدة الأمريكية اليوم.
يمكن تصنيفه حسب اتجاه العين المنحرفة:أشكال الحولأشكال الحول
- حول داخلي أو أنسي (Esotropia) : تنحرف العين إلى الداخل باتجاه الأنف.
- الحول الخارجي أو الوحشى (Exotropia) يكون انحراف العين إلى الخارج نحو الأذن.
- بحالة الحول الفوقاني (Hypertropia) يكون انحرافها نحو الأعلى.
- أما في حالة الحول التحتاني (Hypotropia) يكون إنحراف العين نحو الأسفل.
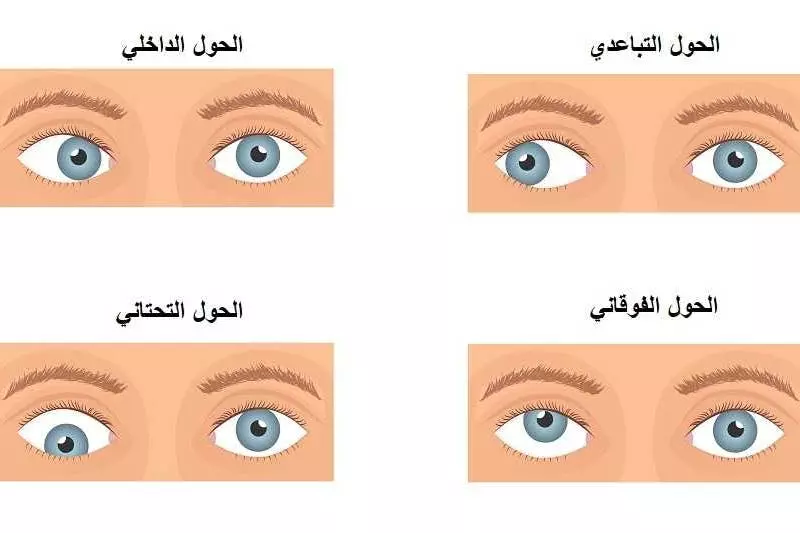
أنواع الحول crossed eyes
للحول أو حول العيون squint نوعان أساسيان:
1. الحول التصاحُبيّ (Comitant strabismus):
بهذه الحالة تكون زاوية الحَوَل ثابتة (مدى انحراف العين) في جميع اتجاهات النظر .
2. الحول اللا تصاحبيّ (Incomitant strabismus):
تختلف زاوية الحول باختلاف اتجاه لنظر، قد ينتج عن شلل أوضعف بعضلات العين.
يحدث الحول في جميع المراحل العمرية وغالباً مايظهر بعمر الطفولة، فالحول الداخلي لدى الطفل يظهر في الأشهر الأولى من العمر، بينما الحول الأنسي التكيفي (Accommodative estropia) يصيب الطفل بعمر سنتين إلى ثلاث سنوات وهو ناتج عن مد لبصر.
الحول الذي يتظاهر مع التقدم في السن يسمى الحول المكتسب ويكون نتيجة ضعف في إحدى العينين أو في كلتيهما ، أو شلل احدى العضلات العينية لسبب ما.
3. الحول الخفي (الشطور):
لايظهر الشطور إلا بحالات الإجهاد أو عند تغطية العين الآخرى اثناء الفحص الطبي ، يتحول عندها الحول الخفي إلى حول ظاهر بسبب التعب كما في وقت المساء ويختفي في الصباح عند الاستيقاظ.
يؤدي هذا النوع لحدوث تغيم بالحروف والكلمات وتشوش بالرؤية وصداع شديد بعد العمل لمدة ساعتين.
4. الحول الكاذب:
يولد بعض الأطفال بجسر أنف عريض وطية جلدية فوق الزاوية الداخلية للعين مما يعطي مظهر الحول.
قد تتراجع هذه الحالة بعمر ستة شهور.
ماهي أسباب الحول؟
تتنوع اسباب الاصابة من حالة لأخرى ، وبحالات معينة يبقى السبب مجهولاً ، إليك أهم مسببات الحوَل :
- ضعف الإبصار في عين واحده (مدّ نظر المتوسط إلى الشديد، وفرق القوة الكاسرة في عين بالنسبة للعين الأخرى، أو بسبب مشاكل أقل شيوعاً كالساد الخلقي).
- الحالات الالتهابية كالتهاب السحايا والتهاب الأعصاب السكريال
- آفات وعائية دماغية كأمهات الدم الدماغية.
- متلازمة داون
- استسقاء الدماغ الذي هو خلل تكويني ينتج عنه تراكم السوائل في الدماغ.
- أورام الدماغ.
- السكتة الدماغية.
- إصابة بالأعصاب المسؤولة عن تحريك عضلات العين ( ولادي أو مكتسب).
ماهي أعراض الحول؟
للحول الكثير من الأعراض المختلفة:
- الإجهاد البصري: احمرار وحرقة في العين، صداع
- صعوبة بالقراءة وتراجع المستوى الدراسي للطفل
- الشفع (الرؤية المضاعفة)
- تحدد بحركات العين
- أحياناً قد يترافق الحول مع إطراق بالجفن العلوي.
تشخيص الحول
يعتمد تشخيص الحول لدى الأطفال اثناء الزيارة الروتينية للطبيب حيث يجرى فحص العين في كل زيارة لطبيب الأطفال، ولكن في حال الشكوى من أعراض الحول أوضعف بالنظر أو أية اضطرابات عينية اخرى في أي عمر، فيجب اجراء فحص كامل للعين من قبل طبيب العيون.
ماهو اختبار الحول؟
اختبار الحول أو مايسمى بالمنعكس الضوئي القرني يوجه الدكتور الضوء بشكل عمودي نحو حدقة المريض، في حالة الحول يلاحظ الطبيب أن المنعكس الضوئي القرني منزاحاً عن مركز الحدقة بالعين المصابه بالحول.
وهذا الاختبار يُشخص الحول.
ماهي مضاعفات الحول؟
ينتج عن الحَوَل العديد من المضاعفات البصريه والشكلية والنفسية أحياناً:
المضاعفات البصريه: إذ يمكن أن يؤدي الحول إلى اضطراب بالرؤية كالشَفَع ، من المضاعفات الأساسية الناجمة عن الحول هي نشوء ظاهرة الغَمَش أي كسل العين التي تنتج عن إهمال المخ للصور القادمة من إحدى العينين.
وفي معظم الحالات يسبب الحول اضطرابًا جماليًا في مظهر الوجه وأحيانًا إلى قد تؤدي لاضطرابات نفسية لدى المصاب.
طرق علاج الحول؟
تتنوع طرق علاج الحول باختلاف العامل المسبب، يمكن أن يشمل العلاج استخدام النظارات الطبية أو العدسات اللاصقة لإصلاح مد لنظر في حال كان هو المسبب ، علاج الغمش الذي قد يكون سبب ونتيجة للحول وذلك بتغطية العين السليمة برقعة بهدف تحفيز العين المصابة. وفي بعض الأحيان قد يكون هنالك حاجة إلى إجراء عمليات جراحية لعضلات العين المصابه بهدف تصحيح توازنها.
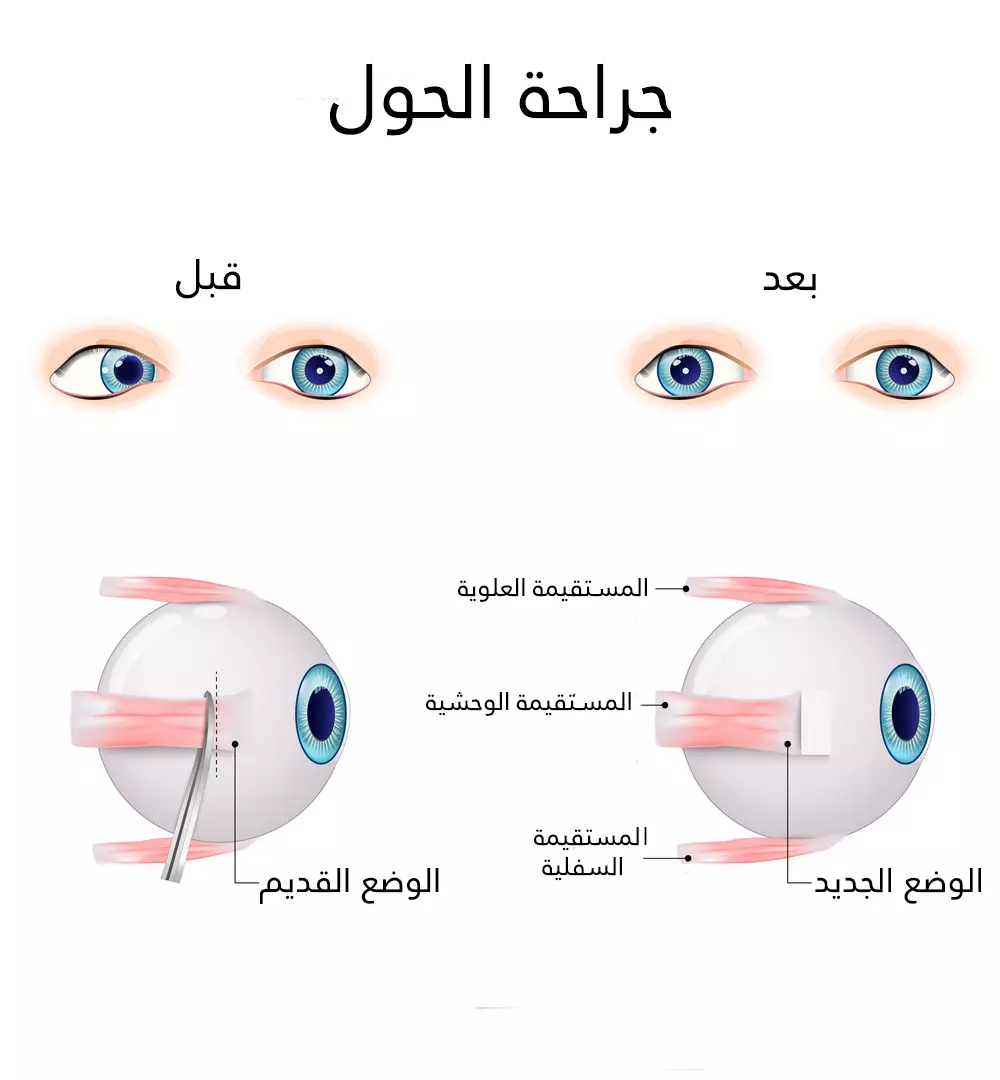
جراحة الحول
المبدأ الأساسي لعمليات تصحيح الحول هو:
- تأخير ارتكاز العضلة القوية على المقلة (Eyeball) أي إعادتها للوراء بهدف إضعاف قدرة العضلة على الشد.
- تقصير العضلة الضعيفة (أي حسر العضلة) وذلك لتقويتها.
ويجرى ذلك بمقادير تختلف باختلاف زاوية الحول يحددها الطبيب.
يستخدم التخدير العام لمعظم الأطفال ، بينما تجرى للكبار تحت التخدير الموضعي، ويعتمد نوع التخدير على المريض ووجود أمراض صحية بالإضافة إلى ما يفضله .
بعد الجراحة من الطبيعي أن تتحول الصلبة ذات اللون الأبيض من العين إلى اللون الأحمر بعد الجراحة.
قد يستغرق الأمر عدة أسابيع أو أحيانًا شهور حتى يختفي الاحمرار.
عادة ما تكون العيون مشوشة ومؤلمة عند الحركة.
يتحسن الألم عادة بعد بضعة أيام اعتمادًا على الجراحة الدقيقة التي تم إجراؤها.
تظهر النتيجة النهائية بعد أربع إلى ست أسابيع من عملية الحول ، قد يحتاج الأطفال تحت عمر ال 10 سنوات إلى إعادة العملية للحفاظ على أفضل نتائج ، وفي بعض الحالات قد تساعد النظارات الموشورية على ضبط حركة العينين معاً.
ثمة طريقة علاج حديثة تعتمد على حقن البوتوكس، هذه الطريقة فعالة في حالات الحول البسيطة.
وقد يلجأ البعض لاستخدام المواشير وتمارين تقويم البصر كعلاج متمم للجراحة بحالات معينة كالحول الوحشى المتقطع ، أما المواشير والنظارات المشورية تستخدم بحال وجود شفع.
علاج الحول بالتمارين
تستخدم هذه الطريقة في علاج الحول الوحشي أثناء الرؤية القريبة يمكن أن يجرى التمرين البسيط كالتالي:
يمسك قلم باليد ويقرب ببطء نحو الأنف مع تثبيت النظر عليه حتى حدوث الشفع، ثم يكرر هذا التمرين مرات عديدة باليوم ولفترة أسابيع حتى تصغر المسافة التي يعاني عندها من حدوث الشفع.
لسوء الحظ إن تمارين العضلات تفيد لفتر مؤقتة ويجب تكراره بين فترة و أخرى ليستمر غياب الأعراض.
هل يمكن الوقاية من حول؟
لا يمكن الوقاية من الحول، لكن التشخيص المبكر يقي الطفل من المضاعفات.
يبقى مركز بيمارستان الطبي خيارك الأول للعلاج في تركيا.
نوجهك لأفضل و أشهر الاختصاصين الخبراء بكافة المجالات، لا تتردد بالتواصل معنا، مركز بيمارستان الطبي عائلتك في تركيا. يمكنك أن تقرأ على موقعنا أيضاً عن أحدث تقنيات طب العيون في تركيا.
