تتضمن الجراحة الروبوتية لسرطان الرئة استخدام كاميرا توفر عرضًا تفصيليًا لداخل صدر المريض.
يمكن أن يكون مصطلح “الروبوت” مضللًا بعض الشيء، حيث إنه ليس الروبوت من ينفذ الجراحة.
بدلاً من ذلك، يستخدم الجراح الأدوات الجراحية التي يوجهونها عبر وحدة التحكم، مما يعني أن الجراحة تتم بمساعدة الروبوت.
الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت هي قليلة التوغل (جرح أقل) بكثير من جراحة الصدر المفتوحة، حيث توفر العديد من العوامل المساعدة على الشفاء.
كما أن لديها مخاطر أقل.
تعريف الجراحة الروبوتية لسرطان الرئة
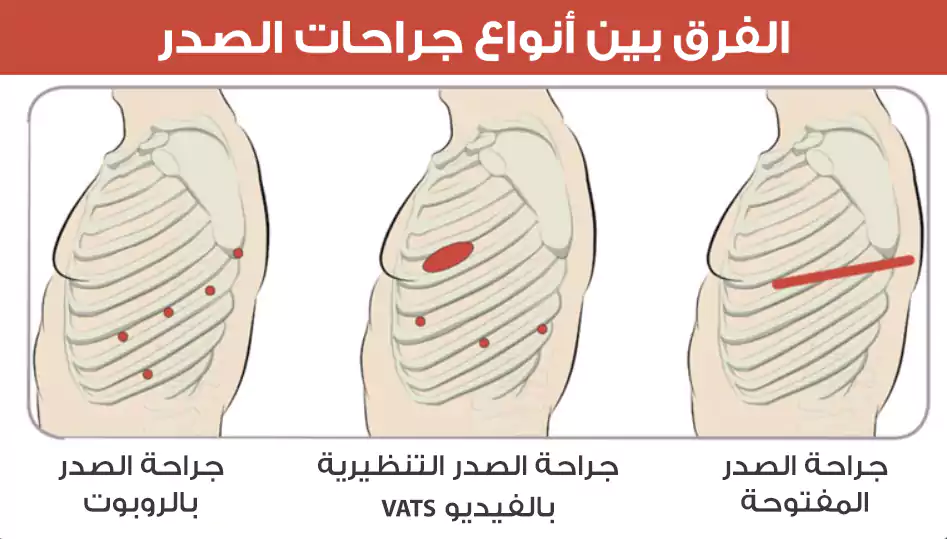
تعد الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت أحد بديلي التدخل الجراحي قليل التوغل لعملية جراحة الصدر المفتوحة لسرطان الرئة.
وفقًا لجمعية الرئة الأمريكية. الخيار الآخر للتدخل الجراحي قليل التوغل هو جراحة تنظير الصدر بمساعدة الفيديو (VATS). يعني الحد الأدنى من التدخل الجراحي بحيث أن الجراح يقوم بإجراء جروح صغيرة فقط عند إجراء الجراحة.
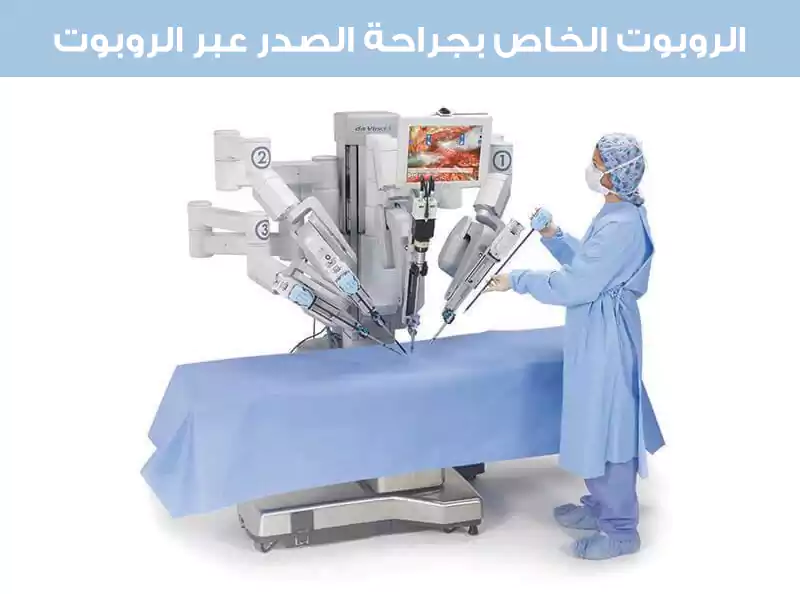
تستخدم الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت تقنية روبوتية محسّنة بالكمبيوتر تسمى نظام دافنشي الجراحي.
حيث يسمح هذا النظام للجراح بالعمل في منطقة الصدر باستخدام كاميرا ثلاثية الأبعاد عالية الدقة وأدوات دوارة صغيرة.
تتحرك هذه الأدوات بطريقة مشابهة لليد البشرية ولكن مع نطاق أكبر من الحركة والدقة.
منذ عام 2000، عندما تم إدخال أول نظام آلي للجراحة، تم اعتماد جراحة الصدر بمساعدة الروبوت (RATS) من قبل عدد متزايد من المراكز حول العالم، وهي تُستخدم اليوم في 10٪ من عمليات استئصال الفصوص.
هنا، نقوم بمراجعة خصائص ووظيفة النظام الآلي المتاح اليوم (أي نظام دافنشي الجراحي)، وتحديد التقنيات المختلفة لاستئصال الرئة الرئيسي عبر RATS، ومقارنة RATS بجراحة تنظير الصدر بمساعدة الفيديو (VATS) وبضع الصدر (بضع الصدر تعني جراحة الصدر المفتوحة)، والتكهن بالتطورات المستقبلية
كيف يحصل الإجراء الجراحي؟
أثناء الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت، يجلس الجراح عند وحدة التحكم ويقوم بعمل جروح صغيرة يتم من خلالها إجراء العملية.
ثم يقومون بإدخال كاميرا وأدوات جراحية مصغرة في منطقة سرطان الرئة. تنقل وحدة التحكم عرض الكاميرا بزاوية 360 درجة للمجال الجراحي.
يمسك الجراح بأدوات التحكم، ويقوم بحركات يد صغيرة.
يترجم النظام هذه إلى حركات صغيرة بواسطة الأدوات الجراحية داخل الرئتين.
أخيرًا، يقوم الجراح بإزالة أنسجة الرئة من خلال إحدى الجروح جنبًا إلى جنب مع الأدوات الجراحية.
سينظر الطبيب في حالة الشخص وتاريخه المرضي قبل أن يقرر ما إذا كانت الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت خيارًا مناسبًا له أو لا.
يمكن أن يكون الشخص مناسباً لهذا النوع من الجراحة إذا كان الورم قريبًا من خارج الرئتين وغير متصل بالأوعية الدموية.
أنواع الجراحة الروبوتية لسرطان الرئة
قد يستخدم الجراحون التكنولوجيا الروبوتية لثلاثة أنواع من جراحة سرطان الرئة. وتشمل هذه:
- استئصال الفص الرئوي: يشير هذا المصطلح إلى إزالة الفص المصاب (الجزء المصاب) من الرئة بالكامل.
- استئصال إسفيني: يتضمن هذا الإجراء إزالة الورم، بإزالة الأنسجة المصابة من بين أنسجة الرئة السليمة المحيطة به عن طريقة أداة مثلثة تسمى الإسفين.
- الجزئي Segmentectomy: في هذا الإجراء، يزيل الجراح فيه أنسجة أكثر مما كانت عليه أثناء استئصال الإسفين ولكن أقل أنسجة من استئصال الفص.
وجدت الأبحاث التي قارنت نتائج الأشخاص المصابين بسرطان الرئة ذو الخلايا الغير الصغيرة بعد الأنواع الثلاثة للجراحة وجود صلة بين استئصال الفص الرئوي ومعدلات البقاء على قيد الحياة المرتفعة.
من بين المشاركين الذين لم يكن استئصال الفص الرئوي مناسبًا لهم، كانت النتائج أفضل عندما قاموا بجراحة التجزئة مقارنةً بالاستئصال الإسفيني.
قد يؤدي استئصال الفص الرئوي إلى نتائج أفضل، ولكن لا يمكن للجميع إجراء هذه العملية.
على سبيل المثال، لاحظ الباحثون في إحدى الدراسات أن الأطباء قد يوصون إما بالاستئصال أو التجزئة للأشخاص الذين لديهم كمية محدودة من سرطان الرئة في مراحله المبكرة.
يسمى هذان الخياران الاستئصال الجزئي الفرعي.
ما هي فوائد ومخاطر الجراحة الروبوتية لسرطان الرئة؟
الفوائد
نظرًا لأن الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت ذات تدخل جراحي بسيط، فإن لها العديد من الفوائد. وتشمل هذه:
- إقامة أقصر في المستشفى.
- عودة أسرع للحياة الطبيعية.
- ألم أقل.
- مضاعفات أقل.
- فقدان دم أقل.
- ندوب أصغر.
- عدم قطع عظم القص أو الأضلاع.
استجابة الجسم للعملية الجراحية بمساعدة الروبوت تختلف من شخص لآخر.
حيث تعتمد استجابة الشخص على عدة عوامل، مثل تاريخه المرضي ونوع سرطان الرئة.
قارنت دراسة في حوليات جراحة الصدر آثار استئصال الفص الروبوتي بآثار استئصال الفص الصدري المفتوح.
حيث وجد الباحثون أن الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت أدت إلى انخفاض معدلات المضاعفات وإقامة أقصر في المستشفى.
قالت أبحاث أخرى في مجلة جراحة الصدر والقلب والأوعية الدموية في معدلات البقاء على قيد الحياة على المدى الطويل للأشخاص الذين خضعوا لاستئصال الفص الروبوتي لعلاج سرطان الرئة ذو الخلايا غير الصغيرة.
بأن معدلات البقاء على قيد الحياة لمدة 5 سنوات واعدة.
بالإضافة إلى الميزات التي تفوق جراحة الصدر المفتوحة، قد يكون للجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت بعض المزايا الإضافية مقابل جراحة الصدر بمساعدة الفيديو.
على سبيل المثال، يوفر للجراح رؤية أفضل ودقة أكبر في الحركة.
ومع ذلك، من الضروري إجراء المزيد من الأبحاث لتحديد ما إذا كانت الفوائد تؤدي إلى نتائج أفضل للمرضى.
المخاطر
جميع العمليات الجراحية، حتى العمليات الجراحية بسيطة التدخل الجراحي لسرطان الرئة تحتوي على مخاطر، مثل:
- تسرب الهواء من الرئتين.
- نزيف.
- الالتهابات.
- ألم.
- عدم انتظام ضربات القلب.
ما الذي يجب أن تتوقعه قبل دخولك للعملية؟
عادةً ما يتضمن إجراء الجراحة بمساعدة الروبوت الخطوات التالية:
- يخضع الشخص المصاب للتخدير العام قبل العملية.
- يقوم الجراح بإدخال أنبوب التنفس في مجرى الهواء للمريض.
- يقوم الجراح بعمل من 1 إلى 5 جروح صغيرة بين ضلوع المريض.
- يقوم الجراح بإدخال الكاميرا والأدوات الجراحية بين الضلوع.
- بمجرد اكتمال العملية، يقوم الجراح بإدخال أنبوب صدري من خلال أحد الجروح لتصريف أي هواء أو سوائل زائدة.
- يبقى أنبوب الصدر في مكانه لعدة أيام، وسيقوم أخصائيو الرعاية الصحية بإزالته قبل عودة المريض إلى المنزل.


