يشهد العالم في الوقت الحالي ارتفاع خطر الإصابة بـ سرطان المريء الذي يعد واحدًا من الأورام الخبيثة النادرة ولكن الشفاء منه ليس مستحيلًا وانما يمكن علاجه بتركيا.
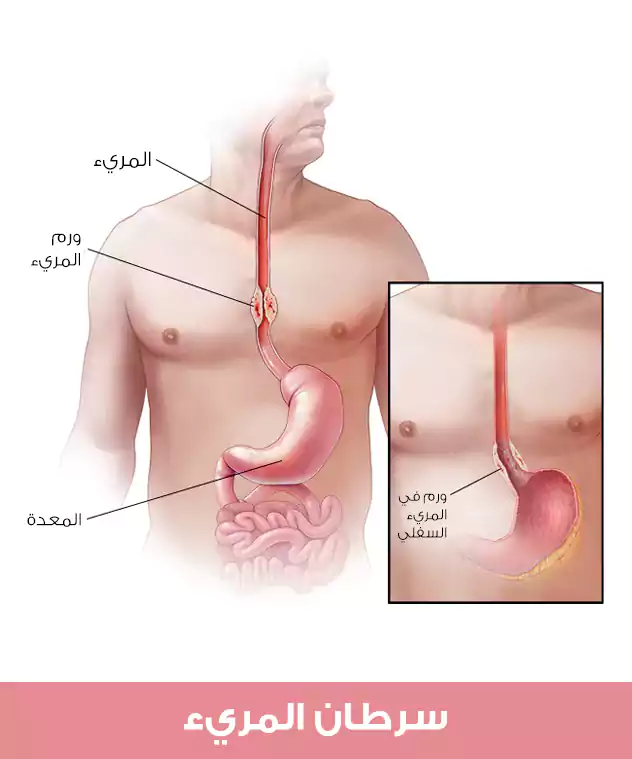
المريء هو انبوب عضلي يشكل الممر الذي يستخدمه الطعام والسوائل للوصول إلى المعدة حيث يتم هضمه.
النوعان الأساسيان لسرطان المريء هما سرطان الخلايا الحرشفية (الذي يتكون في بطانة المري) والسرطان الغدي (الذي ينشأ على حساب النسيج الغدي للمري).
نظرة عامة عن سرطان المريء وعلاجه
ما هو سرطان المريء الخبيث؟
المريء عبارة عن أنبوب عضلي طويل يمتد من الحلق إلى البلعوم والمعدة.
يتكون من عدة طبقات من العضلات تتقلص للمساعدة في نقل الطعام إلى أسفل الأنبوب في اتجاه باقي الجهاز الهضمي.
يوجد عضلة خاصة العضلة العاصرة للمريء كصمام، تفتح وتغلق للسماح للطعام والسوائل بالمرور من المريء بسهولة كما تمنع عودة الطعام من المعدة مرة أخرى للمري.
ينتج سرطان المريء (esophageal cancer) عندما تنمو الخلايا غير الطبيعية بشكل خارج عن السيطرة.
في النهاية تشكل الأنسجة النامية كتلة تعرف على أنها ورم خبيث.
هناك نوعان رئيسيان من سرطان المريء:
يبدأ سرطان المرئ الحرشفي في مجموعة نسيج بطانة المريء ويصيب هذا السرطان عادةً الجزء العلوي والأوسط منه.
يتطور السرطان الغدي في الأنسجة التي تنتج المخاط الذي يساعد في مرور الطعام ويصيب بشكل عام الجزء السفلي من المريء.
الاعراض والأسباب لسرطان المريء
ما هي أسباب سرطان المريء؟
السبب الدقيق لورم المريء غير معروف، ولكن هناك العديد من العوامل المرتبطة بآلية حدوث المرض.
تضم عوامل خطر الإصابة بسرطان المري ما يلي:
- كبار السن: يحدث سرطان المريء في كثير من الأحيان لدى الأشخاص الذين تزيد أعمارهم عن 60 عامًا مقارنة بمن هم في عمر 60 عامًا أو أصغر
- الجنس: الرجال أكثر عرضة للإصابة بالمرض ثلاث مرات ضعف نسبة النساء
- العرق: يحدث سرطان المريء الحرشفي في كثير من الأحيان عند الأمريكيين الأفارقة والآسيويين
ينتشر السرطان الغدي في كثير من الأحيان في البيض - استخدام التبغ: ويشمل ذلك التدخين واستخدام التبغ من غير المُدخَّنين
- تعاطي الكحول: يزيد الاستخدام المزمن و المفرط للكحول وشرب الخمر من خطر الإصابة بسرطان المريء.
- متلازمة باريت والارتجاع الحمضي المزمن: حيث يحدث تغير في بنية الخلايا في الطرف السفلي من المريء نتيجة ارتداد حمض المعدة المزمن إلى المرييء.
حتى بدون تطور مريء باريت، يكون الأشخاص المصابون بحرقة المعدة طويلة الأمد أكثر عرضة للإصابة بسرطان المريء. - فيروس الورم الحليمي البشري (HPV): حيث ترتفع نسبة الإصابة بسرطان المرىء في بعض المناطق حول العالم(مثل آسيا وجنوب إفريقيا)، تعتبر الإصابة بهذا الفيروس خطرًا متزايدًا للإصابة بسرطان الخلايا الحرشفية (الصدفية)
فيروس الورم الحليمي المعدي هو فيروس شائع يمكن أن يسبب تغيرات في أنسجة الأحبال الصوتية والفم وفي اليدين والقدمين والأعضاء الجنسية - اضطرابات أخرى: تم ربط حالات أخرى بسرطان المريء
وتضم هذه الحالة تعذر الارتخاء المريئي (وهو مرض غير شائع يسبب صعوبة في البلع)، ومتلازمة تيلوسيس (وهو اضطراب وراثي نادر يظهر فيه الجلد الزائد على راحتي اليدين وباطن القدمين). - التعرض المهني لبعض المواد الكيميائية: يتعرض الأشخاص الذين يتعرضون لمذيبات التنظيف الجاف لفترات طويلة لخطر الإصابة بسرطان المريء
- تاريخ الإصابة بالسرطان: الأشخاص الذين أصيبوا بسرطان العنق أو الرأس يكونون معرضون بنسبة أكبر للإصابة بسرطان المريء
ما هي أعراض سرطان المريء؟
قد لا يكون لأورام المريء أعراض واضحة في المراحل المبكرة.
العرض الذي يلاحظه الناس أولاً هو عسر البلع، مع ازدياد حجم الكتلة فإنها تضيق فتحة المريء مما يجعل البلع صعبًا و مؤلمًا.
يمكن أن تشتمل الأعراض الأخرى لسرطان المريء التي يجب عليك معرفتها ما يلي:
- ألم في الحلق أو الظهر أو خلف عظم القص أو بين لوحي الكتف
- القيء أو سعال الدم
- حرقة من المعدة
- بحة في الصوت أو سعال مزمن
- فقدان الوزن حيث يعتبر فقدان الوزن السريع من أهم علامات السرطان أولاً بسبب عدم القدرة على تناول الطعام وثانياً بسبب كتلة السرطان نفسها
التشخيص والاختبارات لـ ورم المريء
كيف يتم تشخيص سرطان المريء في تركيا ؟
سيسألك أطباء الجراحة عن تاريخك المرضي، بما في ذلك الأعراض الحالية.
بعد الفحص البدني، قد يطلب الطبيب بعض الاختبارات التي يمكن أن تساعد في تشخيص وتقييم سرطان المريء.
- أشعة باريوم: حيث يستخدم سلسلة محددة من الأشعة السينية لتصور المريء.
حيث يشرب المريض سائلاً يحتوي على الباريوم، مما يجعل رؤية المريء أسهل في الأشعة السينية. - تنظير المريء: هو إجراء يسمح للطبيب بالنظر إلى داخل المريء باستخدام أنبوب رفيع مضاء يسمى المنظار الداخلي.
بالنسبة للاختبار، يتم تمرير المنظار من خلال الفم وأسفل الحلق إلى المريء أثناء نومك.
كما يمكن أيضًا استخدام التنظير الداخلي لتخفيف الانسداد.
حيث يمكن للطبيب إدخال بالون لتوسيع المريء المسدود.
يُطلق على النظر إلى المريء والجزء العلوي من المعدة التنظير العلوي. - الخزعة: أثناء تنظير المريء، قد يأخذ الطبيب خزعة صغيرة من الأنسجة لفحصها تحت المجهر لمعرفة ما إذا كانت هناك أي خلايا سرطانية
- الموجات فوق الصوتية: تستخدم بالمنظار المريئي الموجات الصوتية لإنشاء صور للهياكل الداخلية
في هذا الإجراء، يتم إجراء الموجات فوق الصوتية من خلال منظار المريء - التصوير المقطعي (CT): غالبًا ما يستخدم لتقييم مدى انتشار السرطان في الصدر والبطن
- تصوير الطبقي المحوري ذو الاصدار البوزيتروني PET /CT: حيث يستخدم أيضاً لمعرفة مدى انتشار السرطان
كيف يتم تصنيف سرطان المريء؟
يتم تجميع معظم السرطانات حسب المرحلة، حيث يساعد هذا التصنيف على التخطيط واختيار نهج العلاج المناسب.
تعتمد مرحلة السرطان على موقع الكتلة وعمقها: إصابة الغدد الليمفاوية، ودرجة انتشار السرطان إلى الأنسجة والأعضاء الأخرى.
بالإضافة إلى تحديد مرحلة السرطان، يمكن أيضًا تصنيف أنواع الاورام.
التصنيف هو طريقة لتصنيف الكتل بناءً على شكل خلاياها ومدى عملها كخلايا طبيعية.
يمكن لتصنيف الاورام أيضًا أن يخبر الاطباء بمدى سرعة نمو الكتلة وتزايد حجمها.
تسمى الاورام التي تكون الخلية فيها شبه الطبيعية التي تنمو ببطء أورام متمايزة (درجة منخفضة).
تسمى الكتل التي تكون الخلية فيها مختلفة وغير طبيعية والتي تنقسم بسرعة أورام غير متمايزة (درجة عالية).
من المرجح أن تنتشر هذه الكتل عالية الدرجة أسرع من الأورام منخفضة الدرجة.
علاج أورام المريء في تركيا
كيف يتم إدارة وعلاج سرطان المريء في تركيا؟
يعتمد أسلوب إدارة الحالة على مرحلة السرطان لديها ودرجته.
تتعدد خيارات المعالجة التي يمكن استخدامها لسرطان المريء وهي كما ما يلي:
- الجراحة هي الأسلوب الأكثر شيوعًا في علاج هذا النوع من السرطانات.
حيث يمكن إجراء الجراحة لإزالة جزء من المريء أو معظمه، وكذلك بعض الأنسجة المحيطة به، في إجراء يسمى استئصال المريء.
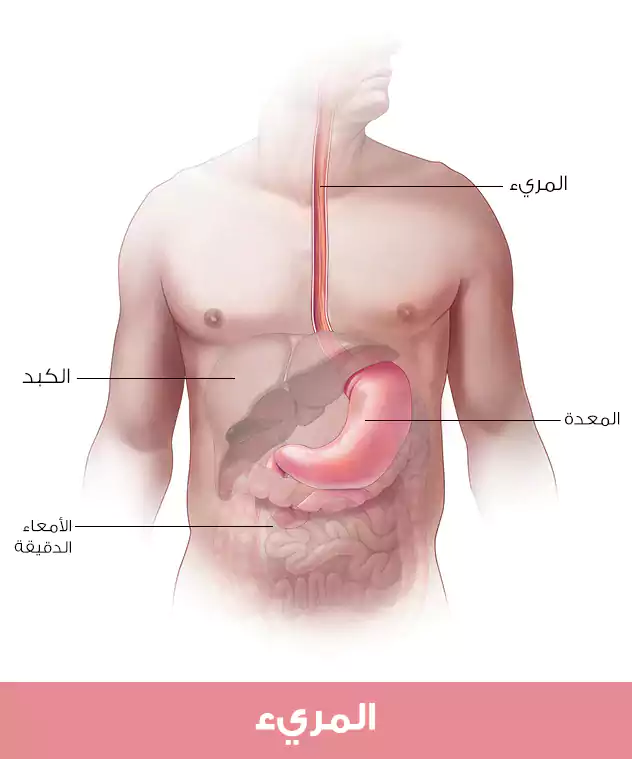
إذا تمت إزالة المريء، فقد يقوم الطبيب بإعادة المعدة (تحريكها لأعلى في الصدر)، أو استخدام قطعة من الأمعاء للحفاظ على الوظيفة.
قد يقوم الطبيب أيضًا بإزالة العقد الليمفاوية حول المريء والنظر إليها تحت المجهر لمعرفة ما إذا كانت تحتوي على خلايا سرطانية.
يمكن للجراحة أن تعالج السرطان لدى بعض المرضى الذين لا ينتشر الورم خارج المريء.
لسوء الحظ، نسبة اكتشاف سرطانات المريء مبكرًا أقل من 25 بالمائة، غالبًا ما يتم تقديم الجراحة لتخفيف الأعراض.
غالبًا ما تتطلب جراحة سرطان المريء دخولًا طويلاً إلى المستشفى.
يقوم بعض الجراحين الآن بالإجراءات باستخدام تقنيات قليلة التوغل: جراحة الصدر بواسطة الفيديو(المنظار) والجراحة بواسطة الروبوت والتي يتم إجراءها في معظم الأحيان على سرطان الرئة.
تشمل المضاعفات: مشاكل تفريغ الطعام وتحريكه لأسفل، تضييق مكان إجراء الجراحة بالإضافة إلى وحرقة المعدة.
- العلاج الإشعاعي هو طريقة لعلاج المرض باستخدام الإشعاع (الأشعة عالية الطاقة) أو المواد المشعة.
يتم استخدامه لقتل الخلية السرطانية أو إتلافها، غالبًا عن طريق توجيه حزمة من الإشعاع إلى الورم.
يدمر الإشعاع الخلية السرطانية بالتدخل في نموها وانقسامها.
يمكن استخدام الإشعاع بمفردها، قبل الجراحة لتقليص الأورام، أو بعد الجراحة لقتل أي أجزاء وكتل سرطانية قد تبقى.
أثناء تطبيق الإشعاع على مرضى سرطان المريء، يتم أحيانًا إدخال دعامة (أنبوب صغير) في المريء لإبقائه مفتوحًا.
وهذا ما يسمى بالتنبيب والتوسيع داخل اللمعة.
يستخدم العلاج الإشعاعي بشكل أساسي كجزء من نظام علاجي أكبر لتخفيف الصعوبة في البلع.
- العلاج الكيميائي يستخدم الأدوية لقتل أو وقف تزايد الكتل السرطانية.
يتم تناول بعض أدوية العلاج الكيميائي على شكل أقراص ويتم وضع بعضها مباشرة في مجرى الدم عن طريق الوريد.
تنتقل هذه الأدوية عبر مجرى الدم ويمكن أن تقتل الخلايا في جميع أنحاء الجسم.
بالنسبة لسرطان المريء، تستخدم المعالجة الكيميائية أحيانًا قبل الجراحة للمساعدة في تقليص الورم.
يمكن إعطاءه العلاج الكيميائي للسيطرة على الأعراض (مع الأدوية المسكنة)، أو قبل الجراحة لتقليص الورم، أو يمكن استخدامه مع الإشعاع للقضاء على الورم.
- يعتبر التشريح تحت المخاطي بالمنظار (EDS) أو استئصال الغشاء المخاطي بالمنظار (EMR) إجراءات لعلاج الأورام المبكرة الصغيرة.
يمكن إزالة الأورام بالتنظير الداخلي دون الحاجة إلى إزالة المريء. - معالجة الاورام بالليزر بالمنظار يمكن استخدامه لعلاج الأورام المتقدمة بشكل خطير والتي قد تسبب انسدادًا في المريء. كجزء من الرعاية الملطفة، يمكن استخدام الليزر لعمل ثقب في الانسداد لتحسين البلع والسماح للمريض بتناول الطعام.
- العلاج الضوئي (PDT) يستخدم الأدوية النشطة ضوئيًا (الأدوية التي يتم تنشيطها بواسطة الضوء غير الحراري) التي تمتصها الكتل السرطانية، وبالتالي تدمر الخلايا السرطانية.
يمكن استخدام هذا الأسلوب للمساعدة في تخفيف أعراض سرطان المريء، وخاصة صعوبة البلع.
للمزيد من التفاصيل حول الجراحات الموجودة في تركيا ننصحك بزيارة الرابط.
الوقاية من سرطان المريء
كيف يمكن منع حدوث سرطان المري؟
على الرغم من أنه لا يمكن الوقاية من سرطان المريء، فإن السيطرة على مسببات الخطر، مثل عدم تعاطي التبغ والكحول، قد تساعد في تقليل خطر الإصابة بالمرض.
أشارت دراسة جديدة إلى أن الأشخاص المشخصين بمريء باريت والذين يعالجون بالاستئصال بالترددات الراديوية تقل معدلات الإصابة لديهم بسرطان المريء.
ما هي التوقعات بالنسبة للأشخاص المصابين بسرطان المريء؟
تعتمد فرصة الشفاء على مرحلة السرطان والصحة العامة للشخص.
إذا تم اكتشاف سرطان المريء مبكرًا، غالبًا ما يمكن علاجه بنجاح.
لسوء الحظ، عادةً لا يتم اكتشاف سرطان المرئ حتى يتطور إلى مرحلة متقدمة، عندها يكون العلاج أقل نجاحًا. وقد يكون قاتلًا.