تعد لمفوما لا هودجكن أشيع سرطانِ لمفاوي، وتظهر بأنواع عديدة أغلبها خارج الجهاز اللمفاوي، وتشخيصها وعلاجها يحتاج إلى أفضل الأيادي وأمهرها من اطباء تركيا.
ما هي اللمفوما lymphoma؟
يمكن للخلايا الليمفاوية السرطانية أن تنتقل عبر الدم والجهاز الليمفاوي وتنتشر وتنمو في أجزاء كثيرة من الجسم، بما في ذلك العقد الليمفاوية والطحال ونخاع العظام والعديد من الأعضاء الأخرى.
سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن non-Hodgkin lymphoma: وهي الأشيع، وتضم جميع الأورام التي لا تدخل ضمن تصنيف الليمفوما الهودجكينية.
لمحة عن الجهاز اللمفي والخلايا اللمفاوية
إن الجهاز الليمفاوي هو جزء مهم من الجهاز المناعي في جسم الإنسان ويقوم بتخليص الجسم من العديد من السموم والقضاء على العديد من الأجسام الممرضة التي تهاجم الجسم.
يتشكل الجهاز اللمفي من اللمف، الأوعية الليمفاوية، العقد اللمفاوية، نقي العظم، الطحال، الغدة التيموسية واللوزات.
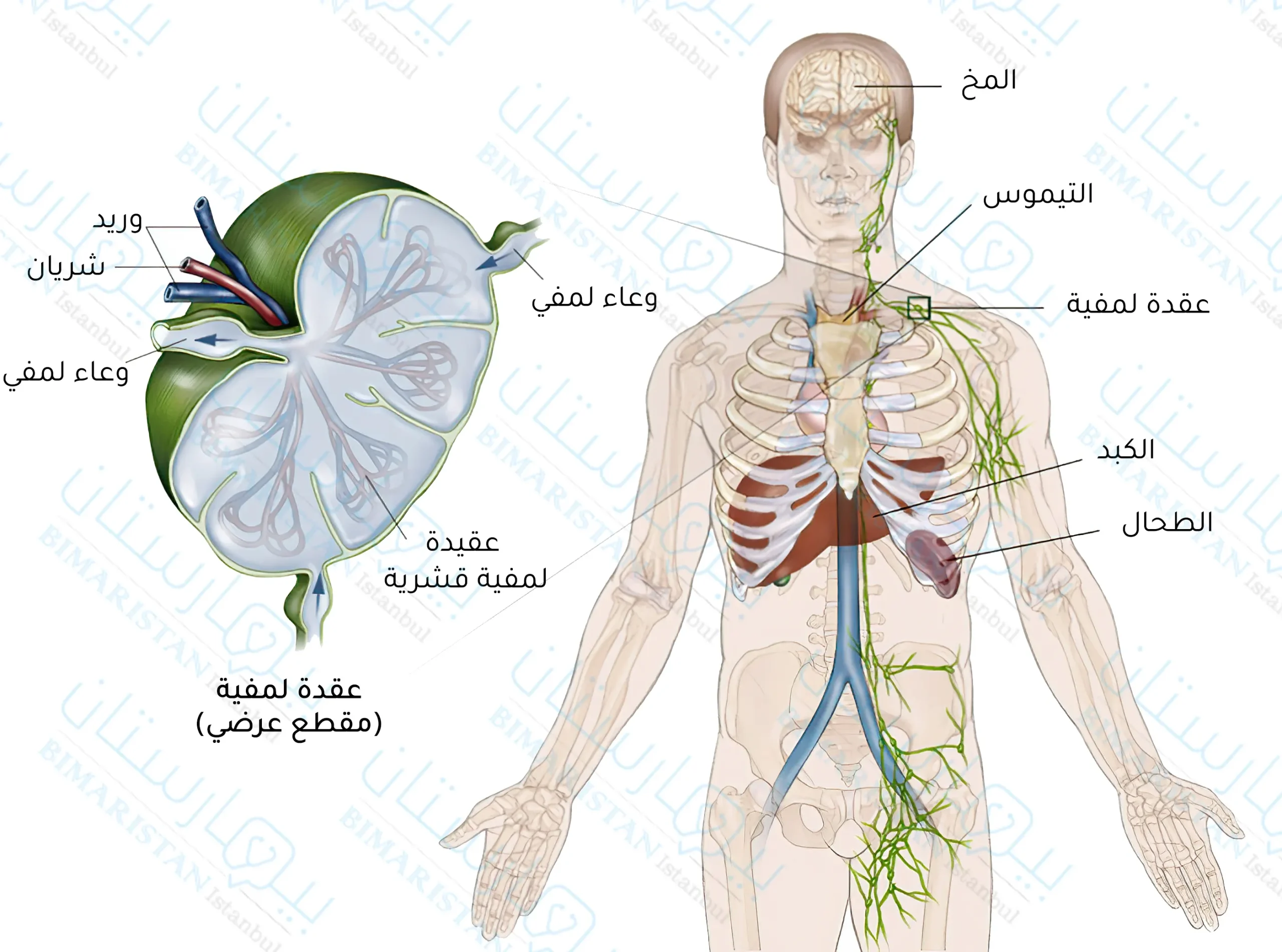
حيث تعبر الخلايا الناضجة إما عن CD4 وتسمى في هذه الحالة الخلايا التائية المساعدة، أو عن CD8 وتسمى هنا بالخلايا التائية القاتلة أو المثبطة Suppressor.
سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
كيف يميز الأطباء لمفوما هودجكن Hodgkin’s Lymphoma عن لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma؟
أنواع سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
ليمفوما الخلايا اللمفاوية من النوع B
لمفوما خلايا B الكبيرة المنتشرة Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
اللمفومة الجريبية Follicular Lymphoma
ابيضاض الدم الليمفاوي المزمن CLL/ورم الغدد اللمفاوية الصغيرة SLL
لمفوما بوركيت Burkitt Lymphoma
- بوركيت المستوطنة Endemic: وهي كما ذكرنا تنتشر عند الأطفال واليفع في إفريقيا وهي غالباً ما ترتبط بالإصابة بفيروس إبشتاين-بار، وهي غالباً ما تؤثر على الفك وعظام الوجه عندهم، كما يمكن أن تنشأ في الأمعاء والكليتين و أعضاء أخرى.
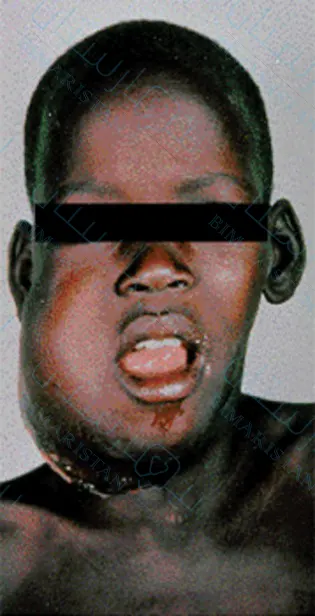
تحتاج لعلاج فوري ومكثف نظراً لانتشارها ونموها السريع، وعلى الرغم من ذلك فإن نصف المرضى يشفون بعد العلاج الكيميائي المكثف.

لمفوما الخلايا العبائية Mantle Cell Lymphoma
لمفومة المنطقة الهامشية Marginal Zone Lymphoma MZL
- الهامشية الخارج عقدية Extra-Nodal MZL: الأشيع، وهي تنشأ في مناطق خارج الغدد اللمفاوية وغالباً في MALT حيث يمكن تسمية هذا النوع بليمفوما مالت MALT Lymphoma، وتكون إما معدية Gastric أو خارج معدية، يظهر هذا النوع مع وجود تاريخ طبي بالإصابة بالإنتانات المزمنة (الملتوية البوابية).
- الهامشية العقدية Nodal MZL: وهي تنشأ في العقد اللمفاوية أو نقي العظم.
- الهامشية الطحالية Splenic MZL: وهي تنشأ في الطحال أو الدم أو نقي العظم.
سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن البلازمية الخلوية Lymphoplasmacytic Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
سرطان ليمفوما لا هودجكن من النوع T
ابيضاض الدم الليمفاوي من النوع T
لمفوما الخلايا T المحيطية
- الليمفومة الكشمية كبيرة الخلايا Anaplastic Large cell Lymphoma: يمكن أن تكون ALCL جهازية Systemic (تحدث في جميع أنحاء الجسم) أو جلدية Cutaneous (تقتصر على الجلد)، عادةً ما تكون ALCL الجهازية في مرحلة متقدمة عند تشخيصها وهي سريعة النمو.
يُصنف النوع الجهازي إلى تحت نوعين أيضًا بناءً على إيجابية (ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase أو سلبيته، تستجيب ALCL الجهازية للعلاج بشكل جيد، وخاصة المرض الإيجابي ALK ولكن قد يحتاج المرضى سلبيي ALK إلى علاجات أكثر قوة، ويحدث الانتكاس بشكل متكرر أكثر من المرض الإيجابي ALK. - لمفوما لا هودجكن التائية المناعية الوعائية Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma: وهي نوع نادر وشديد يمثل حوالي سبعة في المائة من جميع المرضى الذين يعانون من الأورام اللمفاوية للخلايا التائية في الولايات المتحدة.
معظم المرضى هم في منتصف العمر إلى كبار السن ويتم تشخيص المرض لديهم في مراحل متقدمة، وهناك بعض الأدلة على أن AITL تتطور من استجابة مناعية مستمرة يحتمل أن تكون بسبب عدوى فيروسية كامنة (مثل فيروس ابشتاين بار).
غالباً ما تشمل الأعراض الأولية الحمى والتعرق الليلي والطفح الجلدي والحكة وبعض اضطرابات المناعة الذاتية مثل فقر الدم الانحلالي المناعي ونقص الصفيحات المناعي ومع مستويات رمتفعة من غاما غلوبيولين في الدم. - لمفومة الخلايا T الجلدية Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: وهي مصطلح عام يشمل عدة تحت انواع بطيئة النمو معظمها محدد في الجلد، و أحد هذه الأنواع هو Mycosis Fungoides وهو اشيع نوع ويتميز بوجود حطاطات ولويحات وآفات جلدية حاكة على مسار الجسم، نوع آخر هو متلازمة سيزاري Sézary syndrome وهي متلازمة تصيب الدم والجلد وتتظاهر بجلد أحمر حاك بشدة في معظم أجزاء الجسم كما يمكن رؤية خلايا T ورمية تدعى بخلايا سيزاري Sézary Cells.
- لمفومة الأرومة الليمفاوية Lymphoblastic lymphoma: وهي نادرة وتنشأ من الأرومات الليمفاوية وهي أشيع على حساب أرومات الخلايا T.
أسباب وعوامل خطورة الإصابة بسرطان ليمفوما لا هودجكن
- سن المريض: كلما كان سن المريض أكبر ارتفعت نسبة الإصابة بليمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma حيث شخصت أكثر من ثلث الحالات عند المسنين فوق 75 عام.
- الجنس: حيث يوجد ميل بسيط لحدوث الإصابة عند الذكور بشكل أكبر من عند الإناث.
- العرق: يعتقد أن البيض لديهم ميل لللإصابة بلمفوما لا هودجكين بشكل أكبر من السود إلا أن هذا الاعتقاد يحتاج لدراسات تفصيلية أكثر.
- قصة عائلية سابقة: تزداد نسبة الإصابة بلمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma عند وجود إصابة عند الأقارب من الدرجة الأولى (أخ,أب,ابن…).
- البدانة: أظهرت دراسات حديثة أن اللأشخاص البدينين ترتفع لديهم نسبة الإصابة ببعض أنواع سرطان الغدد الليمفاوية هودجكين.
- مرض مناعي وراثي: مثل نقص غاما غلوبيولين الدم Hypogammaglobulinemia أو متلازمة فيسكوت-ألدريك Wiscott-Aldrich.
- قصة تعرض سابق للإشعاع: كالذين خضعوا لعلاج إشعاعي سابق أو نادرا الناجون من الكوارث النووية والكيمياوية.
- أمراض المناعة الذاتية: مثل الحمى الرثوية, متلازمة شوغرن Sjögren’s disease، الذئبة الحمامية الجهازية SLE أو الداء الزلاقي كلها ربطت بالإصابة بلمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, وكما يمكن لمتلازمة عوز المناعة المكتسب AIDS المسببة بفيروس HIV أن بكون لها يد في الإصابة بهذا السرطان.
- فيروس ابشتاين بار EBV وفيروس تي الليمفاوي البشري من النوع الأول Human T-lymphotrophic Virus type I: وقد أثبت أن لهم دور كبير في حدوث الطفرات الجينية لدى مرضى سرطان الغدد الليمفاوية لا هودجكن.
- الالتهابات المزمنة: كالالتهاب المسببة بالملتوية البوابية، فيروس التهاب الكبد والمتدثرة الببغائية.
الأعراض والعلامات
يمكن ألا يتظاهر سرطان الغدد اللمفاوية بأية أعراض حتى يكبر الورم إلى حجم معين.
- تعرق ليلي غزير
- فقدان وزن غير مفسر
- طفح أو كتل جلدية مع جلد حاك حول الجسم كله
- حمى غير مفسرة
- الشعور الدائم بالتعب والإرهاق
- زيادة إمكانية حدوث النزوف كالنزوف الأنفية و الطمث الغزير
- الشعور بانقطاع النفس Breathlessness
- الشعور بالشبع بعد تناول كمية قليلة من الطعام
- إنتانات متكررة
تشخيص سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma في تركيا
- التصوير بأنواعه المختلفة: كالتصوير بالأمواج فوق الصوتية، التصوير المقطي المحوسب CT، التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني PET-Scan، الصورة الشعاعية البسيطة للصدر و التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي MRI.
- الفحوصات الدموية: كتعداد الدم الكامل CBC، والفحوصات الكيميائية الدموية كما يمكن إجراء معايرة لأنزيمات معينة في حال الشك بنوع معين من لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
- فحص العظم Bone Scan.
- الخزعة: وهي أهم وسيلة تشخيصية وأكثرها دقة، لكن لا تطلب إلا بعد نفي الأسباب الأخرى ومن أنواعها خزعة نقي العظم.
إن كانت لديك أي مشكلة او استفسار فمركز بيمارستان الطبي سيجيبك على جميع اسئلتك، لا تتردد بالتواصل معنا، مركز بيمارستان عائلتك في تركيا.
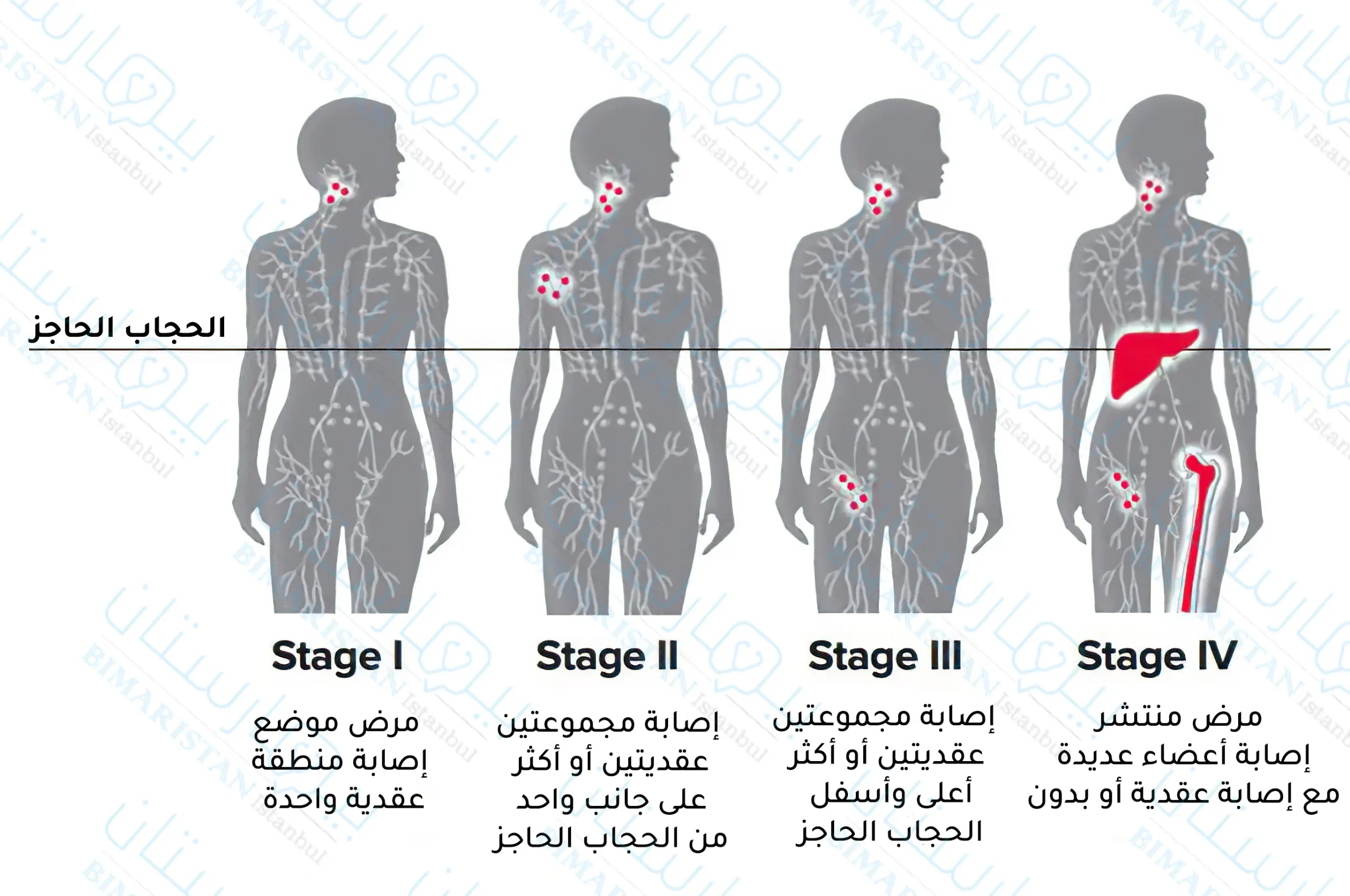
التقييم المرحلي لسرطان ليمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
ويتم استخدام نفس التصنيف المستخدم في تصنيف لمفوما هودجكن Hodgkin’s Lymphoma وهو تصنيف لوغانو.
علاج سرطان لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma في تركيا
ليس بالضروري دائما اللجوء إلى العلاج في حال شخصت الإصابة بليمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s حيث يمكن المراقبة في حال عدم وجود أعراض أو عدم تأثر حياة المريض.
ومن أشيع العلاجات في تركيا:
علاج سرطان الليمفوما اللاهودجكينية الكيميائي
إن الأدوية الكيميائية تستهدف أي خلية تنقسم باستمرار في الجسم ومنها الخلايا السرطانية، ونتيجة ذلك فإن لها أعراض جانبية كثيرة فالخلايا السرطانية ليست الوحيدة التي تتجدد بسرعة وباستمرار في الجسم (فخلايا الشعر، الجلد، الدم… تتجدد باستمرار أيضاً).
عادةً ما يعطى العلاج على شكل مشاركات دوائية بين عدة أدوية للحصول على نتيجة أفضل وتتضمن العديد من مشاركات العلاج الكيميائي للمفوما لا هودجكن non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma الجسم المضاد أحادي النسيلة ريتوكسيماب (ريتوكسان)، والذي يُختصر عادةً بالحرف R ويوضع في بداية أو نهاية اختصار المشاركة الدوائية، مثل R-CHOP أو CHOP-R التي تتألف من سيكلوفوسفاميد ، دوكسوروبيسين ، فينكريستين ، بريدنيزون.
يمكن أيضاً استخدام العلاج الكيميائي داخل القراب (في القناة الشوكية أو المسافة تحت العنكبوتية) في علاج الأورام اللمفاوية البدئية التي تنشأ في الخصيتين أو الجيوب الأنفية، سرطان الخلايا الليمفاوية B-cell الكبيرة المنتشر، سرطان لمفوما Burkitt، لمفومة الأرومة اللمفاوية أو بعض الأورام اللمفاوية التائية العدوانية (سريعة النمو)، حيث يُعطى للتقليل من انتشار خلايا الليمفوما إلى الدماغ والحبل الشوكي.
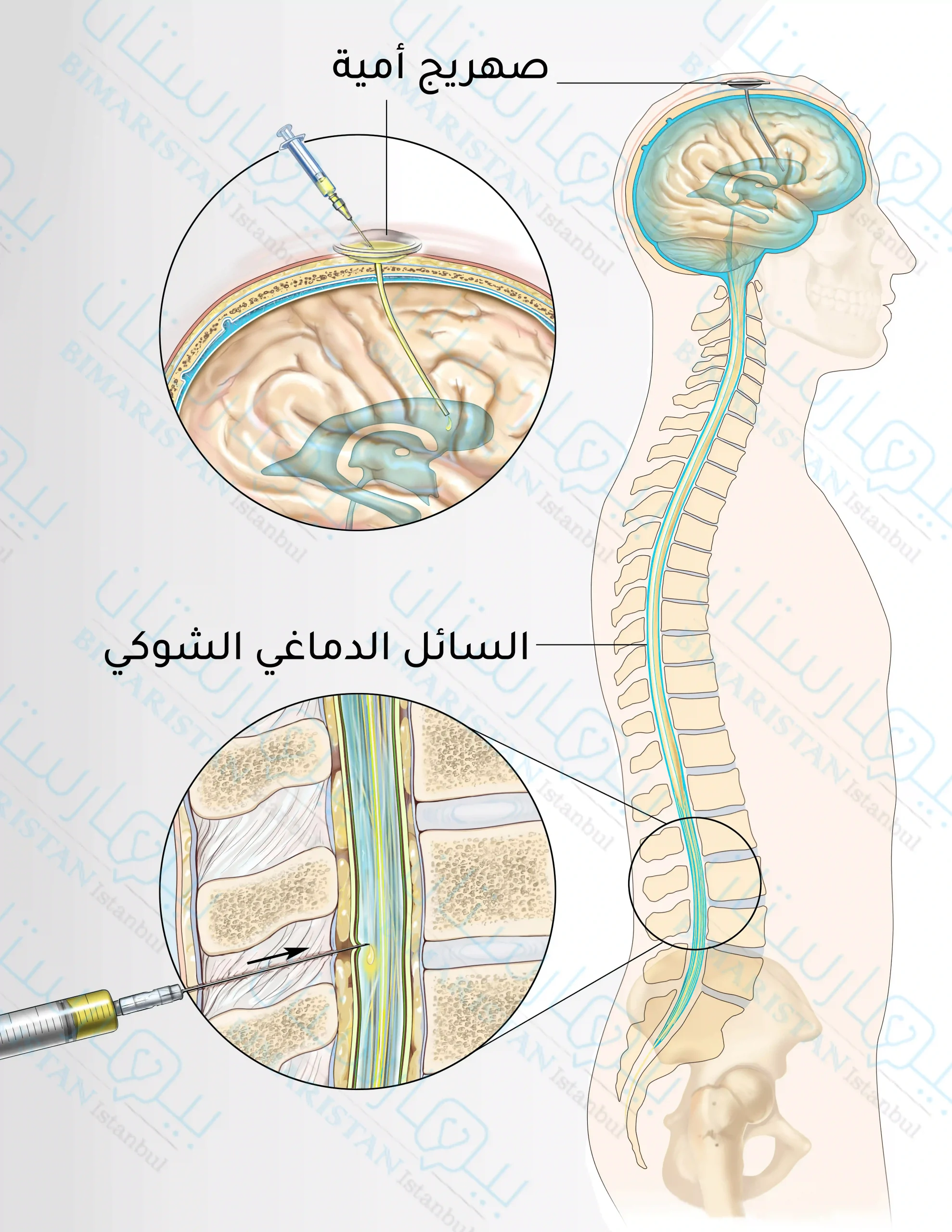
بروتوكول علاج الليمفوما المناعي
إن مجال العلاج المناعي في تركيا توسع بشكل كبير في الآونة الأخيرة وظهرت أجيال جديدة من الأدوية والجزيئات الصنعية للتقليل من الأضرار الجانبية، وإن الدراسات ما زالت قائمة لتطوير الطرق العلاجية المناعية.
إن العلاج المناعي يُبنى أساساً على تقوية مناعة جسم الإنسان الطبيعية أو استخدام أضداد صنعية للقضاء على الخلايا المشوهة السرطانية ومن اشيع هذه الطرق:
الأضداد وحيدة النسيلة
وهي بروتينات صنعية تقوم بمهاجمة خلايا ذات واسمات معينة مما يخفف الآثار الجانبية بشكل كبير ونذكر منها:
- الأجسام المضادة التي تستهدف المستضد CD20: إن CD20 بروتين موجود على سطح الخلايا البائية، تشمل هذه الأدوية ريتوكسيماب (ريتوكسان) وأوبينوتوزوماب (غازيفا) وأوفاتوماب (أزيرا) وإيبريتوموماب تيوكسيتان (زيفالين).
- الأجسام المضادة التي تستهدف المستضد CD30: هو بروتين موجود على سطح الخلايا التائية، من أمثلة هذه الأدوية برنتوكسيماب فيدوتين (brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris.
- الأجسام المضادة التي تستهدف المستضد CD52: وهو بروتين موجود على سطح الخلايا التائية، ومن الأدوية التي تستهدف هذا المستضد الألمتوزوماب.
يوجد العديد من الأدوية الأخرى لكن لم تذكر للاختصار.
الخلايا التائية ذوات المستقبلات الخيمرية Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cells
تعد هذه الطريقة نقلة نوعية في علاج لمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma وما زالت الدراسات قائمة حول هذه الطريقة.
وتُؤخذ هنا الخلايا التائية من دم الشخص وتُعدل في المختبر ليكون لها مستقبلات محددة على سطحها، يمكن لهذه المستقبلات الخيمرية أن تلتصق بالبروتينات الموجودة على سطح خلايا الليمفوما السرطانية، ويمكّن هذا الارتباط الخلايا التائية من تدمير الخلايا الورمية.
معقد ضد-دواء (ADC Antibody-Drug Conjugate)
وهو ضد وحيد النسيلة محمل بدواء كيميائي، وبعد ارتباط الضد وحيد النسيلة مع الخلية السرطانية يقوم بتحرير الدواء الكيميائي الذي يعمل على قتل وتعطيل الخلية الورمية بآلية معينة.
تشمل اقترانات الأجسام المضادة والأدوية المعتمدة ما يلي:
- Brentuximab Vedotin (Adcetris)
- Loncastuximab Tesirine-lpyl (ZYNLONTA)
علاج سرطان الليمفوما اللاهودجكينية الموجه
العلاج الموجه هو نوع من العلاج المتخصص الذي يستهدف البروتينات التي تتحكم في كيفية نمو الخلايا السرطانية وانقسامها وانتشارها، وهو يشبه نوعاً ما العلاج المناعي، وقد ظهرت دراسات جديدة تؤكد أهمية هذا العلاج في علاج لمفوما لا هودجكن، ومن بعض أنواع هذا العلاج نذكر:
- المماثلات البيولوجية: وهي أدوية مماثلة للأدوية البيولوجية.
- مثبطات البروتون تيروزين كيناز: البروتون تيروزين كيناز هو أنزيم ضروري لنمو الخلايا الورمية.
- مثبطات PI3K: إن PI3K جزيء ينقل الإشارات التي تساعد الخلايا البائية على النمو والتحرك والانقسام والبقاء، لذلك تساعد مثبطات PI3K على إيقاف أو إبطاء نمو خلايا الليمفوما السرطانية.
- مثبطات متيلة الDNA (مثبطات DNA Methyltransferase): إن أنزميات المتيلة لها تأثير كبير على عملية تنظيم الجينات، وهي علامة حيوية تنبؤية محتملة للاضطرابات الجينية والأمراض، وإن تثبيط هذه الأنزيمات يساعد في إيقاف النمو الخلوي وتنشيط الموت الخلوي المبرمج.
العلاج الشعاعي للمفوما لا هودجكن
إن العلاج الشعاعي هو علاج يستخدم اشعة سينية عالية الطاقة لتدمير الخلايا الورمية والإنقاص من حجم الورم الموضع، حيث أنه يمكن أن يستخدم في علاج بعض أنواع اللمفوما الموضعة أو في تشعيع بعض الأورام الكبيرة التي أثرت على الأعضاء المجاورة.
إن مجال العلاج الشعاعي والعلاج بالأشعة التداخلية شهد قفزة نوعية في تركيا، وذلك لأهميته في البرتوكول العلاجي للكثير من السرطانات الشائعة حول العالم.
علاج لمفوما لا هودجكن بزرع الخلايا الجذعية ونقي العظم
إن زرع (حقن) الخلايا الجذعية هو علاج يستخدم لتعويض النقص في الخلايا الطليعية لمكونات الدم الخلوية بعد الخضوع للعلاجات الأخرى وخاصة العلاج الكيميائي المكثف عالي الجرعة، حيث تستنزف هذه العلاجات الخلايا المكونة للدم ويمكن أن يدخل جسم المريض في اضطرابات لا تحمد عاقبتها.
وإن هذه العملية تجرى بطريقتين:
- زرع خلايا جذعية من الشخص نفسه: وفي هذه الطريقة نقوم بأخذ الخلايا الجذعية السليمة قبل الخضوع للعلاجات الأخرى (لأنها تستنفد بعد العلاج)، ولهذا النوع طريقتين يمكن اتباعهما اعتمادا على المكان الذي أخذت منه هذه الخلايا، ففي النوع الأول تؤخذ الخلايا الجذعية من الدم، وهي الطريقة الأكثر شيوعاً واستخداماً نظراً لسهولة الحصول على هذه الخلايا ووفرتها، وأما في الطريقة الأخرى تؤخذ الخلايا من نقي العظم، حينها يطلق على العلاج اسم زرع نقي العظم.
- زرع خلايا جذعية من شخص آخر: وهو غالباً ما يكون قريب للمريض كأخ أو أخت، كما يمكن أن يكون شخصاً غريباً بعد إجراء فحوصات التطابق الخلوي اللازمة.
ولكثرة العلاجات وأنواعها يمكنك التواصل معنا ليساعدك مركز بيمارستان الطبي في اختيار أفضل علاج عند أفضل الأيادي الخبيرة في تركيا.
شهر التوعية حول سرطان ليمفوما لا هودجكن Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
يمكن أن تحدث أورام الغدد الليمفاوية هودجكين ولا هودجكين عند الأطفال والبالغين وبأية عمر.