علاج مرض باركنسون (الشلل الرعاش) يحسن من نوعية حياة المرضى، لعلاج مرض الباركنسون نستخد أدوية تؤثر في مستوى الدماغ وقد نلجأ في هذا المرض إلى العلاج الجراحي.
مرض الباركنسون ومراحل تطوره
يُعد مرض باركنسون (Parkinson Disease (PD من الأمراض التنكسية العصبية (تنكسي مزمن)، ومن المعروف أن الخلايا العصبيّة حين موتها لا يمكن تعويضها وبالتالي لا يوجد علاج شافي من مرض باركنسون.
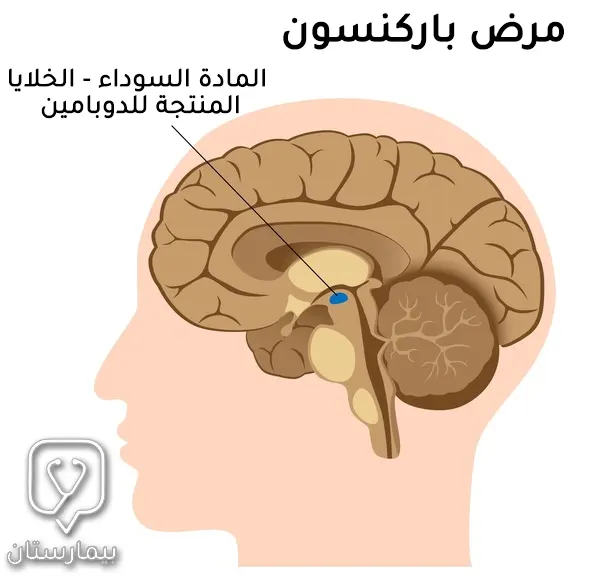
يعتمد علاج مرض باركنسون على السيطرة على الأعراض التي نجمت عن خسارة عصبونات المادة السوداء في الدماغ ونقص الدوبامين في الجسم.
يصنف علاج مرض باركنسون إلى علاج الباركنسون الدوائي وعلاج الباركنسون الجراحي وذلك حسب مرحلة المرض وشدة تقدمه، لذا بداية يجب أن يشخص بشكل دقيق لمعرفة سبب المرض ويتم ذلك عبر فهم آلية حدوث المرض، ومن ثم تطبيق المعالجة المناسبة.
اقرأ المزيد حول: كيفية الوقاية من مرض باركنسون قبل حدوثه.
الآلية المرضية لحدوث مرض باركنسون
يحدث مرض باركنسون بسبب تراكم بروتينات طافرة (غير طبيعية) ينتجها الجسم لتستقر في خلايا عصبية تقع في منطقة المادة السوداء من جذع الدماغ، يبدأ غالباً في ال 60 من العمر.
تكون هذه العصبونات مسؤولة عن انتاج نواقل عصبية تسيطر على عضلات المريض في حالتي الحركة والسكون لذا فإن فقدها يؤدي إلى ظهور أعراض مرض باركنسون مثل الرعاش (الاهتزاز والرجفان) وبطء الحركَة.
قد تؤدي أمراض وأذيات أخرى إلى إصابة المناطق المسيطرة على الحركَة مسببة مرض الباركنسون، تتضمن هذه الأذيات الجلطات الدماغية أو تناول أدوية تؤثر على النواقل العصبيّة الكيميائية في الدماغ.
اقرأ المزيد حول: أسباب مرض باركنسون العصبي.
تشخيص مرض باركنسون
يَتم تشخيص مرض باركنسون سريرياً عبر سماع القصة المرضية من المريض إضافة للقيام بالفحص العصبي لمرض باركنسون، تصوير الطبقي المحوري والرنين المغناطيسي غير مفيدين في كشف مرض باركنسون.
قد يَتم كشف مرض باركنسون المبكر بِاستخدام تقنيات حديثة مضافة للتصوير الطبقي المحوري، تعتمد هذه التقنيات على كشف مستويات الدوبامين في جذع الدماغ في الجهاز العصبي المركزي.
في حال شاهدنا مرض باركنسون في أعمار مبكرة يجب الشك ببعض الأمراض والمتلازمات الوراثية، من أمثلتها داء ويلسون ومرض الرقص لهنتنغتون.
علاج مرض باركنسون الدوائي
يَتم علاج مرض باركنسون غالباً بشكل دوائي، يكون هدف المعالجة هو تخفيف الأعراض وليس الشفاء الكلي، تقوم المعالجة على تعويض الدوبامين الناقص في الجهاز العصبي وبالتالي زوال الأعراض الحركية.
علاج مرض باركنسون المبكر
يَتم علاج المراحل المبكرة من الشلل الرعاش بِاستخدام أدوية تستطيع دخول الجهاز العصبي المركزي والتصرف كما الدوبامين لتزول الأعراض الحَركية للمرض.
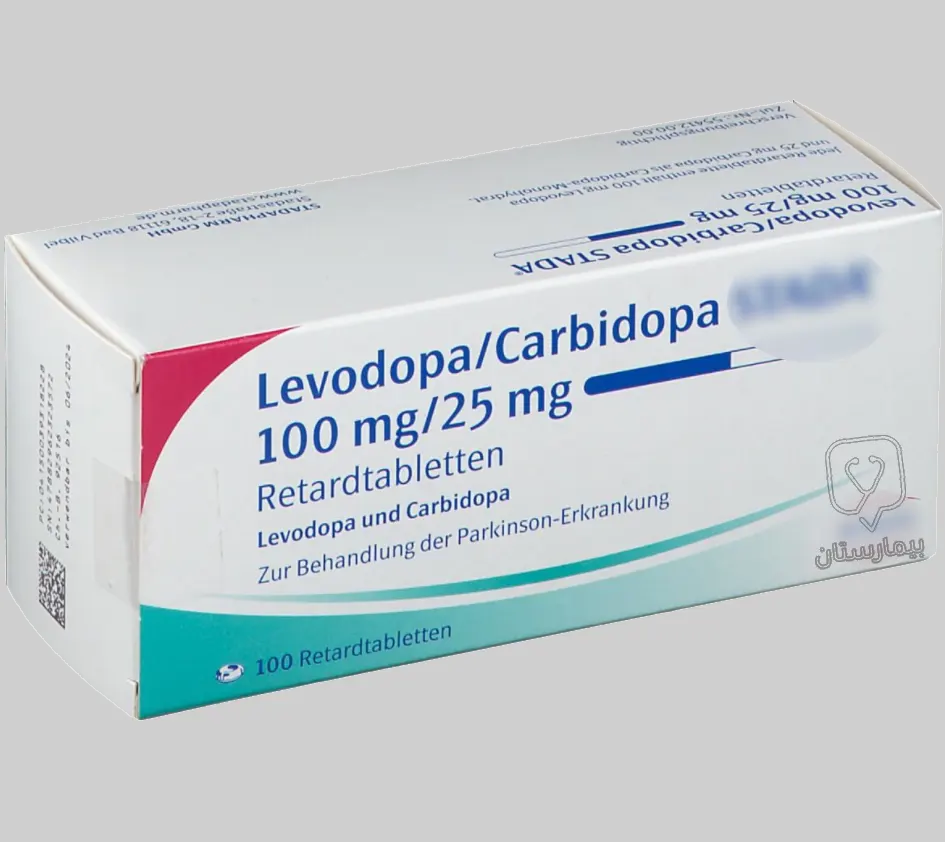
علاج مرض باركنسون باستخدام ليفودوبا
يعمل الليفودوبا عن طريق دخوله الدِماغ وتحوله إلى دوبامين (ولا نعطي الدوبامِين مباشرة لأنه لا يستطيع الدخول لِلدماغ) وحين يتحول الليفودوبا إلى دوبامين يرتبط بالمستقبلات المناسبة فتزول أعراض الشلل الرعاش الحَركية.
يعتبر الليفودوبا أفضل دواء لعلاج مرض باركنسون العصبي، لكن لا يتم إعطاءه وحده، يتم إعطاء مركب يدعى كاربيدوبا معه، يمنع هذا المركب تحطم الليفودوبا في الجهاز المحيطي ويؤمن سلامته إلى أن يصل لِلدماغ.
يعطى بجرعة 300 – 600 ملغ باليوم مقسمة على 3 أو 4 جرعات، ورغم اعتباره الأكفأ من بين الأدوية، يؤمن الليفودوبا علاجاً من الأَعراض العصبيّة لمدة 4 ل 6 سنوات فقط.
تظهر بعد ذلك الأثار الجانبية لاستخدام الدواء وتتضمن عسرة الحركة، الغثيان والإقياء وقد نشاهد هبوط ضغط الدم الانتصابي أو تفاقم الهلوسة والهذيان.
إضافة لعدم الاستفادة بِشكل كبير من الليفودوبا في تحسين الأَعراض غير الحَركية من المرض، إذ توصف لهذه الأَعراض أدوية مختلفة تستهدف تخفيف هذه الأَعراض.
مثبطات الأنزيم MAO-B
ومنها سيليجيلين (5 ملغ باليوم صباحاً)، راساجيلين، تستخدم هذه الأدوية لعلاج الشلل الرعاش (الباركنسون) عبر إيقاف عملية تحطم الدوبامِين (التي تجري بِشكل طبيعي) في الجهازِ العصبِي وبذلك تزيد مستوياته في الدِماغ.
تُستخدم في العلاج للمراحل المبكرة من الشلل الرعاش وتؤمن أَعراض جانبية أخف من الليفودوبا وقد يدوم مفعولها مدة أطول منه في علاج الأَعراض الحَركية.
منبهات مستقبلات الدوبامين
روبينرول، براميبيكسول تؤمن سيطرة معتدلة على أَعراض المَرض الحَركية، لكنها تتأخر حتى تُظهر التأثيرات الجانبية المشابهة لتلك الموجودة عند استخدام الليفودوبا، على أي حال هي ليست بلا أَعراض جانبية، فهي تسبب:
- النعاس والنوم خلال النهار
- الهلوسة
- الوذمات
الأدوية المضادة للأستيل كولين
وهي فعالة في علاج الرجفان والاهتزازات بِشكل خاص لدى مرضى باركنسون، لكن لديها العديد من الأَعراض الجانبية مثل جفاف الفم وصعوبة التبول، من أهمها: أورفينادرين، تريهيكسيفينيدين.
الأمانتادين
مضاد فيروسي له خاصية مضادة للباركنسونية لذا يستخدم في علاج مرض باركنسون (الشلل الرعاش)، يعطى بجرعة 100 ملغ باليوم ويتم زيادتها تدريجياً حتى 300 ملغ باليوم.
الواقيات العصبية
وهي من أحدث طرق علاج مرض باركنسون ولازالت قيد الدراسة، تتضمن آلية عملها في العلاج على إيقاف تطور المَرض عبر إنهاء تموت الخلايا العصبيّة في المادة السوداء أو على الأقل إبطاء هذه العملية.
قد يمكنها أيضاً عكس التفاقم لمرض الباركنسون عبر توليد خَلايا عصبية جديدة، هذه الأدوية لازالت قيد التجربة ولم تطرح في الأسواق بعد.
علاج الأعراض غير الحَركية لمرض الشلل الرعاش
تتضمن الأَعراض غير الحَركية للباركنسون الاكتئاب، اضطرابات النوم، العتاهة وفقدان المحاكمة العقلية، الضعف الجنسي، هبوط الضغط الانتصابي والإمساك ويتم علاج الأَعراض المزعجة للمريض بما يلي:
- السيلدينافيل: يستخدم في عِلاج الضعف الجنسي.
- بولي إثينيل غليكول: عِلاج الإمساك.
- مودافينيل: يُستخدم في عِلاج النوم أثناء النهار.
- هنالك دراسات على إمكانية عِلاج بعض الأَعراض غير الحَركية بِاستخدام الليفودوبا.
علاج مرض باركنسون المتأخر
قبل اللجوء إلى العلاج الجراحي عند تطور مرض الشلل الرعاش قد يمكننا أيضا استخدام بعض الأَدوية أو تغيير طريقة إعطاءها ووصف وجرعة أعلى منها للسيطرة على أعراضه.
مثبطات أنزيم COMT
تُستخدم أيضًا مثبطات هذا الأنزيم لعلاج مرض باركنسون المتأخر، يعمل هذا الأنزيم على تفكيك الدوبامِين في الدِماغ (بِشكل طبيعي) وبالتالي إيقاف عمله يوفر مزيداً من الدوبامِين في الجِهاز العصبِي.
علاج مرض باركنسون جراحياً في تركيا
في السابق كان العلاج الجراحي لمرض الباركنسون يشتمل على التداخلات الجراحية المخربة لمناطق معينة في الدِماغ كعلاج مما يؤدي لتحسن بعض الأَعراض الحَركية، لكنها قد تؤدي لأذيات ونتائج متفاوتة للمرضى.
علاج مرض باركنسون عبر التحفيز العميق للدماغ في تركيا DBS
في حال وصل مريض الباركنسون لمراحل متقدمة وتطور المرض لديه وأصبح غير مستجيباً على العلاج الدوائي أو ظهرت لديه أَعراض جانبية للأدوية المستخدمة، حينها يلجأ للعلاج الجراحي.
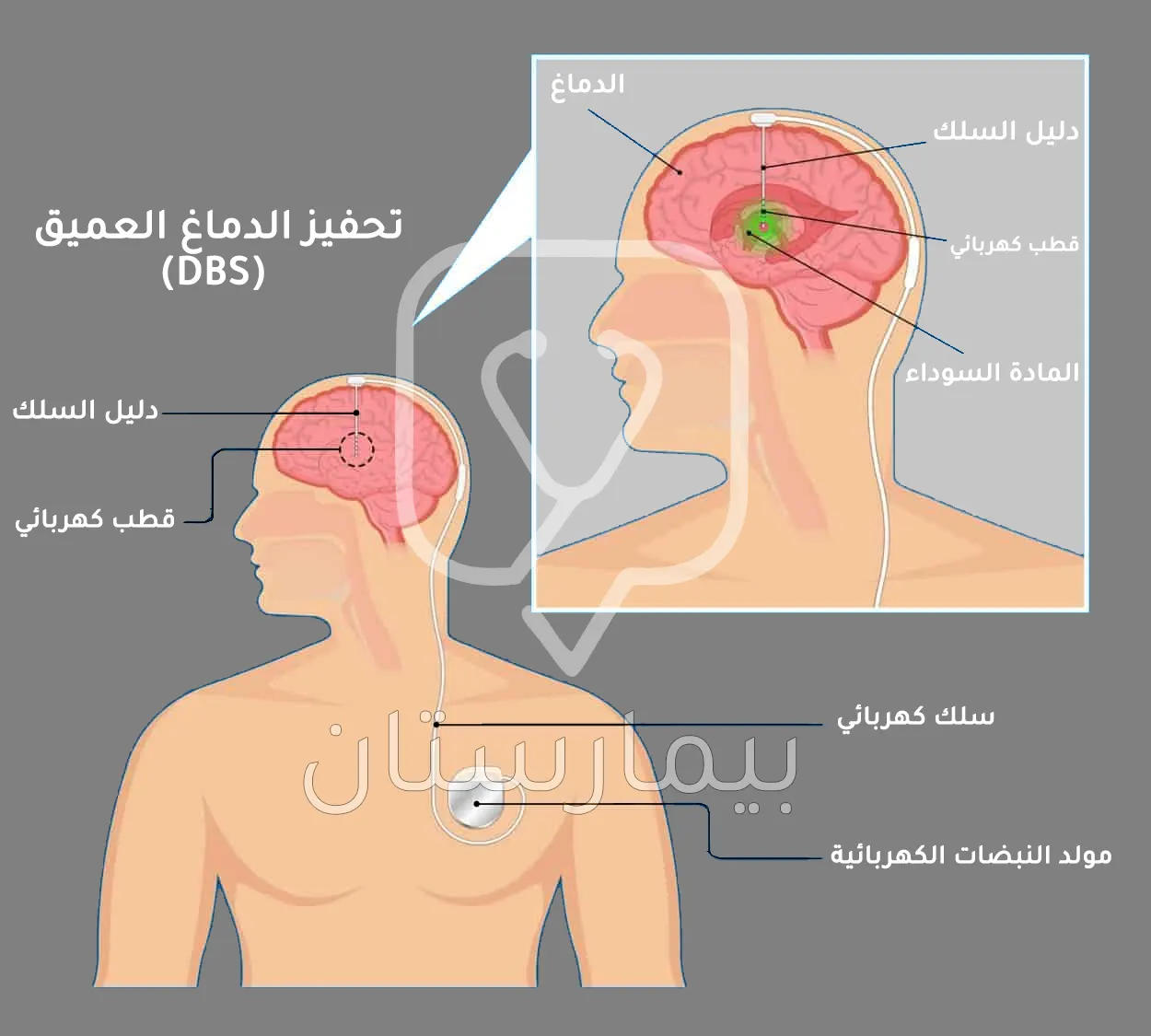
يتضمن التحفيز العميق لِلدماغ لعلاج مرض باركنسون وصل اسلاك كهربائية ببطارية توضع في الصدر (زراعة جهاز)، توصل هذه الأسلاك إلى مناطق معينة في الدِماغ العميقِ، تحوي هذه المناطِق تجمعات بالخلايا العصبيّة المسؤولة عن تنظيم الحركات.
بتحفيز هذه المناطِق نعطي أمراً لهذه الخلايا إما بالتنشيط أو بالإيقاف والتثبيط (عدم العمل) حسب الغاية العلاجية وحسب المنطقة التي زرع فيها هذا السلك.
نصل إلى هذه المناطق عبر حفر ثقوب صغيرة في الجمجمة وإدخال الأسلاك عبرها (يكون التيار الكهربائي المار خفيفاً وغير ضار ولا يشعر به المَريض)، تعد هذه العملية من أشهر الطرق العلاجِية التي أجريت حالياً.
أبرزت هذه العملية في تركيا نجاحاً كبيراً لعلاج مرض باركنسون المتأخر من حيث السَيطرة على الأَعراض وتحسين نوعية حياةِ الأشخاص اللذين أصيبوا بهذا المَرض.
تتضمن مزايا هذه العملية الطبية التي يقوم بها جراح الأعصاب ما يلي:
- لا تتضمن تداخلات مدمرة على أي نسيج دماغي.
- نستطيع إزالتها في حال فشلها بدون أي أثر يذكر.
- نستطيع تعديل النبضات الكهربائية المستخدمة (غير المؤذية) بحسب التطور لمرض الباركنسون وتقدم مرحلته (حدة المَرض) أو في حال ظهور أي تأثيرات جانبية.
- يمكن إجراء هذه العملية لنصفي الكرة في المخ بدون أي مساوئ تذكر.
يتم حديثاً اختبارات لعلاج مرض باركنسون في تركيا بِاستخدام الطعوم الجنينية (الجذعية) أو إعطاء عوامل نمو (مادة لتنشيط تكاثر الخَلايا العصبيّة) في الأماكن المتموتة والشفاء من مرض الشلل الرعاش.
في حال كنت تشكو من مرض الباركنسون (الشلل الرعاش) المتقدم تواصل معنا، سيرشدك مركز بيمارستان الطبي لأكثر الأطباء خبرة وكفاءة في تركيا لعلاج مرض باركنسون لديك، العلاجات التي يرشدك إليها المركز هي الأكثر تطوراً.
المصادر:
