سرطان اللوزتين يعد من أورام البلعوم الفموي، يتظاهر بعدة أعراض منها التهاب الحلق ورائحة الفم، الإصابة بسرطان اللوز مقلقة لكن العلاج باكراً يقي من مخاطر السرطان.
مع تعدد أسباب سرطان اللوزتين إلا أن المسبب الحقيقي بشكل مباشر لا يزال مجهولاً، يتظاهر السرطان بعدة أعراض ولكن قد يبقى غير عرضي ولا يشعر به المريض لفترة طويلة.
يتوجب تشخيص سرطان اللوزتين باكراً لتجنب المخاطر والاختلاطات المحتملة لسرطان اللوز، لأن العلاج الباكر يلعب دور أساسي في إنذار المرض ونوعية حياة المريض بعد علاج الورم. يبقى خطر الإصابة بسرطان اللوز الأشخاص الذين أجروا عملية استِئصال اللوزات سابقاً بسبب بقاء جزء من نسيج اللوزة وعدم الإزالة الكاملة لها. تابع معنا في هذه المقالة لتتعرف على سرطان اللوزتين وطريقة علاجه في تركيا.
مقدمة عن سرطان اللوزتين
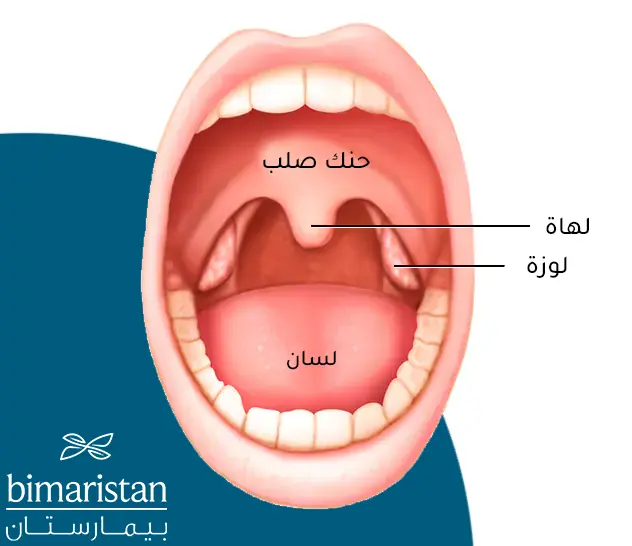
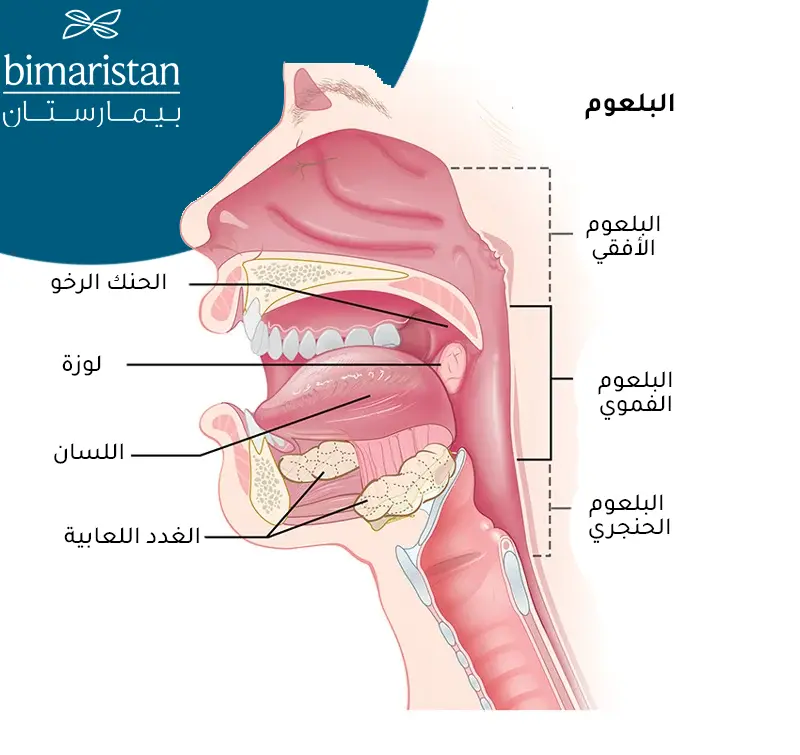
كي نتعرف على سرطان اللوزتين الحنكيتين وكيف يتم تشخيصه يجب أولاً معرفة موقع اللوزات بدقة وطريقة نشوء الورم فيها، يُعد مرض سرطان اللوزتين من أَورام البلعوم. والبلعوم هو أنبوب عضلي يقع في الجزء الخلفي من الفم والأنف والحنجرة مغطى بنسيج مخاطي ويقع أسفل المخاطية نسيج لمفاوي وظيفته الدفاع عن الجسم ضد الجراثيم والفيروسات القادمة من الوسط الخارجي.
تنشأ سرطانات البلعوم والحلق إما على حساب النسيج المخاطي فتسمى أَورام الخلايا الحرشفية، أو على حساب الخَلايا اللمفاوية فتسمى لمفوما البلعوم، في سرطانِ اللوزتين يكون سرطان خلايا الظهارة الحرشفية هو الأكثر شيوعًا Squamous Cell Carcinoma. ثم يليه في الشيوع اللمفوما (سرطان الغدد الليمفاوية في اللوزتين).
تختلف أسباب كل نوع من سرطان اللوزتينِ ولكن غالباً ما تكون الأعراض متشابهة، يوجد في البلعوم عدة تجمعات للنسيج اللمفاوي منها لحميات الأنف (اللوزات البلعومية) واللوزات خلف اللسان (اللوزات اللسانية) واللوزتان الحنكيتان. اللوزتان الحنكيتان هما الأشيع للإصابة بالسرطان في البلعوم.
ما هي أعراض سرطان اللوزتين؟
قد يبقى سرطان اللوزَتين بدون أعراض فترة زمنية طويلة في بعض الأحيان والوضع في هذه الحالة أخطر، أو قد تكون أعراضه ثانوية ولا يشعر المريض بأهميتها، يؤدي ذلك إلى تأخر تشخيص السّرطان وبالتالي تظهر الأَعراض السرطانية بعد انتشار الورم ويصبح العلاج صعباً ونسبة الشفاء قليلة.
أحياناً تظهر أَعراض المرض من البداية أو قد تكشف صدفة في المراحل الباكرة مما يحسن إنذار سرطان اللوز ويجعل نسبة شفاءه عالية. يوجَد العديد من الأَعراض، وتشمل أهم اعراض وَرم اللوزتين ما يلي:
- ظهور تورم في أعلى الرقبة من الجانب يتميز بأنه غير مؤلم
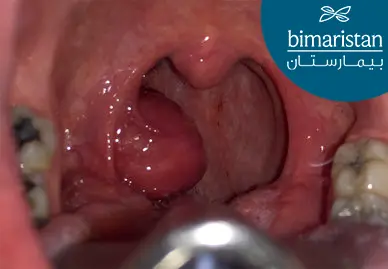
- تضخُّم أَحد اللوزتين في جهة واحدة وكبر حجمها أكثر من الأخرى
- بحة الصوت
- الشعور بتعب عام وإرهاق
- فقدان الوزن غير المفسر (بدون سبب محدد)
- ألم في الأذن (عادةً أذن واحدة وليس الأذنين معا) أو في الفك
- التهاب الحلق المتكرر والمستمر (مزمن)
- خروج الدم من الفم
- رائحة الفم الكريهة
- آلام مع صعوبة أثناء البلع تزيد عند تناول الطعام
- الصعوبة في فتح الفم
يتضمن ما سبق أعراض سرطان اللوزتين عند الكبار لكن ذلك لا يعني أن هذه الأَعراض خاصة بسرطان اللوزتين فقد تتظاهر في أَمراض أُخرى عديدة غير السرطان. لكن ما يدلنا على السرطان اجتماع هذه الاعراض مع وجودِ عواملِ خطَر منذرة بالورم مثل تقدم عمر المرضى.
أسباب سرطان اللوزتين
لا يزال السبب المباشر لحدوث سرطان اللّوزتين أو سرطان الحلق غير معروف، رغم ذلك توجد عواملُ خطرٍ أكيدة تؤدي للإِصابة بِسرطان في اللوزة (وَرم الحلقوم) وهي:
التقدم بالعمر
يعتبر كبر السن من أهم عوامِل الخطر لِلإصابة بورم اللوز، ولا يقي استئصال اللوزتين سابقاً من سرطان اللوزتين لأن الاستئصال يكون غير تام عادةً وبالتالي توجد بقايا من نسيج اللوزتين يتطور فيها الورم.
الإصابة بفيروس HPV
وهو فيروس مصنف لعدة أنواع أخطرها HPV رقم 16 و18، ينتقل الفيروس الحليمي البشري (ال HPV) عبر الجنس ويسبب الثآليل في المنطقة التناسلية. في حال وصل هذا الفايروس إلى منطقة البلعوم واللوزات فسوف يسبب الإصابة بِسرطان اللوزتين من النوعِ حرشفي الخلايا.
التدخين وإدمان الكحول
يعتبر مضغ التبغ أو تدخينه لمدة طويلة من الأسباب المؤدية لزيادة خَطر الإصابة بمرض سرطان اللوزتين أو ورمِ الحلق، وكذلك يفعل الإدمان الكحولي.
قد تشاهد حاليا حالات إصابة بسرطان اللّوز عند الشباب بدون وجود عوامل الخطر السابقة، يرجع ذلك لوجود دور وراثي وبيئي وراء الإصابة بسرطان اللوزتين.
تشخيص سرطان اللوزتين
يَتم تشخيص السرطان في اللوزات أو في الحلق والبلعوم وحتى سرطان الحنجرة بواسطة طبيب الأذن أنف حنجرة ENT، حيث يقوم بدايةً بتأمل وجه ورقبة المريض بحثاً عن أي تورم، بعد ذلك تأتي مرحلة الجس حيث يتحسس المناطق التي قد تخبئ تحتها تورماً سرطانياً في الوجه والرقبة.
ينظر الطبيب أيضا إلى تجويف الفم بحثاً عن أي ضخامة في لوزات الشّخص المريض، ويرتفع الشك بِالسرطان عند وُجود ضخامة لوزة واحدة فقط.
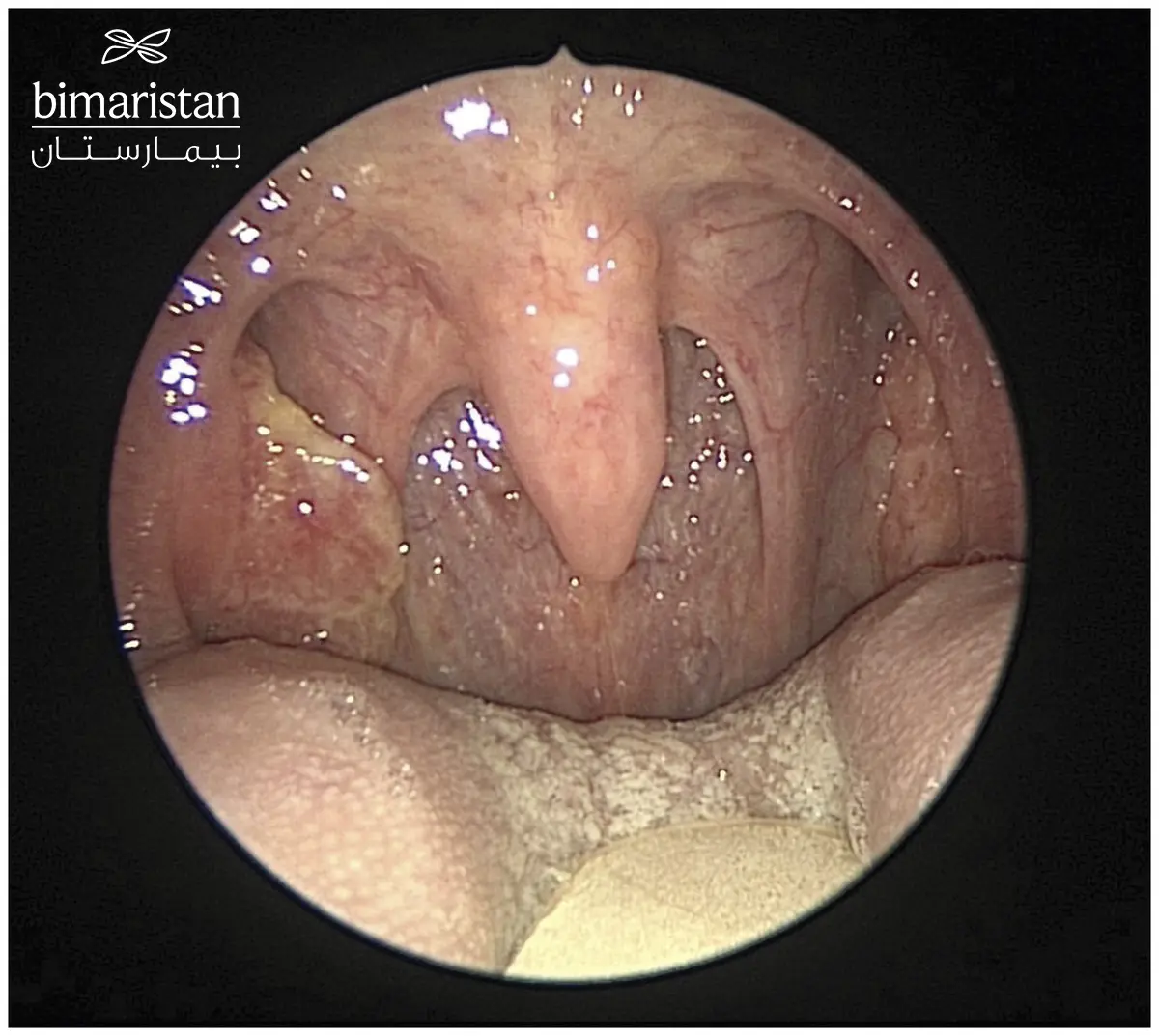
قد يلجأ دكتور ال ENT إلى تنظير الحنجرة بواسطة المنظار المرن في حال الشك بوجود انتقالات أو ارتشاحات للورم في حنجرة المصاب بالمرض.
بعدها يقوم الدكتور بأخذ خزعة من اللوزة المتضخمة وإرسالها إلى المشرح المرضي الذي يفحصها تحت المجهر ويبين سببَ الضخامة ونوع السرطان ودرجته وعلاقة فيروس HPV من عدمها بحدوث سرطان اللوزتين.
تطلب بعد ذلك استقصاءات تصويرية لكشف انتقالات السرطان البعيدة وانتشاره الموضعي ومن أهمها:
- الإيكو للعنق: من أجل كشف انتشار سرطان اللوزات في المناطق المجاورة.
- صورة الصدر البسيطة: لكشف الانتقالات إلى الرئتين في حال وجودها.
- الطبقي المحوري CT والرنين المغناطيسي MRI: لكشف الانتقالات في مختلف أنحاء جسم المريض.
- التصوير بالإشعاع البوزيتروني PET Scan: ويمكنه من كشف النقائل بدقة أينما كانت.
يُقرر نوع العلاج الذي يجب اتباعه في حالة سرطان اللوزتين حسب نتائج الفحوصات الشعاعية وبعد معرفة امتدادات السرطان وتوضعاته لدى المريض.
علاج سرطان اللوزتين في تركيا
يختلف علاج سرطان اللوزتين Tonsil Cancer بحسب حجمه، نوعه، غزوه لمجاوراته وإعطاءه لنقائل بعيدة. أي أن كل مريض يوصف له نوع علاج أو خطة علاجية تناسب حالته من أجل تحقيق أفضل النتائج في علاج السرطانات. وبشكل عام تتضمن خطط علاج سرطان اللوَز ثلاث طرق وهي: العلاج الجراحي، الشعاعي والكيماوي وجميعها يجرى في المستشفى المخصص لعلاج الأورام وبإشراف أَفضل الأطباء في تركيا.
العلاج الجراحي (عملية استئصال اللوزتين الحنكيتين المصابتان بسرطان خبيث)
تستخدم الجراحة في علاج سرطان اللوزتين بشكلٍ شافي في معظم الحالات عندما يكون الورم صغيراً ومحدداً داخل اللوزة ولم ينتشر خارجها إلى الأعضاء المجاورة. وفي هذه الحالة تعتبر العملية خط أول في العلاج (الخط الأول أي أول خيار علاجي نلجأ له).
تتم عملية استئصال اللوزتين حينها تحت التخدير العام وترسل العينة إلى التشريح المرضي بعد انتهاء العمل الجراحي للتأكد من أن الورم قد تم استئصاله بالكامل. نسبة الشفاء هنا من سرطان اللوزتين هي 100% ويكمل المريض حياته بشَكل طبيعي.
العلاج الشعاعي
نلجأ للعلاج بالأشعة في حال كان الورم كبيراً ومؤثراً على البلع بِشكل واضح أو في حال تم الاستئصال الجراحي ولكن نتيجة التشريح المرضي أخبرتنا بأن الورم لم تتم إزالته بشكل كامل.
العلاج الكيماوي
نعتمد على المركبات الكيميائية في علاج سرطان اللوزتين في حال كان نوع الورم يستجيب لهذا النوع من العلاج. نستخدمه أيضًا في حال انتشار الورم لأماكن بعيدة في الجِسم من أجل تخفيف أعراض السرطان.
أحياناً قد نعتمد اختيار طريقتين مما سبق أو الطرق الثلاثة جميعها معاً في علاج الورم، كما يختلف ترتيب استخدامها من مريض لآخر حسبَ مرحلة تقدم مرض السرطان لدى كل شخص.
إنذار ورم اللوزة (نسبة الشفاء من سرطان اللوزتين)
كما أسلفنا يعتمد إنذار سرطان اللوزتين ونسبة الشفاء منه على المرحلة التي تم إكتشافه فيها وحجمه وانتقالاته ونوعه. يصيبُ سرطان اللوزتين البالغين بين 60 و70 عام ويعتبر ذو إنذار سيء إذا ترافق مع أمراض أخرى لدى المريض.
حديثاً أصبح سرطان الحلق والبلعوم واللوزتين ذو الخلايا الحرشفية يصيب الشباب (تحت 40 عاماً) وذلك لارتباطه بإصابة الحلق بفيروس HPV ومع ذلك يبقى ذو إنذار أَفضل من إصابة كبار السن (رغم الإصابة بفيروس HPV لدى الشباب وذلك بِسبب كون صحتهم العامة أفضَل من المتقدمين بالسن).
الإصابة بسرطان اللوزتين مقلقة لكنها لا تعني الوفاة الحتمية، إنما بتقدم مرحلة الورم يصبح العلاج أصعب وبناءاً على ذلك أجريت دراسات على مرضى سرطان اللوز لمعرفة النسبة المئوية لإمكانية الحياة ل 5 سنوات مع هذا المرض وجاءت النتائج وفقًا للدراسات كالتالي:
علاج السرطان في المرحلة الباكرة: تشير الدراسات إلى أن نسبة البقاء على قيد الحياة لمدة 5 سنوات على الأقل هي 85%.
علاج السرطان الذي انتشر بالأعضاء المجاورة وأعطى نقائل إلى العقد الليمفاوية الرقبية القريبة: نسبة البقاء على قيد الحياة لمدة 5 سنوات على الأقل هي 68%.
علاج سرطان اللوزتين الخبيث في المراحل المتقدمة من المرض: نسبة البقاء على قيد الحياة لمدة 5 سنوات على الأقل هي 40%.
سرطان اللوزتين هو عبارة عن مرض خَبيث يسير بأعراض صامتة إلى أن ينتشر ويسبب تدهوراً في الحالة الصحية للمريض، الشفاء منه ممكن وكلما كان العلاج أبكر كانت النتيجة أَفضل، يفضل عدم التهاون بأصغر عرض قد يظهر عند مسن والتوجه به فوراُ إلى أقرب مركز رعاية صحية. تواصل معنا واحجز موعدك مباشرة كي نرشدك إلى افضل أطباء تركيا من أجل علاج سرطان اللوزتين.
المصادر:
