عملية لحمية الأنف ضرورية عند الأطفال الذين يعانون من أعراض ضخامة اللحمية، يتم استئصال اللحمية الأنفية بإجراء جراحة بسيطة تؤدي لتحسن التنفس لدى الطفل.
تعد عمليات لحمية الانف من أَكثر العمليات شيوعًا التي تجرى للأطفال الصغار (أقل من خمس سنوات غالباً). تجرى عملية لحمية الأنف عند تضخم اللحميات (تسمى أيضًا الناميات في بعض البلدان) عند الأَطفال وإحداثها لأعراض شديدة تعيق التنفس الطبيعي لديهم.
ولكن ما هي اللحمية الأنفية أساساً؟ أين توجد؟ حسناً قد تعرفون ما هي، ولكن لماذا تتضخم بالأصل أو لم هي شائعة؟ هل الحل الجراحي هو الوحيد لعلاج اللحمية؟ هل عملية لحمية الأنف خطيرة أو لها مضاعفات؟ متى يتحسن الطفل بعد العملية؟ أجوبة كل هذه الأسئلة وأكثر سوف تتعرفون عليها في مقالتنا هذه فتابعوا معنا.
لمحة عن عملية لحمية الأنف
إن عملية لحمية الأنف من عمليات الانف البسيطة وغير الخطيرة، فهي عملية غير مهددة للحياة ونسبة النجاح فيها عالية جداً مع تحسن ملحوظ لدى المريض بعد العمليه.
إن عدم إجراء عملية لحمية الأنف قد تؤدي لعدم تحصل الطفل على تنفس طبيعي ونقص في الأوكسيجين الذي يتحصل عليه وبالتالي مشاكل في النمو والتطور العقلي (وخاصة إذا ترافقت مع ضخامة اللوزتين الحنكيتين).
قد يترافق إجراء عملية استئصال اللحمية الأنفية مع إجراء إزالة اللوز الحنكية إذا كانت جميعها متضخمة وتعيق تنفس الطفل أو تسبب له أعراضاً أخرى.
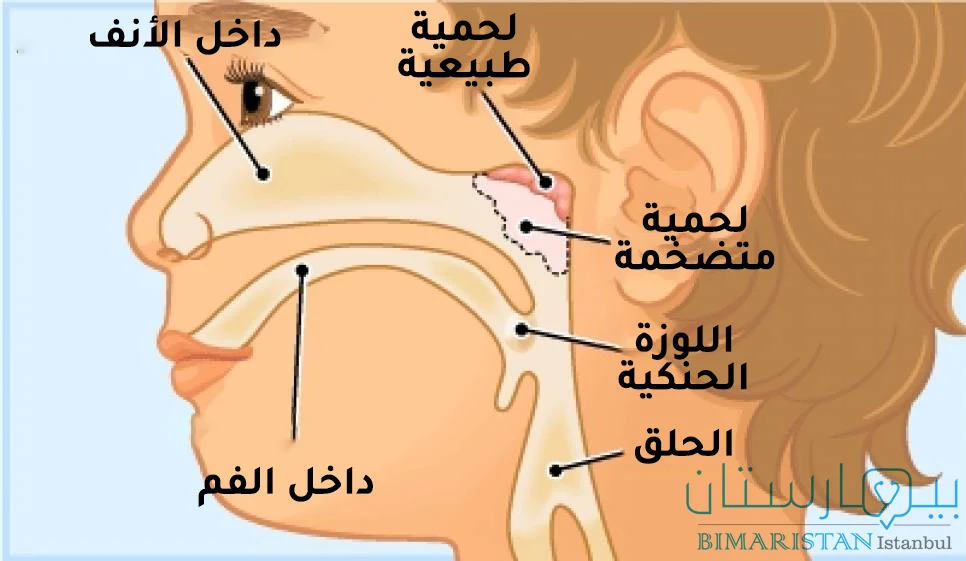
ما هي لحمية الأنف؟ أين توجد لحمية الأنف؟
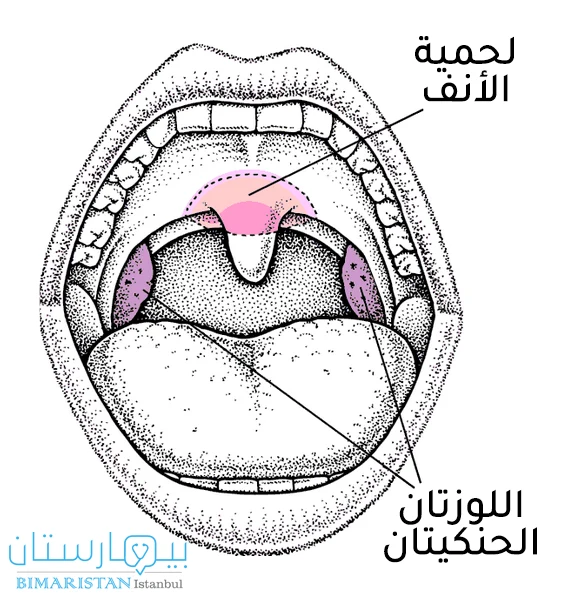
إن اللحمية الأنفية (الناميات) هي نسيج دفاعي لمفاوي يوجد في سقف الأنف وظيفتها حماية الطفل من الجراثيم والفيروسات التي تأتي من الوسط الخارجي عبر الأنف حيث تلتقطها أول دخولها عبر مجرى الهواء وتتخلص منها. تكون مغطاة بظهارة من الغشاء المخاطي التنفسي.
تشبه اللوزتان الحنكيتان اللحمية الأنفية من حيث التركيب وتقومان بنفس الوظيفة، حيث تحميان الطفل من الكائنات الضارة (بكتيرية) التي تدخل الفم عبر الطعام المتناول أو عبر الهواء.
في بعض الحالات تتضخم اللحمية في الانف مما يؤدي إلى انسدادِ مجرى الهواء في الأنف وإعاقة التنفس، نتيجة لذلك يتنفس الطفل من فمه مما يؤدي لحدوث أَعراض عديدة، تابع معنا لتتعرف عليها وفيما إذا كان بحاجة لجراحة للتخلص منها.
أعراض تضخم لحمية الأنف
تختلف شدة أعراض لحمية الأنف حسب ضخامة اللحمية، كلما كانت اللحمية أكبر سببت أَعراض مزعجة أَكثر حتى تصل لمرحلة تصبح فيها جراحة استئصال اللحمية (عملية لحمية الأنف) ضَرورية. ومن أهم أَعراض لحمية الأنف:
صعوبة التنفس من الأنف
يحدث في ضخامة لحمية الأنف (الناميات) انسِداد لفتحة الأنف الخلفية مما يعيق مرور الهواء فيصبح التنفس عبر الأنف صعباً مما يؤدي إلى: سيلان الأنف، الشخير وانقطاع التنفس أثناء النومِ ولعدة مرات في الليلة الواحدة. وعند حصول الانسداد التام يتنفس الطفل من فمه.
التنفس من الفم
يؤدي إلى عدة أَعراض وهي: جفاف الفم، تشقق الشفتين، رائحة النفس الكريهة، التهابُ اللثة والنخور السنية.
اضطرابات النوم
نوم غير مريح بسبب عدم كفاية الأوكسجين لدى الطفل أثناء النّوم مما يؤدي إلى البلادة والنعاس أثناء النهار ونقص التركيز والنشاط، وقد يؤثر مستقبلاً على المستوى التعليمي للطفل.
التهاب الأذن الوسطى المتكرر
توجد في البلعوم الأنفي فتحة لقناة موصولة مع الأُذن الوسطى من أجل تساوي الضغط على طرفي طبلة الأُذن، تؤدي ضخامة لحمية الانف لانسداد هذه الفوهة مما يؤدي لحدوث التهابِ الأُذن الوسطى عند الأَطفال وتستطب في هذه الحالة عملية لحمية الأنف (جراحة استئصال اللحمية الأنفية).
التِهاب الجيوب الهوائية المجاورة للأنف المتكرر
تؤدي ضخامة لحمية الأنف إلى سد فوهات التصريف للجيوب المجاورة فتتراكم المفرزات فيها ويحدث بسبب لذلك الالتهاب فيصيب المريض الصداع وارتفاع الحرارة.
أسباب ضخامة لحمية الأنف
لا يوجد سبب محدد لضخامة لحميات الأنف، لكن تعتبر الأسباب التالية غالبا المسبب الرئيسي وهي:
- ضخامة اللحمية الولادي: يولد الطفل وتكون اللحميات (الغدانيات) متضخمة لديه منذ ولادته ويزداد حجمها مع مرور الوقت.
- ضخامة لحمية الأنف بسبب العدوى: بما أن اللحمية هي نسيج دفاعي لمفاوي فسوف تتضخم عند الإصابة بالعدوى والانتان.
- تضخم لحمية الأنف بعد الانتان: قد تبقى اللحميات متضخمة بعد العدوى مسببة حدوث الأعراض التي ذكرناها.
تشخيص ضخامة لحمية الأنف
يتم التشخيص من قبل طبيب الأُذن أنف حنجرة المختص بعدة طرق. من طرق تشخيص ضخامة لحمية الأنف هو ادخال مرآة صغيرة في الفم تكشف البلعوم الأنفي وتظهر الضخامة في لحمية الانف إن وجدت. وفي بعض الحالات تكون متضخمة جداً فتظهر حدودها السفلية في الفم.
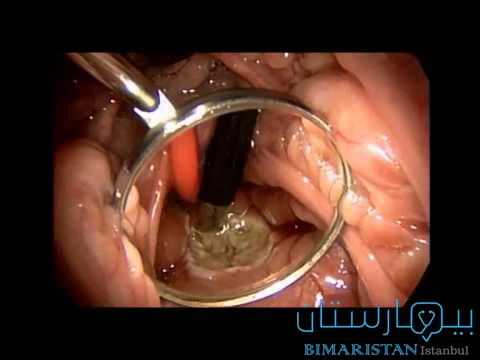
يمكن التشخيص أيضاً عبر منظار الأنف الذي يتكون من انبوب في مقدمته كاميرا ويكون موصلاً بشاشة جانب الطبيب حيث تدخل الكاميرا في الأنف وتظهر ضخامة في اللحمية الأنفية وما هو حجمها.
يمكن التشخيص أيضاُ بشكل غير مباشر عن طريق صورة الأشعة السينية، حيث نلاحظ تضيق عمود الهواء في البلعوم الأنفي عن الهواء الموجود خلف الحنجرة، وذلك في صورة الرأس الجانبية.
علاج لحمية الأنف بدون جراحة
قبل اللجوء إلى عمليات استئصال اللحمية قد يفضل دكتور الأُذن والأنف والحنجره أولاً القيام بمحاولة علاج اللحمية باستخدام الأدوية من أجل اللحمية الأنفية (بدون إجراء عملية لحمية الأنف). ويستخدم هنا قبل عمليات اللحمية:
الصادات الحيوية
بما أن ضخامة اللحمية قد تَكون ناجمة عن العدوى والانتان بالجراثيم فإن استخدام الصادات الحيويّة قد يساعد في قتل هذه الجراثيم والتخلص منها وبالتالي قد تزول ضخامة اللحمية ولا نحتاج لإجراء عملية استئصال اللحمية.
الستيروئيدات
قد يفيد العلاج باستخدام بخاخة أنفية تحتوي على الستيروئيد في التقليل من حجم اللحمية في الانف وبالتالي تزول الأعراض ولا نحتاج إلى عملية استئصال اللحمية أو جراحة في الأنف.
عملية لحمية الأنف في تركيا
ليس كل لحمية متضخمة تتطلب الجراحة أو العلاج. اللحمية الانفيه هي نسيج دفاعي لمفاوي عند الاطفال يستمر وجوده حتى عمر الخامسة، بعد ذلك تبدأ اللحمية بالإنكماش وتصغر حتى تختفي تقريباً في عمر البلوغ، لذلك يندر وجود ضخامة لحمية الأنف عند الكبار.
في حالِ كانت ضخامة لحمية الأنف شديدة وتسبب الكثير من الأعراض المزعجة للطفل ولم تستجب على العلاج غير الجراحي حينها يجب التفكير بِإجراء عملية لحمية الأنف، وسوف يرشدك مركز بيمارستان الطبي لأفضل المستشفيات وأمهر الجراحين في تركيا لذا تواصل معنا.
يقوم الجراح المختص بأمراض الأُذن والأنف والحنجرة (أخصائي ENT) بِإجراء عملية استئصال لحمية الأنف حيث يقوم بدايةً بتخدير الطفل باستخدام التخدير العام (تخدير بمخدر قصير الأمد يدوم فترة العمل الجراحي فقط). أي أن الطفل ينام ولا يشعر بشيء خلال العملية الجراحية لأنه تحت تأثير المخدر.
يضع أولاً قطعة بلاستيكية لإبقاء الفم مفتوحاً أثناء العمل الجراحي. ثم يدخل المرآة والمجرفة (أداة أو مشرط بشكل ملعقة لتجريف اللحمية الأنفية واستئصالها). يقوم بعد ذلك بتطبيق الحرارة ودك المنطقة باستخدام الشاش المعقم لإيقاف النزف.
قد يستخدم بدلاً من ذلك التخثير الكهربائي في جراحة استئصال لحمية الانف لضمان الإزالة مع تخثير المنطقة في نفس الوَقت وبالتالي ضمان نزف أقل.
عندما تكون اللوزتان الحنكيتان متضخمتين أيضاً مع وجود شكاية من التهابها المتكرر حينها نقوم بِإجراء عملية استئصال اللوزتين الحنكيتين مع عملية لحمية الأنف.
عادة لا تستمر عمليات استئصال لحمية الأنف أكثر من 30 دقيقة، يخرج بعدها الطفل إلى غرفته بعدها ليرتاح بضع ساعات ويراقبه جراحه، ثم يتم تخريج الطفل في نفس اليوم.
ما بعد عملية لحمية الأنف
تعتبر عملية لحمية الأنف من عمليات الانف الآمنة للغاية لكن مع ذلك تظهر بعض الأعراض المزعجة لدى الطفل بعد جراحة استئصال الأنفية لمدة أسبوع أو 10 أيام فقط (ولكن في الغالب تكون المدة يومين أو ثلاث)، ومن هذه الأعراض:
- ألم في الأُذن
- عدم القدرة على فتح الفم
- صعوبَة في البلع
- التِهاب الحلق
وبعد هذه المدة الوجيزة يصبح الطفل قادراً على التنفس بشكل طبيعي من أنفه، ينام بِشكل أفضل ويصبح أكثر انتباهاً وتركيزاً ونشاطاً خلال يومه، بالإضافة إلى زوال التِهاب الأُذن الوسطى والتهاب الجيوب المتكرران لديه. يمكنك رؤية هذه النتائج والتحسن للأفضل عادةً بعد اسبوعين على أبعد تقدير من العملية.
مضاعفات عملية لحمية الأنف
تعتبر عملية لحمية الأنف كما أسلفنا من أكثر عمليات الأطفال أماناً، ومع ذلك لا تخلو عمليه جراحية من احتمالية -ولو حتى بسيطة- لحدوث مضاعفات أو أضرار، ومن هذه المخاطر المحتملة (اضرار عملية لحمية الأنف):
- النزف
- كسر سن
- عدوى وارتفاع حرارة
- انسِداد في الأنف
- وجود مفرزات بالأنف
- تغيّر في الصوت
لذلك في حال صادفت أي من الأعراض التالية بعد عمل جراحة استئصال اللحمية في الانف يجب مراجعة الطبيب فوراً وهي:
- نزيف دم أحمر من فم الطفل
- دم أسود أو بني أو أحمر في الإقياء
- ارتفاع درجة الحرارة والقشعريرة (الارتجاف)
- ألم شديد رغم المسكنات
- عدم القدرة على شرب السوائل بعد مدة الراحة من العمل الجراحي
تعتبر ضخامة اللحمية في الأنف أمر شائع لدى الأطفال ومع ذلك لا تتطلب جميعها إِجراء عمليات جراحية، لأن اللحمية في الأنف يتراجع حجمها مع نمو الطفل حتى تختفي في عمر البلوغ. قد يعاني بعض الأطفال من ضخامتها بِشكل طفيف في مرحلة ما من حياتهم ثم تمر وتتحسن حالة الطفل بدون علاج، لكن بعضهم من تتضخم لديهم لحميات الأنف (الناميات الأنفية) بِشكل كبير.
يكون الحل هنا باستئصال اللحمية النامية بشدة من أجل إراحة الطفل من هذه الأعراض وضمان حياة طبيعية ونمو سليم له. قد تشفى بعض حالات ضخامة اللحمية الأنفية على العلاج غير الجراحي، ومع ذلك تبقى الراحة وإجراء عملية لحمية الأنف أساس العلاج.
المصادر