عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي في تركيا هي الطريقة المعيارية الناجحة في علاج التهاب مفصل الركبة لتحقيق تخفيف فعال للألم واستعادة حركة الركبة الطبيعية وتحسين وظيفتها.
مقدمة عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
تزداد الحاجة إلى عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة الكلي (Total Knee Replacement) كنتيجة لعدة أسباب تشمل التهاب المفاصل والإصابات الرضية، ويُعد التهاب المفاصل أحد أكبر مشاكل العظام في العالم وله شكلين رئيسيان هما التهاب المفاصل التنكسي (الفصال العظمي) والتهاب المفاصل الرثياني (الروماتيزمي).
يمكن للمرضى الذين يعانون من كلا الشكلين الاستفادة من عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، وقد تؤدي الإصابات الرضية في الحوادث أيضًا إلى الحاجة إلى عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة بناء على نوع الكسر ومقدار فقدان العظم في المفصل أثناء وقوع الحادث.
لقد تبين أن عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة يكون فعالاً جداً من حيث تحسين جودة الحياة المتعلقة بالصحة مع استثناء للناحية الاجتماعية إلى حد ما
يجب الأخذ بعين الاعتبار أن المرضى الذين هم أقل رضاً عن عملية تبديل مفصل الركبة هم الذين يعانون من شكاوى خفيفة قبل تبديل المفصل، لذلك يجب استنفاد جميع طرق العلاج المحافظ قبل التوجه نحوالعلاج الجراحي.
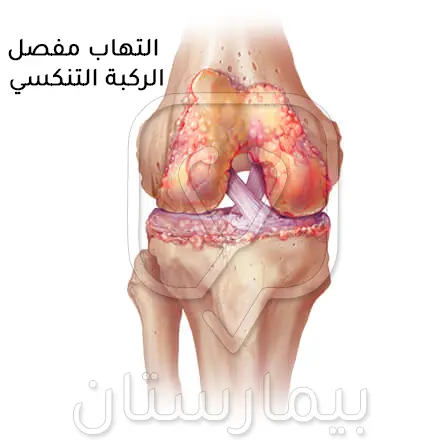
ما يحدث في الشكل التنكسي أن الغضروف يُصبح متصلباً فتنقص مرونته ويزيد من فرص تعرضه للتلف، إذ يقوم الغضروف المفصلي بدور ممتص للصدمات والذي يتآكل تدريجياً في مفصل الركبة، وبالتالي تُصبح الغضاريف والأربطة التالفة مشدودة مما يُسبب الألم ويؤدي في النهاية إلى ملامسة العظام مفصل الركبة لبعضها البعض مما يسبب ألماً شديداُ، وهذا ما يلاُحظ عادة لدى المسنين.
ينتشر التهاب المفاصل الرثياني بشكل شائع عند النساء في الفئة العمرية من 40-60 سنة، وفيه يتأثر الغشاء الزليلي مسبباً تورماً وألماً في مفصل الركبة، وعدم الخضوع للعلاج سيؤدي إلى حدوث تشوه في مفصل الركبة المصاب.
أسباب عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
يعتبر التهاب مفاصل الركبة التنكسي في المرحلة النهائية هو السبب الأساسي الأكثر شيوعاً في اللجوء لاستبدال مفصل الركبة، إذ يتم إجراء حوالي 94-97% من عمليات عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة بسبب التهاب المفاصل التنكسي الأولية أو التالي للرضوض، ويُشترط أن يعاني هؤلاء المرضى من تغيرات تنكسية مصحوبة بألم وتقييد في وظيفة مفصل الركبة لا تستجيب للتدابير العلاجية المحافظة (غير الجراحية).
تتضمن الأسباب الشائعة الأخرى في عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة:
- التهاب المفاصل التهابي المنشأ
- الورام العظمي الغضروفي
- الالتهاب في الغشاء الزليلي العقدي
- التهاب المفاصل استقلابي المنشأ
- التنخر العظمي
- النقرس والنقرس الكاذب
- التهاب المفاصل التالي للرضوض
- الكسور داخل المفصل
حالات تمنع إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة
يجب معرفة الحالات التي يُمنع في إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة ومراعاتها قبل اتخاذ قرار العملية الجراحية، وتشمل الحالات التي يكون فيها المنع تاماً ومؤكداً في عملية إستبدال المفصل:
- انتانات بالركبة
- الانتان المزمن
- خلل في آلية بسط الركبة
- أمراض الأوعية الدموية الشديدة
- تشوه محجني الشكل تالي لضعف العضلات
- وجود إيثاق مفصل الركبة جيد وظيفياً.
هناك حالات التي يكون فيها المنع نسبياً وقابلاً للنقاش تشمل: الحالات الطبية التي تُعيق التخدير الآمن، عدم كفاية تغطية الأنسجة الرخوة، البدانة المرضية، اعتلال المفاصل العصبي، سوابق التهاب عظم ونقي حول مفصل الركبة، والحالات الجسدية والنفسية التي تحول دون القيام بإعادة تأهيل مناسب للمريض.
لا يُعتبر عمر الشخص من موانع العمل الجراحي، ولا يوجد حد للعمر فيمكن للمرضى من جميع الأعمار أن يكونوا مرشحين مناسبين لجراحة عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة.
إجراءات الرعاية ما قبل عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة
يعتبر التقييم السريري قبل العمل الجراحي مهماً للغاية في تقدير الحالة طبياً وتحديد المخاطر النسبية التي قد يتعرض لها المصاب، ويبدأ التخطيط ما قبل العملية باختيار مرشح مناسب لإجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة.
تلعب توقعات المريض وعوامل الخطر العامة دوراً مهماً في اتخاذ قرار إجراء العمل الجراحي، فالسؤال عن الشكاية ونوعية الحياة وتقييم الحالة و إجراء فحص سريري مفصل هي من أساسيات التقييم السريري ما قبل استبدال المفصل
يجب السؤال عن السوابق الدوائية للمريض، كما يجب استبعاد مصادر للانتانات مثل انتانات الأسنان أو الانتانات الجلدية والبولية والتنفسية، ويخضع كل مريض للفحوصات المخبرية وتخطيط القلب الكهربائي والصورة الشعاعية للصدر.
يجب أن يتمتع المرضى قبل العملية بقدرة قلبية رئوية ذات كفاءة عالية (كون معظمهم من كبار السن) لتحمل التخدير وتحمل إمكانية فقدان الدم بمقدار 1000-1500 مل خلال عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة.
عادة ما تكون الصورة الشعاعية البسيطة كافية للتقييم الشعاعي الأولي وتأكيد التشخيص أو تقييم شدة المرض، وقد يكون اللجوء إلى التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي أو التصوير المقطعي المحوسب ضرورياً في حالات استثنائية مثل الخلع الخلقي للرضفة والتشوهات التالية للرضوض والتشوهات الشديدة والأورام والتشوهات الخلقية.
يجب التحري عن أمراض العظام الكامنة (التي لا تظهر فيها الأعراض) والتي قد تتداخل مع نتائج عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، والأمثلة على هذه الحالات ما يلي:
- انحباس الأعصاب الذي يؤثر على الوظائف الحركية للأطراف السفلية
- التهاب المفاصل التنكسي المجاور
- وجود أي حالة التهابية في المفصل قد تتظاهر بعد الجراحة
- أي عجز عضلي هيكلي يؤثر على الحركة بعد الجراحة
- وجود سوابق الانصمام الخثاري أو عوامل مؤهبة له.
يجب أن يشمل الفحص الحالة الفيزيائية للمفصل مدى الحركة وحالة الأربطة المحيطة به والدورة الدموية وتقييم حالة الجلد، وعلاوة على ذلك يجب تقييم محاذاة الأطراف السفلية وعدم استقرار الرضفة وتحليل طريقة المشي.
يعد الاختيار الصحيح للمفصل الصناعي بالحجم المناسب أحد المراحل المهمة في التخطيط ما قبل العمل الجراحي، ويجب أن تؤخذ توقعات المصاب والجراح بالاعتبار لتحسين النتائج وزيادة الرضا بعد العملية، كما أن التخطيط لطريقة قطع العظام قد يبسط إجراء عملية استبدال المفصل.
يهدف الجراح خلال التحطيط للجراحة إلى الحصول على التركيب الأمثل للمفصل الصناعي والمحاذاة المثلى للأطراف، وهو أمر ممكن من خلال التفكير بطريقة ثلاثية الأبعاد، ويجب أن يساعد التنبؤ المسبق بسير العملية الجراحية في تحسين دقة العملية وتقصير مدتها إضافة إلى تقليل معدل الاختلاطات.
طريقة إجراء عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
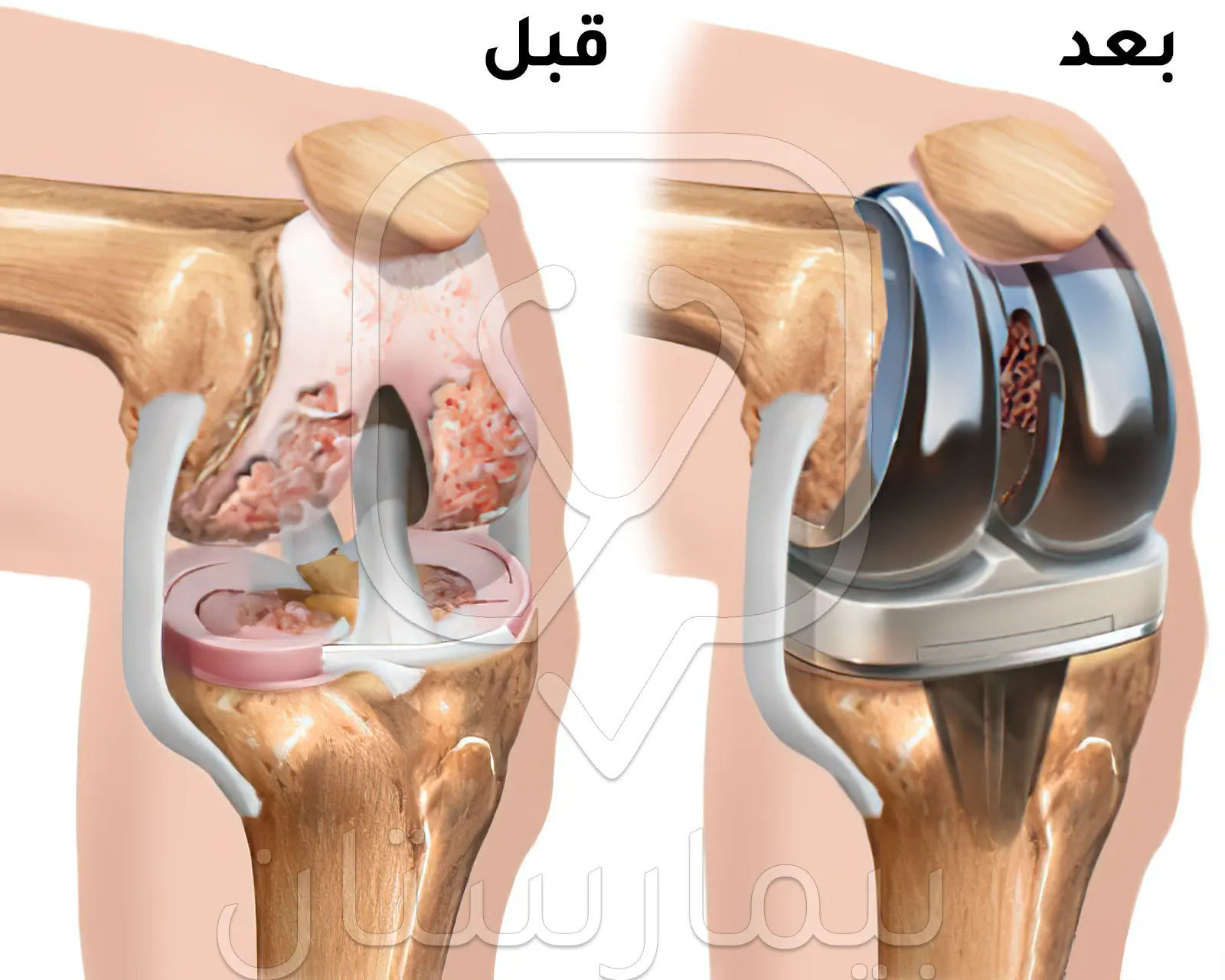
يتم إجراء استبدال الجزء التالف من العظام والغضاريف خلال عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة بآخر صناعي يحتوي أسطح معدنية وبلاستيكية لاستعادة حركة الركبة ووظيفتها، ويتم تثبيت مكونات المفصل الصناعي في معظم العمليات التي تجري حالياً بواسطة مادة تثبيت لاصقة (اسمنت).
يتألف المفصل الصنعي التي يتم زرعه في عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة من ثلاثة أجزاء:
- الجزء المعدني للفخذ، ويحل محل السطح الحامل للوزن في عظم الفخذ وله أخدود لعظم الرضفة للتحرك على طوله.
- الرضفة، ويتم توصيل زر بلاستيكي بالجزء الخلفي من رضفة الركبة للسماح بحركة أفضل على طول الجزء الفخذي.
- الجزء المعدني للظنبوب (عظم الساق)، يتضمن مكون بلاستيكي (بولي إيثيلين) يُشكل سطحاً أملساً يساعد على أن يتحرك فيه الجزء الفخذي أثناء حركة مفصل الركبة.
خلال عملية تركيب مفصل صناعي للركبة يتم استخدام عاصبة (شريط ضيق) حول أعلى الفخذ لمنع النزيف، ويتم إجراء شق جراحي في مقدمة الركبة يسمح بكشف نهايات عظام الفخذ والساق، ومن ثم تتم إزالة الأجزاء المتضررة من من سطح عظام الفخذ والساق مما يتيح مساحة مناسبة تتيح زراعة المكونات المعدنية والبلاستيكية للمفصل البديل.
تُعتبر موازنة أربطة الركبة بهدف تقويم أي تشوه في المفصل جزء مهم من العملية الجراحية، بعدها يتم وضع مكونات المفصل البديل في الركبة واختبارها من حيث الحركة والاستقرار ومن ثم يتم إغلاق الشق الجراحي، وعادة ما تستغرق عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة حوالي 1-2 ساعة.
الاستشفاء وإعادة التأهيل بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
عادة ما يحتاج المرضى بعد إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة الكامل للبقاء ليلة واحدة في المستشفى بناء على عوامل عديدة، ولكن في بعض الحالات قد يعودون إلى المنزل في نفس اليوم إذا كانوا مؤهلين لبرنامج التعافي وإعادة التأهيل.
إنه يوم مزدحم للغاية بالنسبة للمريض وعائلته، فهناك الكثير من تعليمات العلاج الطبيعي والعناية التمريضية التي يتم تقديمها لهم في فترة زمنية قصيرة جداً، كما سيتم تقديم توصيات وإرشادات للمريض قبل التخريج من المستشفى إلى المنزل.
متى تتم المغادرة إلى المنزل؟ كي تتم مغادة المشفى إلى المنزل يجب أن يكون المصاب قادراً على القيام بما يلي:
- تنفيذ برنامج التمارين المنزلية بشكل مستقل.
- المشي مع الاستخدام الصحيح للجهاز المساعد للحركة (مثل العكازات أو العصا) بشكل مستقل.
- الصعود والنهوض من السرير بشكل مستقل.
- الاستحمام وارتداء الملابس بشكل مستقل.
- الصعود والنزول من السلالم بأمان وبشكل صحيح إذا لزم الأمر.
- اتباع احتياطات تحمل وزن الجسم حسب تعليمات الجراح.
- الدخول والخروج من السيارة بشكل صحيح وآمن.
- قادر على تحديد الأدوية ومعرفة وقت تناولها وآثارها الجانبية.
- إمكانية رعاية مكان العمل الجراحي والضماد بنفسه أو بمساعد أحد أفراد الأسرة.
- توفير المعدات المنزلية الضرورية والقدرة على استخدامها بفعالية.
الحركة المبكرة بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة
تُعد الحركة المبكرة عنصراً أساسياً في برنامج التعافي بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، فالراحة المطولة في الفراش تنطوي على آثار فيزيولوجية ضارة كزيادة مقاومة الأنسولين، الاعتلال العضلي، انخفاض وظائف الرئة، ضعف أكسجة الأنسجة وزيادة خطر الإصابة بالجلطات الدموية، ويُعتبر تسكين الألم الآمن والفعال شرطاً أساسياً لتشجيع المريض على الحركة الباكرة بعد العمل الجراحي.
هناك أدلة جيدة على الحركة المبكرة تسهل الاستشفاء بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، فقد أظهرت الدراسات التحليلية الحديثة حدوث انخفاض كبير في مدة الإقامة في المستشفى (بمقدار 1.8 يوماً) عندما يتحرك المرضى خلال 24 ساعة من عملية استبدال المفصل، كما أنها تساعد على تحسين التعافي الوظيفي وخفض معدل الإصابة بالخثار الوريدي العميق.
الوقاية من الغثيان والإقياء وعلاجه بعد عملية تبديل مفصل الركبة
يمكن أن يكون الغثيان والإقياء بعد العمل الجراحي أكثر إزعاجاً من الألم، ويتعلق حدوثه بعوامل خطر مثل النساء وعدم التدخين وسوابق دوار الحركة، ويجب أن يتلقى هؤلاء المرضى ديكساميثازون في بداية العملية ومضاد لمستقبلات السيروتونين عند نهايتها.
ألم بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة
من الطبيعي أن يتم الشعور بألم وتورم وحتى بعض الكدمات بعد العمل الجراحي، وستبدأ شدة ومقدار الألم بالانخفاض مع مرور الوقت، وقد يستغرق الألم والتورم مدة قد تصل حتى 6 أشهر قبل أن يختفي تماماً.
سيتم إعطاء وصفة طبية لمجموعة من المسكنات قبل مغادرة المستشفى للمساعدة على التحكم بالألم بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة، وقد يُنصح المصاب بأخذ ما يلي:
- مسكن آلام يجب تناوله بانتظام لمدة 4 أيام ثم حسب الحاجة
- مسكن أقوى للألم يمكن تناوله كل ساعتين حسب الحاجة
- مضاد الالتهابات غير الستيروئيدية (كالبروفين) يتم تناوله بانتظام لمدة 4 أيام.
يمكن تناول المسكنات بشكل مسبق قبل 30-45 دقيقة من جلسات العلاج الفيزيائي، إذ تُسبب بعض العلاجات والتمارين ألماً خفيفاً إلى متوسط لفترة من الزمن، وإذا استمر الألم يمكن إيقاف العلاج الفيزيائي.
العلاج الطبيعي بعد تغيير مفصل الركبة في المشفى (العلاج الفيزيائي)
يعمل المعالج الفيزيائي غالباً على تمارين تحريك الركبة والمشي، ويبدأ العمل مع المريض في يوم العمل الجراحي، وسيقوم المعالج بتعليم المريض جميع الاحتياطات اللازمة للسماح بالشفاء السليم وتحسين وظيفة المفصل الجديد من خلال المشي باستخدام جهاز المشي أو عكازات بعد العملية.
سيتم تعليم المريض تمارين لتحريك الركبة وتقنيات التنقل (للدخول إلى السرير والنهوض منه) والمشي بواسطة جهاز المشي أو العكازات وطريقة صعود الدرج وأنشطة الحياة اليومية (كارتداء الملابس والاستحمام).
سيقوم أخصائي العلاج الفيزيائي بإرشاد المريض إلى مقدار وزن جسمه الذي يضعه على ساقه عند النهوض، ويمكن للغالبية تحمل كامل وزن الجسم على الفور بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، وعادة ما يتم تحديد قدرة تحمل وزن المريض من قبل الجراحين خلال عملية استبدال الركبة ويبقى كما هو لمدة 6 أسابيع.
المعالجة الفيزيائية في المنزل بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة
قد يختار بعض المرضى حضور جلسات خاصة للعلاج الفيزيائي بعد الخروج من المستشفى إلى المنزل، بينما يمكن لمعظمهم تنفيذ نظام التمارين بشكل مستقل، ويبدأ برنامج التمارين المنزلية الأساسية بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة مباشر حيث تهدف لاستعادة نطاق الحركة والقوة في مفصل الركبة، يجب التدرب على هذه التمارين قبل العمل الجراحي للتعرف عليها.
النظام الغذائي بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
يساعد النظام الغذائي الصحي على تحضير الجسم للجراحة، ويحتاج الجسم إلى تغذية جيدة لعلاج وشفاء العظام والعضلات والجلد بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، فالأشخاص الذين يتغذون جيداً هم أقل عرضة للإصابة الانتانات بعد عملية استبدال المفصل.
إن الهدف من التغذية الصحية الحصول على مصدر للبروتين والخضار أو الفاكهة والحبوب الكاملة في كل وجبة، فيمكن أن يكون البروتين مهماً بشكل خاص بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة حيث ستزداد احتياجات البروتين لأنه يمكن أن يساعد في عملية الشفاء.
مضاعفات عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
في دراسة أجريت 1990-2004 على 4 ملايين عولجوا بإجراء جراحة استبدال مفصل الركبة بعد الخروج من المستشفى كان النسبة الإجمالية لحدوث مضاعفات مرتبطة بالإجراءات المطبقة في المستشفى 8.4%، وكانت معظم المضاعفات جهازية (تتعلق بجسم المريض) وليست ناتجة عن عملية الاستبدال بحد ذاتها.
وفي دراسة جماعية أخرى على مجموعة المرضى خلال فترة 90 يوماً بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة تبين أن 6.7% منهم تعرضوا لمشاكل قلبية جديدة كاحتشاء عضلة القلبية أو قصور القلب أو عدم انتظام ضربات القلب، فيما تعرض 4.9% لمشاكل الانصمام الخثري ، كالتخثر الوريدي العميق أو الانصمام الرئوي.
وكانت الأسباب الأكثر شيوعاً لإعادة دخول المرض إلى المستشفى بعد عمليات جراحة استبدال مفصل الركبة: تحدد حركة الركبة 18.2%، مضاعفات الشق الجراحي 14%، انتان مكان جراحة المفاصل 9.9%، النزف 9.9%، والانصمام الخثاري الوريدي 3.3%.
فشل عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة وإعادة اجراء الجراحة
قد يكون ما يصل إلى 20% من مرضى عمليات جراحة استبدال مفصل الركبة غير راضين عن النتائج، ومع ذلك لا تُجرى إعادة جراحة المفاصل ما لم يتم فهم سبب حدوث الفشل، وعادة ما تكون نسبة بقاء عمليات استبدال مفصل ركبة ناجحة لمدة 10-15 عاماً تتجاوز 90%.
انتان مفصل اصطناعي تالي لعملية استبدال الركبة
تبلغ نسبة إصابة المفصل الاصطناعي بالانتانات بعد عمليات جراحة استبدال مفصل الركبة حوالي 0.4-2%، وتحدث الانتانات الحادة خلال مدة تصل إلى شهرين بعد إجراء جراحة المفاصل، بينما تحدث الانتانات متوسطة الشدة غالبًا خلال شهرين إلى عامين بعد إجراء عملية استبدال مفص الركبة، فيما تحدث الانتانات المتأخرة بعد أكثر من عامين.
الأذية العصبية
هناك أعصاب رئيسية تعبر عبر جميع المفاصل الرئيسية وبالتالي هناك احتمال ضئيل لأذية أحد هذه الأعصاب أثناء إجراء جراحة المفاصل أو بعدها، وإذا حدث ذلك بعد عمليات استبدال مفصل الركبة فسيؤدي إلى ضعف أو تنميل أسفل الساق والقدم.
تآكل البولي إيثيلين في المفاصل
يُعد من المضاعفات المتأخرة المتكررة بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، وينتج عن العملية الميكانيكية لتآكل الأسطح حيث يطحن الجزء الفخذي المعدني جزء البولي إيثيلين
انحلال العظام
وهو أحد الأسباب الرئيسية المتأخرة لإعادة إجراء عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، ويحدث في عمليات المفاصل بنسبة تصل حتى 16% والتي يتم فيها استخدام مادة تثبيت للعظم وبنسبة تتراوح بين 6-30% في عمليات استبدال المفاصل التي لا يستخدم فيها هذه المواد.
عدم استقرار وخلع مفصل الركبة
ينتج عن انزياح غير طبيعي ومفرط لأجزاء مفصل الركبة الصنعي وهو أحد الأسباب الأكثر شيوعاً للفشل المبكر في عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، ويستوجب عادة إجراء إعادة الجراحة خلال 4 سنوات بعد عملية استبدال المفصل.
التوقعات والنتائج بعد عملية تركيب مفصل الركبة الصناعي
يتأثر متوسط العمر المتوقع لمفصل الركبة الجديد بعد عمليات استبدال مفصل الركبة بمقدار الضغط الواقع عليه، فسيؤدي التحكم في وزن الجسم والالتزام بتوصيات النشاط إلى زيادة عمر مفصل الركبة، وغالبًا يجب أن يستمر مفصل الركبة الصناعي مدة 15 عاما على الأقل في 90% من الحالات
لقد أظهر غالبية المرضى تحسناً ملحوظاً في حالة المفصل بعد إجراء عمليات استبدال مفصل الركبة مقارنة بحالتهم قبلها، فيما أظهرت نسبة 10-20% منهم درجة معينة من الضعف الوظيفي أو عدم الرضا على الرغم من عدم وجود قصور تقني جراحي أو مضاعفات..
فقد لوحظ وجود عدد من العوامل المتعلقة بالمريض قد تساهم في نتائج جراحية سيئة بعد عمليات استبدال مفصل الركبة، وتشمل على سبيل المثال لا الحصر كل من السمنة والأمراض المصاحبة والتوقعات غير الواقعية.
السمنة
وجدت دراسات حديثة أن السمنة تؤثر سلباً على نتائج جراحة استبدال مفصل الركبة ومعدل حدوث المضاعفات ومدة بقاء مفصل الركبة الاصطناعي وتكلفة عملية استبدال مفصل الركبة، فيمكن للسمنة أن تزيد من خطر الإصابة الانتانات السطحية والعميقة للشق الجراحي (وهي واحدة من أهم المضاعفات التي يمكن أن تظهر وتؤثر على نجاح جراحة الاستبدال) كما يمكن أن تُساهم في زيادة مدة الإقامة في مستشفى والتكاليف الطبية المباشرة بعد جراحة تبديل مفصل الركبه.(4)
الأمراض المرافقة
تزداد الإصابة بالأمراض مع تقدم العمر وبالتي يمكن أن تؤثر سلباً على نتيجة استبدال مفصل الركبه، وتؤدي هذه الأمراض إلى: زيادة مدة الإقامة وتكلفة المستشفى، ضعف نتائج استبدال مفصل الركبة الصناعي، وانخفاض رضا المريض بعد عملية استبدال مفصل الركبه، كما يجب الأخذ بعين الاعتبار مشاكل الصحة النفسية مثل القلق والاكتئاب ما قبل تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي فقد ثبت أنها من العوامل التي تساهم في عدم الرضا والنتائج السيئة بعد استبدال مفصل الركبة.
توقعات المريض لما بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة الصناعي
يمكن أن تسهم توقعات المريض بشكل كبير في الرضا بعد عمليات استبدال مفصل الركبة، فقد ثبت أن التوقعات غير الواقعية أو القابلة للتحقيق يمكن أن تؤدي إلى استياء المصاب بغض النظر عن المعايير الموضوعية لتقييم وظيفة الركبة، ولضمان التوقعات المناسبة تعتبر مناقشة الإطار العام في جراحة تغيير مفصل الركبة فالمرضى سيصابون حتماً بخيبة أمل من نتيجة عمليات الاستبدال إذا كانوا يتوقعون غياب الألم بنسبة 100% بعد تغيير المفصل أو العودة إلى مستوى عالٍ من الأداء الرياضي أو أن يكونوا قادرين على جلوس القرفصاء والركوع دون عوائق.
تكلفة تغيير مفصل الركبة في تركيا
تختلف تكلفة تغيير مفصل الركبة في تركيا حسب نوع المفصل المستخدم وكفاءة الطبيب الجراح وجودة المشفى الذي سيجرى فيه العملية.
تبدأ تكلفة عملية تركيب أفضل نوع لمفصل الركبة الواحدة في تركيا بنوعية ZIMMER الأمريكية بحوالي 7 آلاف دولار أمريكي، وهذا يتضمن إجراء العملية تحت إشراف طبيب بروفيسور متخصص في جراحة المفاصل في تركيا وبتقنيات حديثة لا تحتاج إلا إلى شق بسيط لا يسب تمزقاً للعضلات،
قد يختلف سعر العملية تبعاً لحالة المريض والتقنية المستخدمة ونوعية المفصل الصناعي. علماً أن إجراء استبدال كلا مفصلي الركبة للمريض يكون حوالي ال9 آلاف دولار أمريكي.
نصائح بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة
استخدم العكازات أو عصي المشي في البداية
جرب المشي بدون مساعدة بعد حوالي 6 أسابيع إذا شعرت أنك جاهز.
انهض وتمشي لمدة 5 دقائق كل ساعة لمنع تجلط الدم
انتظر 6 أسابيع على الأقل للقيادة مرة أخرى إذا كان لديك استبدال كامل للركبة أو 3 أسابيع إذا كان لديك استبدال جزئي للركبة.
تجنب التواء ركبتك والانحناء للأسفل بشكل مبالغ فيه
اتبع التمارين التي أوصى بها أخصائي العلاج الطبيعي
ابق ساقك مرفوعة قدر الإمكان لتقليل التورم
العودة إلى العمل عندما تشعر أنك جاهز – بشكل عام بعد حوالي 6 إلى 12 أسبوعًا ولكنه يعتمد على نوع العمل الذي تقوم به
لا تجلس وساقيك متقاطعتان في الأسابيع الستة الأولى
لا تنام مع وضع وسادة تحت ركبتك (لا داعي للنوم في وضع خاص بعد العملية)
لا تجثو على ركبتك الجديدة حتى يخبرك طبيبك أنه يمكنك ذلك
لا تقف لفترات طويلة لأن هذا قد يكون سبب تورم الرجل بعد عملية تغيير مفصل الركبة
لا تقم بالمهام المنزلية التي تتضمن رفع أو نقل أي شيء ثقيل خلال الأشهر الثلاثة الأولى
المراجع:
- Omar Hussain et al. Implant materials for knee and hip joint replacement: A review from the tribological perspective. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2019, 561;012007.
- Erdogan et al. Preoperative Planning of Total Knee Replacement. InTech. 2013.
- Varacallo M. Total Knee Replacement (TKR) Techniques – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. 2019.
- Dooley P, Secretan C. Total knee replacement: Understanding patient-related factors. BC medical journal 2016; 58:9.
- Omar Alshadokhi et al. Knee Replacement Surgery and Its Effect on Long Term. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine 2018;70 (2):187-191.
- Outpatient Hip and Knee Replacement Information Manual. Winnipeg Regional Health Authority 2020.
- Gorab R et al. The Total Knee Replacement Patient Manual. Orthopaedic Specialty Institute. 8th edition 2020.
- Soffin E. M, YaDeau J. T. Enhanced recovery after surgery for primary hip and knee arthroplasty: a review of the evidence. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2016;117:62–72.
- Mulcahy H, Chew F.S. Current Concepts in Knee Replacement: Complications. AJR 2014; 202: 76-86.








