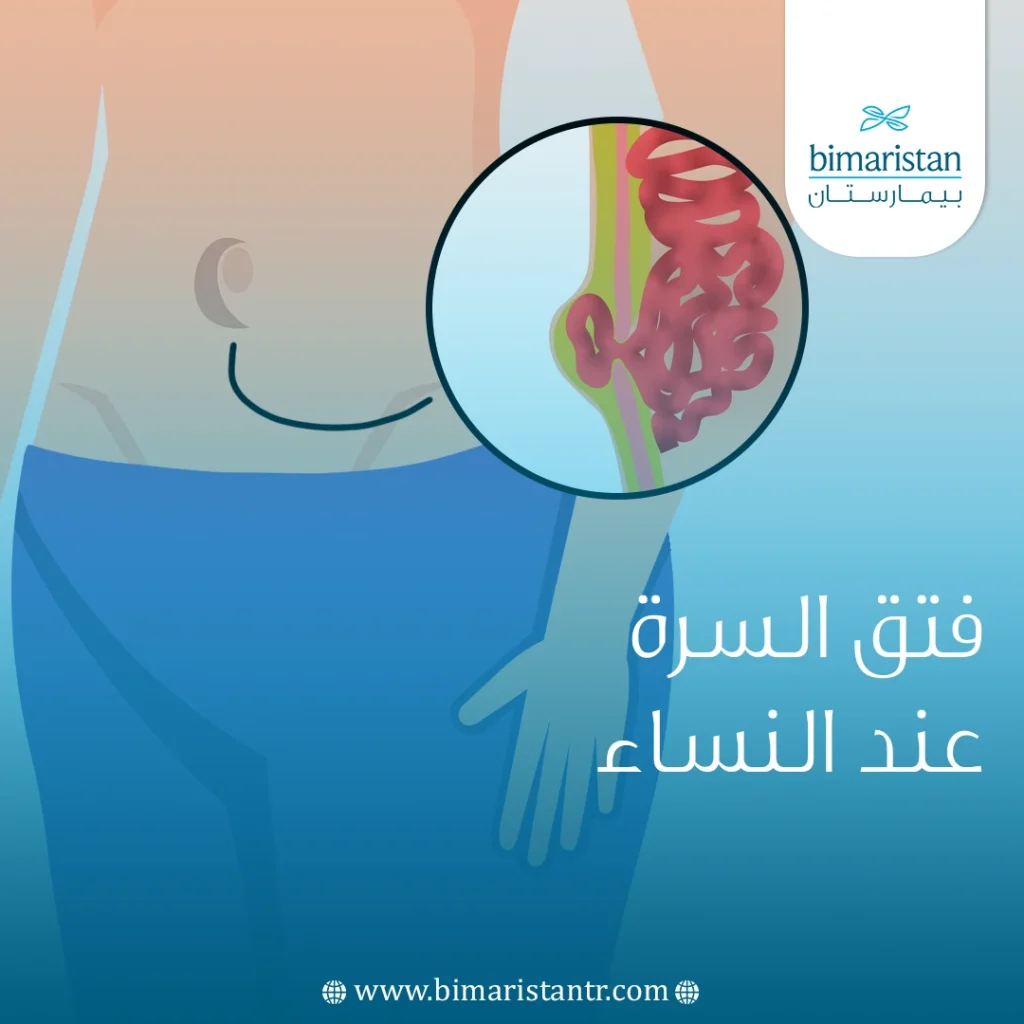
فتق السرة عند النساء (الفتق السري) هو حدوث ضعف في جدارِ البطن وخروج بعض محتوياتها عبر السرة بسبب زيادة الضغط في البطن فتحدث أعراض منها الألم، علاج الفتاق جراحي.
يعتبر فتق السرة عند النساء حالَة شائعة نسبياً عند الولودات وخاصة في حالة الحمول التوءمية وتعدد الولادات فيحدث ضغط زائد على عضلاتِ جدار البَطن فيضعفها.
يؤدي هذا الضعف لخروج النسيج الدهني خلف الجدار وانحصاره، في بعض الحالات قد تخرج الأمعاء مؤدية لأعراض شديدة لدى المرأة تتطلب التدخل الجراحي العاجل، تابع معنا في هذه المقالة لتتعرف على المزيد من الأَعراض وطريقة علاج فتق السرة عند النساء.
مقدمة عن فتق السرة عند النساء
فتق السرة عند النساء هو حدوث ضعف في عضلات جدار البطن لديهن وخروج محتوياتها من نسيج دهني أوعرى معوية عبر فتحة متشكلة في هذا الجدار بين عضلاته غير المتماسكة.

يكون الفتق السري أكثر شيوعًا عند النساء من الرجال في حال حصوله عند البالغين (الأشيع حدوث فتق السرة عند الأطفال حديثي الولادة)، وبشكل عام فإن كل ما يرفع الضغطَ داخل البطن بِشكل مزمن ويضغط على عضلاتها من الداخل بِشكل مستمر يضعفها وبالتالي يحدث الفتق.
أسباب فتق السرة عند النساء
من أهم اسباب فتق السرة عند البالغين ما يلي:
- الوزن الزائد: حالات السمنة الزائدة وارتفاع مشعر BMI لدى الشخص فوقَ 30 يعد من أسباب حدوث انفتاق سري.
- عمليات جراحية سابقة على البطن: يكون مكان الندب الجراحية أضعف من باقي مناطق الجلد مما يجعله أكثر عرضة لحدوث الانفتاق فيه.
- السعال الشديد المزمن: والذي يؤدي إلى ارتفاع ضغط جوف البطن لدى المريض فيحدث فتق سرة لديه.
- تعدد الحمول: الحمل يجعل جدار البطن لدى المرأة ضعيفاً مؤدياً إلى فتق السرة عند النساء (فتق السرة للحامل أو فتاق الحمل).
- الحمول التوءمية: يسبب الحمل التوءمي زيادةً شديدةَ في حجم الرحم لدى الحامل وبالتالي كبر بطنها وضعف العضلات المحافظة على تماسك جدار البطن، يزيد ذلك من نسبة حدوث فتق سرة عند النساء.
- حبن البطن: وهو تراكم شديد للسوائل في جوف البطن بسبب أمراض كبدية مثل تشمع الكبد فيحدث نتنيجتها ارتفاع ضغط داخل البطن فهو من اسباب الفتق السري.
- رفع الأوزان الثقيلة: والتي قد تؤدي كذلك في بعض الحالات إلى الفتق (فتحة أو بعج السر).
أعراض الفتق السري عند النساء
تتعلق أعراض انفتاق السرة بحجم الفتق، محتويات الفتق ووجود أو عدم وجود اختناق لمحتويات الفتق (والتي تكون في الحالات البسيطة نسيجاً دهنياً فقط لكن في الحالات الشديدة قد تنفتق الأَمعاء مؤدية لحدوث اعراض تتطلب العلاج الفوري عند الأطفال والبالغين على حد سواء).
في حال انفتاق النسيج الدهني فقط وانقطاع التروية الدموية عنه وتموته سوف تظهر أعراض فتق السرة عند النساء على شكل:
- ألم مكان الفتق
- انتباج أو تبارز كيسي صغير جداً مكان السرة
أما في الحالات الشديدة عند حدوث انفتاق الأمعاءِ في فتقٍ سري قد نلاحظ اعراض هضمية مثل:
- الإمساك
- الإقياء
وفي الحالات الأشد عند اختناق الأمعاء في الفتق السري وانقطاع التروية الدموية عنها سوف يحصل اعراض احتشاء معوي (ألم شديد جداً مكان الفتق) وهي حالة اسعافية تتطلب التداخل والعلاج الفوري من أجل تحرير محتويات الفتق واعادة ترويتها الدموية بأسرع وقت ممكن.
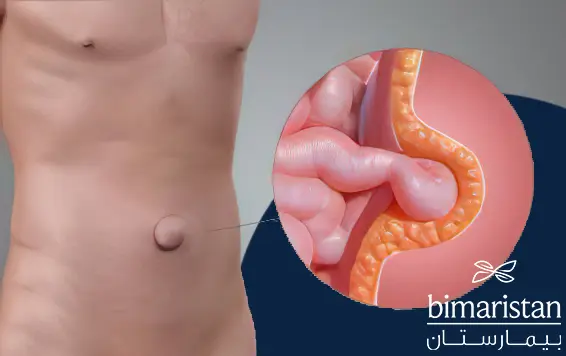
اختلاطات فتق السرة عند البالغين
من أهم اختلاطات الفتق السري عند النساء بشكل خاص والبالغين عامة هو الاحتشاء والتموت للأمعاء المنحصرة في عنق الفتق والذي قد يؤدي في حال عدم المعالجة إلى التهابات خطيرة مهددة للحياة في جوف البطن.
في حال حصول الاختلاطات يحدث لدى المريض ألم شديد جداً مكان الفتق مع ارتفاع في الحرارة (مترافق مع الغثيان والإقياء أحياناً) وتغير في لون الانتباج الكيسي مكان السرة، في حال ظهور هذه الأعراض فحالة مهددة للحياة والتداخل الإسعافي مطلوب أن يتم فوراً.
نتيجة لذلك يوصى بالتداخل الجراحي السريع على جميع الفتوق التي تحتوي عروة معوية خشية حدوث نقص التروية الدموية فيها ولتجنب هذه الاختلاطات.
تشخيص فتق السرة عند الكبار
يعتمد تشخيص فتق السرة بشكل أساسي على الفحص السريري في عيادة الطبيب، حيث يلاحظ خلال الفحص وجود انتباج أو تبارز كيسي (تورم صغير أو كبير) مكان السرة أو حولها ويقوم أيضاً بتحديد محتويات هذا الفتق (نسيج دهني أو عرى معوية).
في حال تعذر التشخيص قد يلجأ الدكتور لاستخدام الإيكو بحيث يوضح محتويات الفتق السري. قد يتم طلب بعض الفحوصات الدموية والشعاعية لنفي الحالات المرضية الأخرى التي تختلط مع انفتاق السرّة.
علاج فتق السرة عند النساء في تركيا
يختلف علاج فتق السرة عند النساء أو الرجال الكبار عن علاج الفتق السري عند الاطفال (وذلك لاختلاف المسببات وشدة اعراض الفتق) حيث قد نلجأ للخيار المحافظ عند للأطفال في بعض الأحيان (أي علاج فتق السرة عند الصغار بدون جراحة)، لكن علاج فتق السرة عند البالغين يتطلب الجراحة لتفادي مخاطر اختلاطات الفتاق المهددة للحياة.
استطبابات الجراحة لعلاج فتق السرة
قد يترك الفتق للمراقبة وعدم اللجوء للجراحة في حال كان الفتاق ثانوياً وصغيراً، لكن التداخل الجراحي العاجل مطلوب في حال وجود أي من الأعراض التالية:
- تورم الفتق أصبح مؤلماً
- تجاوز قطره 1 سم
- حدوث الاختناق وقطع التروية الدموية عن العروة المعوية المنحصرة في الفتق
جراحة فتق السرة عند النساء
يمكن علاج الفتق السري جراحياً إما بالجراحة المفتوحة أو بالجراحة التنظيرية وذلك حسب خبرة الطبيب الجراح وتوفر المعدات التجهيزات المناسبة في المشفى.
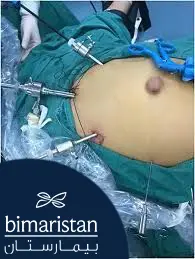
تجرى الجراحة تحت التخدير العام وتستغرق 30 دقيقة يقوم الجراح خلالها برد محتويات فتقِ السرة إلى مكانها ثم يدعم ويقوي عضَلات جدار البطن بوضع شبكة خلف مكان الفتق ويحكم إغلاقه بوضع خرزات لتمكينه ومنع حدوث نكس للفتق السري.
في حال تأخر التداخل الجراحي وتموت العروة المعوية المنحصرة في الفتق يعالج استشاري الجراحة الحالة باستئصال هذه القطعة ويصل طرفي الأَمعاء السليمة كي يعيد استمرارية الأنبوب المعوي.
ما بعد عملية فتق السرة عند النساء
في الحالات السليمة غير المختلطة من الفتق السري غالباً ما يعود المريض إلى منزله في نفس يوم العملية الجراحية بعد زوال أثر التخدير لديه حيث يعطى مجموعة من التوصيات التي يجب اتباعها.
أهم هذه التوصيات هو تجنب الجهد البدني أو أي عمل من شأنه رفع الضغطِ داخل البطن أو تقليص عضلاتها وذلك لمدة تتراوح بين عدة أيام وحتى ثلاثة أسابيع.
قد يعاني المريض من بعض الألم مكان الشق الجراحي بعد العملية لفترة بسيطة، يتم تدبيره بمسكنات الألم وارتداء ملابس فضفاضة ريثما يلتئم مكان عملية الفتق السري عند النساء.
يجب مراجعة الطبيب بعد العمل الجراحي في حال ملاحظة أعراض في مكان العمل الجراحي مثل:
- عدوى في موقع الجرح
- حمى
- غثيان وإقياء
- نكس الفتق
تعاني النساء من فتقٍ في السرة بسبب كثرة الحمول، لكن هذه الحالة ليست حكراً عليهن فالرجال أيضاً قد يعانون من الفتق السري، غالباً ما يكون سببه لديهم هو مرض كبدي مثل تشمع الكبد وذلك عند الكحوليين المزمنين حيث يحدث لديهم تليف الكبد ثم تشمعه مؤديا لتراكم السوائل وحبن في البطن والذي بالنتيجة يؤدي إلى فتق السرة عند الكبار.
يعالج فتق السرة عند النساء بالجراحة لتفادي اختلاطات اختناق محتويات الفتق وانقطاع ترويتها الدموية، يتم التعافي من عملية فتق السرة خلال فترة قصيرة ويعود المريض إلى حياته الطبيعية بسرعة خلال أقل من شهر.
المصادر: