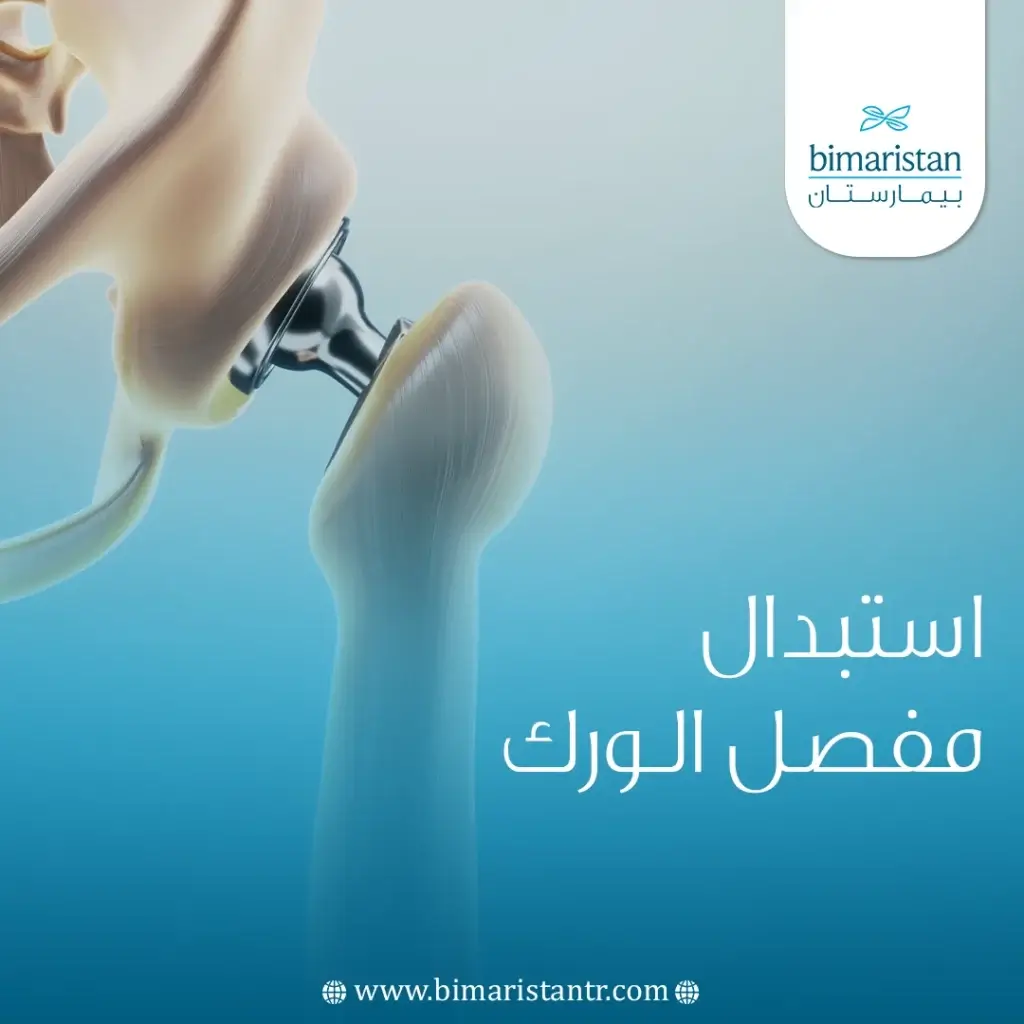
تعد عملية استبدال مفصل الورك الصناعي المرتبطة بمرض التهاب مفصل الورك الحاد جراحة موثوقة وفعالة تهدف إلى تقليل الألم وزيادة الحركة والوظائف وجودة حياة المريض.
مقدمة عن عملية استبدال مفصل الورك الصناعي
أصبحت عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل (Total Hip Replacement) ناجحةً جداً لدرجة أنها باتت تُعرف بعملية القرن، فهي الإجراء الجراحي الرئيسي في جراحة العظام وعلاج فعال من حيث التكلفة لاستعادة الحركة الخالية من الألم لدى المرضى الذين يعانون من أمراض العظام والمفاصل التنكسية مثل التهاب المفاصل التنكسي.(1)
يمكن اعتبار عملية تغيير مفصل الورك بالكامل بشكل عام تدخلاً آمناً ينتج عنه مستوى رضاً مرتفع لدى المرضى، فقد أعلن أكثر من 90% من مرضى التهاب المفاصل التنكسي أنهم راضون عن نتائج عملية تغيير مفصل الورك بالكامل بعد عام واحد من الجراحة، ويستطيع معظمهم العودة إلى حياتهم الطبيعية، وقد أدى هذا النجاح إلى توقعات عالية لنتائج الجراحة بين المرضى وجراحي العظام والباحثين.(1)
سيتعين على المرضى أن يتفهموا ويقبلوا أن عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل “تُمثل بداية العلاج وليس نهايته” على الرغم من حدوث تخفيف فوري تقريباً للآلام واكتساب القدرة على الحركة بعد الجراحة.(1)
أدى تحسين الأساليب الجراحية وإدخال تقنيات جراحية ومواد صناعية تعويضية جديدة إلى تحويل عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل إلى واحدة من أفضل طرق العلاج المعاصرة نجاحاً.(2)
يُعد التهاب مفصل الورك التنكسي (الفصال العظمي) مرضاً تنكسياً يُصيب المفاصل الزليليّة، ويعتبر أكثر الأمراض شيوعاً في الجهاز الحركي وهو منتشر بين البالغين في متوسطي الأعمار وكبار السن، ويُلاحظ لدى هذه الفئة العمرية من السكان وجود علاقة واضحة بين هذا المرض وزيادة الوزن والأنشطة البدنية.(3)
يتميز مفصل الورك المصاب بما يلي: تنكس بؤري في الغضروف المفصلي، الكسور الدقيقة، الخراجات، تصلب العظام تحت الغضروف، ظهور نبتات عظمية في الحدود المفصلية، التشوه التالي لالتهاب المفاصل، وفقدان تدريجي لحركات المفاصل، ولا تتوافق شدة الأعراض دائماً مع درجة الضرر الظاهر على الصورة الشعاعية.(3)
لا يوجد علاج للالتهاب المفاصل التنكسي في الوقت الحالي وتركز العلاجات المتاحة على السيطرة على الألم وتحسين الوظائف (المعالجة الفيزيائية هي إحدى هذه العلاجات) وفي حالة عدم الاستجابة فإن عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل هو الإجراء الجراحي المفضل كونه يُحسن نوعية حياة المريض ويسهل عودته إلى الأنشطة الحياتية اليومية وحتى إلى مزاولة العمل.(3)
أسباب إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الورك الصناعي
يُعتبر التهاب مفصل الورك التنكسي في المرحلة النهائية والمصحوب بأعراض أكثر الأسباب شيوعاً لإجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل.(4)
يرتبط حدوث التهاب مفصل الورك التنكسي بكل من الشيخوخة والنشاط البدني الشاق إذ يُصبح الغضروف أقل مرونة مع مرور الوقت، وهو يُمثل أكثر من ثلثي حالات استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل..(1)
يأتي التهاب مفصل الورك الروماتيزمي في المرتبة الثانية من حيث الشيوع، وهو اضطراب التهابي جهازي ربما يكون سببه استجابة مناعية ذاتية جهازية، وتكون المفاصل المصابة بشدة مرشحة لعملية استبدال المفصل عندما تفشل الأدوية (التي تحتوي على المسكنات والأدوية المضادة للالتهابات والستيروئيدات) في السيطرة على الأعراض.(1)
تشمل الأسباب الأخرى لعملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل:
- خلل أنسجة مفاصل الورك
- العيوب العظمية الناجمة عن الحوادث أو الأمراض
- تنخر الأوعية الدموية (تنخر أنسجة العظام بسبب انقطاع التروية الدموية)
- الأمراض النادرة الأخرى التي تضر بوظيفة منطقة الورك.(1)
يظهر تنخر عظم الورك وسطياً في الفئة العمرية الأصغر سناً 35-50 سنة ويُمثل حوالي 10% من عمليات استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل سنوياً.(4)
الأسباب التي تمنع إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل
يتم الامتناع عن إجراء جراحة استبدال كامل مفصل الورك في الحالات السريرية التالية:
- التهاب أو خراجات الورك
- العدوى البعيدة (أي خارج المفصل) النشطة أو المستمرة أو تجرثم الدم
- الحالات الشديدة من أمراض الأوعية الدموية (4)
تقييم المريض ما قبل عملية استبدال كامل مفصل الورك
التقييم السريري
يتم إجراء فحص سريري شامل مع أخذ التاريخ المرضي قبل إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل، كما يجب السؤال عن التدخلات والعلاجات السابقة.(4)
يجب الأخذ بالاعتبار عمليات استبدال المفصل السابقة أو إجراءات تنظير المفصل أو العمليات الجراحية الأخرى حول مفصل الحوض قبل اتخاذ قرار إجراء العمل الجراحي، إضافة إلى أن وجود مواد صناعية تعويضية في عظم الفخذ أو جوف المفصل يمكن أن يؤثر بشكل كبير على العمل الجراحي المخطط له و/أو اختيار المفصل الاصطناعي البديل.(4)
يجب أيضًا إجراء تقييم طبي شامل وحصول المريض على تصريح طبي وتحديد المخاطر المتوقع حدوثها قبل اتخاذ القرار بإجراء عملية استبدال كامل مفصل الورك.(4)
تشمل الأمور الأخرى الواجب أخذها بعين الاعتبار قبل العمل الجراحي كل من: عادات جسم المريض، النشاط الوظيفي السابق، الأهداف أو التوقعات لما بعد العمل الجراحي، نمط الإصابة بالتهاب المفاصل، وأي سوابق لإصابة رضية في مفصل الورك.(4)
يجب إجراء فحص للورك بحثاً عن أي تصبغات جلدية أو جروح أو ندوب سابقة، كما يجب فحص الأنسجة الرخوة للتحري عن الضمور الشديد والتناظر العام والاستقرار في الورك.(4)
يجب إجراء تقييم للمحور الميكانيكي والمحاذاة الكلية للطرف، فمن المهم التأكد من استبعاد أمراض العمود الفقري و/أو الركبة أو على الأقل أخذها بعين الاعتبار قبل إجراء أي عملية جراحية حول الورك، كما يجب أيضاً التحري عن وجود أي اختلاف في طول الساق.(4)
يعد الانزعاج اللانموذجي في الساق والألم أثناء الراحة من الأعراض الشائعة لأمراض الأوعية الدموية المحيطية، في حين تغيب هذه الأعراض عن حوالي 50% من المرضى لذلك فإن الشك السريري في وجود هذه الأمراض قد يتطلب استشارة جراح الوعائية قبل إقرار عملية استبدال مفصل الفخذ بالكامل.(4)
التقييم الشعاعي
يُوصى بإجراء تقييم شعاعي قبل العمل الجراحي بما في ذلك صورة الحوض الأمامية الخلفية والجانبية للورك المصاب، كما يتم اللجوء إلى التصوير الطبقي المحوري بمقاطع 1 مم عندما يواجه الجراح حالات خلل التنسج الشديد بمفصل الورك.(4)
يتم في التقييم الشعاعي لمفصل الفخذ التحري عن تضييق المسافة بين المفصلية، وجود التنبتات العظمية، وجود التصلب تحت الغضروفي و/أو الكيسات التنكسية.(4)
الإجراء الجراحي خلال عملية استبدال كامل مفصل الورك
يتم في عملية استبدال كامل مفصل الفخذ تبديل العظام والغضاريف التالفة بأسطح من السيراميك أو المعدن أو البلاستيك لاستعادة حركة الورك ووظيفته.(5)
يحل الجوف المفصلي ورأس الفخذ البديلة محل الأسطح المفصلية الطبيعية التالفة في مفصل الورك المصاب، لذلك يجب أن تكون المواد التعويضية ذات احتكاك منخفض وأن تتحمل التآكل والحمل الميكانيكي أثناء الحركة.(1)
يتكون مفصل الورك الاصطناعي من جزأين:
- مكون الجوف المفصلي (الكأس) يلائم تجويف عظم الحوض.
- المكون الفخذي (الساق) الذي يلائم عظم الفخذ. (5)
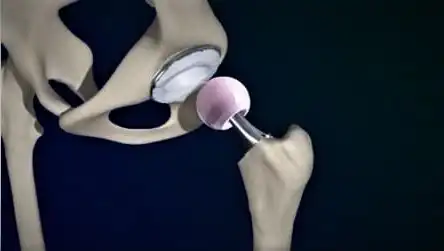
خطوات العملية الجراحية لاستبدال مفصل الورك
- عادة ما يقوم الجراح بعمل شق في الجزء العلوي من عظم الفخذ.
- يتم فصل العضلات التي تثبت الورك في مكانه جزئياً ويكشف الجراح نهاية عظم الفخذ وتجويف الحوض (الجوف الحقي).
- يتم إزالة الغضاريف والعظام التالفة في تجويف الحوض.
- يتم تركيب مكون الجوف المفصلي (الكأس) وبطانة البولي إيثيلين عالية الجودة (الغضروف الجديد) في مكانهما.
- تتم إزالة رأس عظم الفخذ.
- يتم تحضير الجزء الداخلي من عظم الفخذ للمكون الفخذي (الساق المعدني) الذي يتم تثبيته في مكانه ويتم وضع رأس عظمة الفخذ (الجزء الكروي) على الساق المزروعة.
بمجرد وضع المكونات في مكانها تتم إعادة الورك إلى مكانه ثم اختبار حركة واستقرار المفصل، ومن ثم يتم إغلاق الشق الجراحي، ويستغرق العمل الجراحي عادة 45-90 دقيقة.(5)
أنواع التداخل الجراحي
تتم عملية استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل باستخدام ثلاث طرق تعتبر الأكثر شيوعا وهي:
التداخل الخلفي
وهي الطريقة الأكثر شيوعًا لإجراء عمليات استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل وعمليات التصحيح، والميزة الرئيسية لهذا النهج هو تجنب العضلات المبعدة للورك، إضافة إلى الكشف الممتاز لكل من الجوف الحُقي للورك وعظم الفخذ وتحويل التمدد الاختياري في الاتجاه القريب أو البعيد.(4)
التداخل الأمامي المباشر
لقد أصبحت هذه الطريقة شائعةً بشكل متزايد بين الجراحين، ييستشهد المؤيدون لها بالمعدلات النظرية المنخفضة لخلع الورك في فترة ما بعد العمل الجراحي وتجنب العضلات المبعدة للورك، وتشمل مشاكل هذا التداخل زيادة مضاعفات الجروح لدى المرضى الذين يعانون من السمنة المفرطة بشكل خاص، صعوبة كشف الفخذ، خطر حدول تنميل في العصب الفخذي الجلدي الجانبي، واحتمالية ارتفاع معدل كسور عظم الفخذ أثناء العمل الجراحي.(4)
التداخل الأمامي الجانبي (واتسون-جونز)
إن التداخل الأمامي الجانبي هو الطريقة الأقل استخداماً بالمقارنة مع طرق التداخل الأخرى بسبب تأثيره المباشر على العضلات المبعدة للورك.(4)
اختيار مكونات مفصل الورك الاصطناعي
تشير التقارير إلى أن أكثر المواد التعويضية شيوعاً والمستخدمة في تصنيع رأس الفخذ والجوف الحقي في مفصل الورك الصناعي هي معدن على معدن (MoM) أو سيراميك على سيراميك (CoC) أو مزيج كلاسيكي من معدن على بولي إيثيلين (MoP).(1)
إن القرار الأول الذي يجب اتخاذه بخصوص مفصل الورك الاصطناعي هو فيما إذا سيتم تثبيته بمواد تثبيت عظمي (اسمنت) أم لا، يتم حالياً استخدام مواد تثبيت بشكل أساسي في المرضى الذين تزيد أعمارهم عن 60-65 سنة والذين يعانون من ضعف جودة العظام، فيما تُفضل عدم استخدام مواد تثبيت للمرضى الأصغر سناً الذين يتمتعون بجودة عظام جيدة.(1)
الاستشفاء وإعادة التأهيل بعد استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل
تعتبر إعادة التأهيل بعد الجراحة ذات أهمية قصوى بعد جراحة إستبدال كامل مفصل الورك من أجل ضمان وظيفة خالية من الألم للمفصل وتحسين نوعية حياة المريض، فإعادة التأهيل المناسبة وفي الوقت المناسب مهمة جداً لتسريع عملية الشفاء والوقاية من المضاعفات.(2)
إذا لم يتم تطبيق برنامج إعادة التأهيل للمرضى الذين أجروا جراحة استبدال كامل مفصل الورك فإنهم سيصابون بمشاكل وظيفية في غضون عام واحد بعد الجراحات، ويلعب العلاج الطبيعي دوراً مهماً في رعاية هؤلاء المرضى فهو يحسن القوة وسرعة المشي بعد إستبدال كامل مفصل الورك ويساعد في منع المضاعفات المتكررة والتي تشمل خلع المفصل ومرض الانصمام الخثاري.(3)
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تزيد المعالجة الفيزيائية من حركة المريض وتقدم تثقيفاً حول التمارين والاحتياطات اللازمة أثناء العلاج في المستشفى وبعد الخروج إلى المنزل، ورغم ذلك لم يتم التوصل إلى إجماع على نوعية برنامج العلاج الفيزيائية الأكثر فعالية في هذا المجال.(3)
الحركة المبكرة بعد استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل
تُعد الحركة المبكرة عنصراً أساسياً في برنامج التعافي بعد جراحة استبدال كامل مفصل الورك، فالراحة المطولة في الفراش تنطوي على آثار فيزيولوجية ضارة كزيادة مقاومة الأنسولين، الاعتلال العضلي، انخفاض وظائف الرئة، ضعف أكسجة الأنسجة وزيادة خطر الإصابة بالجلطات الدموية، ويُعتبر تسكين الألم الآمن والفعال شرطاً أساسياً لتشجيع المريض على الحركة الباكرة بعد الجراحة.(6)
هناك أدلة جيدة على أن الحركة المبكرة تسهل الاستشفاء بعد جراحة استبدال كامل مفصل الورك، فقد أظهرت الدراسات التحليلية الحديثة حدوث انخفاض كبير في مدة الإقامة في المستشفى (بمقدار 1.8 يوماً) عندما يتحرك المرضى خلال 24 ساعة من جراحة الاستبدال، كما أنها تساعد على تحسين التعافي الوظيفي وخفض معدل الإصابة بالخثار الوريدي العميق.(6)
الألم بعد استبدال كامل مفصل الورك
من الطبيعي أن يشعر المريض بألم وتورم وحتى بعض الكدمات بعد العمليه، وستبدأ شدة ومقدار الألم بالانخفاض مع مرور الوقت، وقد يستغرق الألم والتورم مدة قد تصل حتى 6 أشهر قبل أن يختفي تماماً.(6)
سيتم إعطاء المريض وصفة طبية لمجموعة من المسكنات قبل مغادرة مستشفى لمساعدته على التحكم بالألم، وقد يُنصح المريض بأخذ ما يلي:
- مسكن للألم يتم تناوله بانتظام لمدة 4 أيام ثم حسب الحاجة
- مسكن أقوى للألم يمكن تناوله كل ساعتين حسب الحاجة
- مضاد الالتهابات غير الستيروئيدية (كالبروفين) يتم تناوله بانتظام لمدة 4 أيام(6)
العلاج الفيزيائي في المنزل بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل
قد يختار بعض المرضى حضور جلسات خاصة للعلاج الفيزيائي بعد الخروج من المستشفى إلى المنزل، بينما يستطيع معظم المرضى تنفيذ نظام التمارين بشكل مستقل، ويبدأ برنامج التمارين المنزلية الأساسية بعد جراحة استبدال كامل مفصل الورك مباشر بهدف استعادة نطاق الحركة والقوة في المفصل، يجب التدرب على هذه التمارين قبل جراحة الاستبدال للتعرف عليها.(6)
التغذية بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل
يساعد النظام الغذائي الصحي على تحضير الجسم للجراحة، ويحتاج الجسم إلى تغذية جيدة لشفاء العظام والعضلات والجلد بعد جراحة الاستبدال، فالأشخاص الذين يتغذون جيداً هم أقل عرضة للإصابة الانتانات بعد جراحة الاستبدال.(6)
إن الهدف من التغذية الصحية الحصول على مصدر للبروتين والخضار أو الفاكهة والحبوب في كل وجبة، فيمكن أن يكون البروتين مهماً بشكل خاص بعد استبدال كامل مفصل الورك حيث ستزداد احتياجات البروتين لأنه يمكن أن يساعد في عملية الشفاء.(6)
مدة الشفاء عملية الورك
يعتمد مدة الشفاء من جراحة استبدال مفصل الورك على عدة عوامل، تشمل:
- نوع الجراحة:
- استبدال الورك الكلي: هي الجراحة الأكثر شيوعًا، حيث يتم استبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل بمفصل اصطناعي. عادةً ما يستغرق الشفاء الكامل من هذه الجراحة من 3 إلى 6 أشهر.
- استبدال الورك الجزئي: يتم فيها استبدال جزء من مفصل الورك فقط. عادةً ما يكون وقت التعافي من هذه الجراحة أقصر من استبدال الورك الكلي، وقد يستغرق من 6 إلى 12 أسبوعًا.
- عمرك:
- يميل الشباب إلى التعافي بشكل أسرع من كبار السن.
- صحتك العامة:
- إذا كنت تتمتع بصحة جيدة بشكل عام، فمن المرجح أن تتعافى بشكل أسرع من شخص يعاني من حالات صحية أخرى.
- حجم الشق الجراحي:
- كلما كان الشق الجراحي أكبر، كلما استغرق وقت التعافي أطول.
- نوع التخدير:
- قد يؤدي استخدام التخدير النخاعي إلى تعافي أسرع من التخدير العام.
- التزامك ببرنامج إعادة التأهيل:
- من المهم اتباع تعليمات طبيبك فيما يتعلق بالتمرين والعلاج الطبيعي بعد الجراحة. سيساعدك ذلك على استعادة قوتك وتحسين نطاق حركتك ومنع المضاعفات.
بشكل عام، إليك ما يمكنك توقعه خلال فترة الشفاء من جراحة استبدال مفصل الورك:
- في المستشفى: ستقضي يومًا أو يومين في المستشفى بعد الجراحة. سيعلمك طاقم التمريض كيفية العناية بشقك الجراحي والمشي باستخدام عكازات أو مشاية.
- في الأسابيع الستة الأولى: ستحتاج إلى استخدام عكازات أو مشاية للمشي. ستحتاج أيضًا إلى رفع ساقك المتضررة عند الجلوس أو الاستلقاء. ستعمل مع معالج فيزيائي لتعلم تمارين تساعد على تحسين قوتك ونطاق حركتك.
- من 6 إلى 12 أسبوعًا: ستتمكن من المشي بدون عكازات أو مشاية. ستتمكن أيضًا من القيادة والعودة إلى العمل.
- من 3 إلى 6 أشهر: ستتمكن من استئناف معظم الأنشطة التي كنت تمارسها قبل الجراحة.
من المهم أن تتذكر أن هذه مجرد تقديرات تقريبية. قد يختلف وقت الشفاء الفعلي من شخص لآخر. تحدث إلى طبيبك حول ما يمكنك توقعه في حالتك الخاصة.
نصائح لتسريع عملية الشفاء من جراحة استبدال مفصل الورك
- اتبع تعليمات طبيبك بدقة.
- احصل على قسط كافٍ من الراحة.
- تناول نظامًا غذائيًا صحيًا.
- مارس التمارين بانتظام وفقًا لتوجيهات معالجك الفيزيائي.
- تجنب رفع الأشياء الثقيلة.
- لا تدخن.
- احذر من علامات العدوى، مثل الاحمرار والتورم والحمى.
الاختلاطات/المضاعفات بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل
خلع المفصل: تبلغ نسبة حدوث هذا الاخنلاط ا حوالي 1-3%، وعادةً ما يؤدي الخلع المتكررة إلى إعادة جراحة استبدال مفصل الورك (جراحة تصحيحية) مع تغيير المكونات المفصلية.(4)
كسر حول مفصل الورك الصناعي: يمكن أن تحدث كسور أثناء العمل الجراحي وتشمل إما الجوف الحقي و/أو عظم الفخذ، وتحدث كسور الجوف الحقي في 0.4% وغالبًا أثناء زرع المكونات، فيما تحدث كسور عظم الفخذ أثناء العملية في ما يصل إلى 5% من عمليات استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل.(4)
التفكك العقيم: يحدث بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل كنتيجة لالتقاء الخطوات التي تتضمن تكوين بقايا الجسيمات، والحركة الدقيقة للمفصل الصناعي، وانحلال العظم الناجم عن خلايا البلعمة.(4)
انتانات الجروح: يتراوح طيف اختلاطات الجروح بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل من الانتانات الجراحية السطحية مثل التهاب النسيج الخلوي و/أو التئام الجروح المتأخر إلى الانتانات العميقة التي تؤدي إلى تنخر كامل السماكة، وتؤدي الانتانات العميقة إلى العودة إلى غرفة العمليات من أجل التنضير والتصريف.(4)
انتانات المفصل: تحدث انتانات مفصل الورك الصناعي بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل في حوالي 1-2% كما ورد في الأدبيات الطبية.(4)
الانصمام الخثاري الوريدي: يُشار إلى الانصمام الرئوي والتخثر الوريدي العميق معاً باسم الانصمام الخثاري الوريدي، ويشكلان أكثر الاختلاطات الخطيرة بعد استبدال كامل مفصل الورك، ويبلغ نسبة حدوثه داخل مستشفيات حوالي 0.6%.(4)
الورم الدموي: قد يحدث نزيف (ورم دموي) في العضلات حول المفصل عملية استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل، وقد يتطلب ذلك الذهاب إلى غرفة العمليات لتصريف الدم الزائد المتراكم تحت الجلد.(5)
المضاعفات والمخاطر الأخرى بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل
- شلل العصب الوركي
- اختلاف طول الساق
- إصابة العضلة الحرقفية القطنية
- التعظم غير المتجانس
- إصابة الأوعية الدموية (4)
التوقعات والنتائج بعد استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل
يتأثر متوسط العمر المتوقع لاستبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل (المفصل الجديد) بمقدار الضغط الواقع على المفصل، إذ يؤدي التحكم في وزن الجسم والالتزام بتوصيات النشاط إلى زيادة عمر المفصل، وبشكل عام يجب أن تستمر أكثر من 90% من المفاصل الاصطناعية لمدة 15 عاماً على الأقل.(5)
يتوقع الأشخاص الذين أجروا استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل استعادة الحركة الخالية من الألم والتغلب على القيود في أنشطتهم اليومية والمهنية، وتُعد عملية استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل علاجاً ناجحاً للغاية إذ أن أكثر من 80% من المرضى راضون عن النتيجة بعد جراحة الاستبدال، وفي دراسة استقصائية شملت 806 مرضياً عاد 94% إلى وظيفتهم المعتادة بعد جراحة الاستبدال ، وانخفض عدد المرضى الذين يعانون من قيود وظيفية مرتبطة بالورك من 20% قبل الجراحة إلى 3% فقط بعد جراحة الاستبدال.(1)
يتم تحديد النتيجة السريرية طويلة المدى لعملية استبدال مفصل الورك الكامل من خلال المواد والمكونات المستخدمة من قبل الجراح والمريض نفسه، ولا يمكن تحقيق الحلول الدائمة باستبدال مفصل الورك بالكامل إلا إذا تمكن الجراح من إعادة بناء مفصل الورك بطريقة تمكنه من أداء وظيفته المناسبة، وإذا كان من الممكن تحقيق تثبيت مستقر لجميع لمكونات المفصل الصناعي.(1)
تكلفة استبدال مفصل الورك في تركيا
تختلف تكلفة عملية استبدال مفصل الورك في تركيا حسب نوع المفصل المستخدم وكفاءة الطبيب الجراح وجودة المشفى الذي سيجرى فيه العملية.
تبدأ تكلفة عملية تركيب أفضل نوع لمفصل الورك الواحدة في تركيا بنوعية ZIMMER الأمريكية بحوالي 7.5 آلاف دولار أمريكي، وهذا يتضمن إجراء العملية تحت إشراف طبيب بروفيسور متخصص في جراحة المفاصل في تركيا وبتقنيات حديثة لا تحتاج إلا إلى شق بسيط لا يسب تمزقاً للعضلات،
قد يختلف سعر العملية تبعاً لحالة المريض والتقنية المستخدمة ونوعية المفصل الصناعي. علماً أن إجراء استبدال كلا مفصلي الركبة للمريض يكون حوالي ال9.5 آلاف دولار أمريكي.
المراجع:
- Holzwarth U, Cotogno G. Total Hip Arthroplasty. Publications Office of the European Union, 2012.
- UMPIERRES et al. Rehabilitation after hip arthroplasty: Randomized trial. JRRD 2014;51(10):1567–1578.
- Krastanova MS, Ilieva EM, Valcheva DE. Rehabilitation of patients with hip joint arthroplasty. Folia Medica 2017;59(2):217-221.
- Varacallo M, Luo TD, Johanson NA. Total Hip Arthroplasty Techniques. StatPearls Publishing 2022.
- Outpatient Hip and Hip Replacement Information Manual. Winnipeg Regional Health Authority 2020.
- Soffin E. M, YaDeau J. T. Enhanced recovery after surgery for primary hip and hip arthroplasty: a review of the evidence. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2016; 117:62–72.