Robotic hair transplant in Turkey is considered one of the newest technologies in the field of hair transplantation due to its high precision and excellent results in improving people’s lives.
Hair loss is one of the most prevalent problems worldwide, affecting both men and women. Therefore, resorting to one of the treatment methods is essential to solve this problem radically. One of the most important methods in Turkey is Robotic hair surgery.
This advanced technology is more precise and efficient than traditional techniques for hair transplantation in Turkey, which mainly rely on manual surgery. Follow along in this article to learn more about the process of robotic hair transplantation and who it’s for in Turkey.
What is robotic hair transplant in Turkey?
Robotic hair replacement in Turkey is a development of the FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) technique for hair transplantation, in which hair follicles are extracted from the donor area of the scalp and transplanted after placing them in a Hypothermosol solution to ensure the vitality of the hair follicles. The robot technique for hair transplantation in Turkey is performed using a device that utilizes artificial intelligence, which is currently one of humanity’s most important and latest inventions.
Additionally, it can accomplish some tasks with precision and speed that a human doctor alone cannot achieve. Robotic hair transplant surgery in Turkey also uses 3D technology to plan and design the best grafts that can be taken from the donor’s scalp and then accurately determine the location of the transplantation to achieve smooth and suitable hair for you.
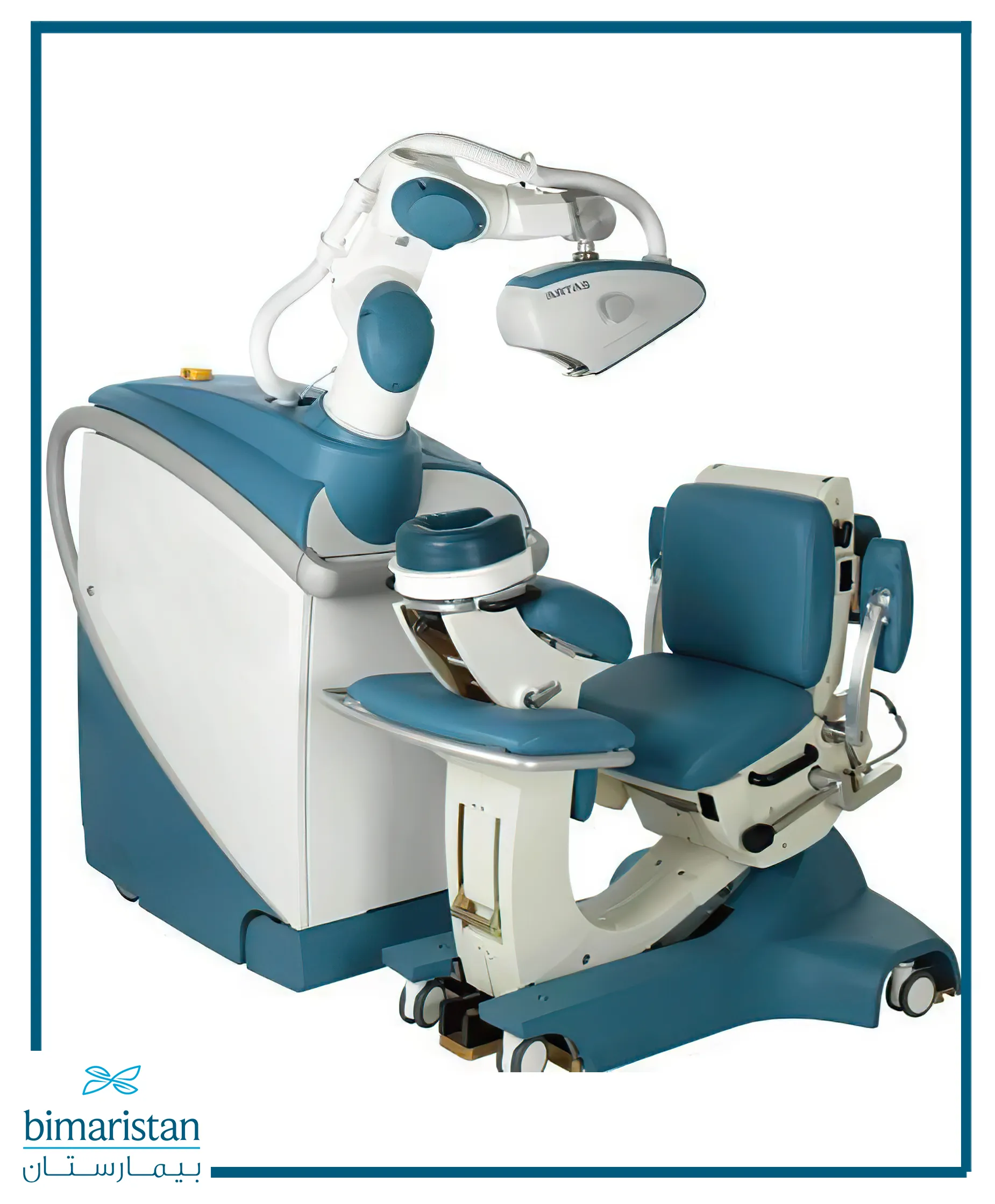
Who is robotic hair transplant in Turkey for?
Any patient suffering from hair loss and wanting to improve their appearance can choose a specific method from various hair transplantation techniques in Turkey. Still, the great benefit of robot hair transplantation in Turkey lies in a limited number of cases, including:
- Genetic baldness, also known as androgenic alopecia, which primarily affects men due to its association with male hormones.
- Hair loss due to injuries or burns on the scalp.
- Hair loss after cosmetic surgeries such as facelifts or Botox injections.
- Hair thinning or breakage, especially in women.
Devices used in robotic hair transplant in Turkey
To this day, two primary devices approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) are used in hair transplantation procedures in Turkey: the ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System and the NeoGraft system.
ARTAS hair transplant
The Artas robotic hair transplant system is a modern and advanced technique used to perform hair transplantation in Turkey with precision and efficiency. The ARTAS robot is used to extract and transplant individual hair units from the donor area of the scalp to the area suffering from hair loss. This technique has several advantages, including natural and permanent results, pain and scar reduction, and the patient’s quick return to daily life.
To ensure the best results, hair transplantation with the ARTAS system should be performed by a qualified and experienced surgeon.
NeoGraft robotic hair transplantation
The NeoGraft system is considered one of the modern techniques used in hair transplantation procedures in Turkey, where an electronic device is used to harvest hair follicles, along with a high-magnification microscope, to ensure the quality of the transplanted hair. Additionally, hair transplantation with the NeoGraft system is known for its use in cases of severe hair loss and the need for high accuracy in hair transplantation, as it uses three-dimensional technology to select the best hair follicles from the scalp and then transplant them.
Instructions before robotic hair transplant in Turkey
There are several necessary tips and instructions that you must strictly follow to ensure the success of hair transplantation with artificial intelligence. The most important of these instructions are:
- It would be best if you quit smoking two months before undergoing robot hair transplantation in Turkey, as it harms the blood circulation to the skin, thus increasing the risk of complications during or after the procedure.
- Many medications and vitamins that affect blood thinning or clotting should be stopped to avoid bleeding during the surgery. The most common of these medications are blood thinners like Aspirin, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like Ibuprofen and Diclofenac.
How is hair transplantation by robot performed in Turkey?
Hair transplantation by robot in Turkey is a procedure with minimal surgical intervention, as no surgical scalpels are used, unlike most other hair transplantation procedures in Turkey. A robot performs it under the supervision of a specialized doctor. The process of hair transplantation by robot in Turkey follows these steps:
- Initially, the hair in the donor area of the scalp is shaved under the supervision of the robot’s program, where the hair length in this area should be about 1 mm to enable the robot to complete the scan and accurately determine the follicles.
- The doctor then sterilizes both the donor and recipient areas of the hair to avoid any infection, then applies local anesthesia to the scalp area using 2% lidocaine along with adrenaline to prolong the effect of the anesthetic.
- The doctor then applies tension (skin tension) to the surgical area, allowing the robot system to determine the extracted follicles’ location accurately.
- The robot then identifies the strongest hair follicles suitable for hair transplantation and extracts them, as it has a three-dimensional optical system with high analytical capabilities that enable it to select these follicles optimally.
- The robot then identifies the best areas for transplantation of the selected hair follicles, as well as their grafting, with high accuracy, behind the hairline, unlike hairline transplantation, which is performed manually by the surgeon.
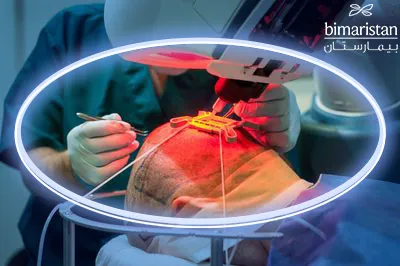
Hair transplant using robotic technology takes about 2-3 hours, which is relatively short compared to other methods used in hair transplantation in Turkey, which may take about 8 hours in some cases.
Results of robotic hair transplant in Turkey
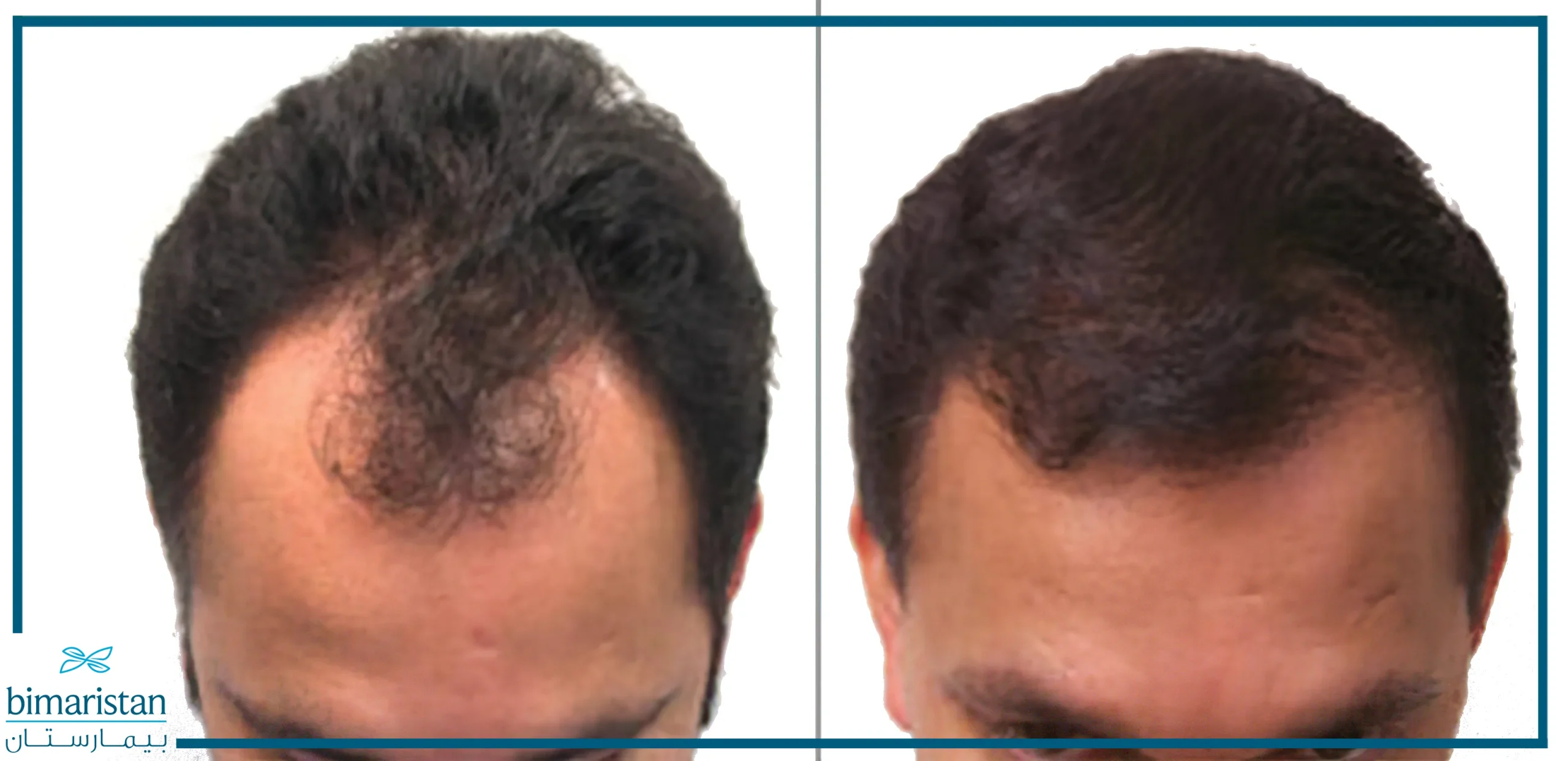
The remarkable results of robotic hair transplantation have amazed the medical world due to the transplant’s quality and how close it is to natural hair. In addition, the success rate of hair transplants with robots in Turkey can reach 100% in most cases. This technique allows patients to enjoy the final results, estimated at four months, shortly after the procedure. Below is a picture of a patient suffering from baldness in the frontal part of the scalp before and after undergoing robotic hair transplantation in Turkey.
Recommendations after robotic hair transplant in Turkey
The patient must adhere to some tips and recommendations to achieve perfect results in robotic hair transplantation. The most prominent of these recommendations are:
- Avoid touching or combing the hair until the transplanted hair is stable.
- Avoid strenuous physical exercises during the first week after the operation.
- Avoid smoking and alcoholic beverages to improve blood circulation to the skin and accelerate healing.
- You can return to work within 2-3 days if the work is not strenuous.
- You can use regular shampoo after about a week of the procedure.
Advantages of hair transplant with robots in Turkey
Hair transplantation experts in Turkey have developed a robotic device to eliminate human errors that may occur due to the length of the operation time, in addition to stopping the process of manually extracting and transplanting hair follicles. The most important features that distinguish this technology are:
- Natural appearance in both the donor and recipient areas, with no noticeable scars.
- Increased hair follicle growth rate compared to other hair transplantation methods.
- Even distribution of hair on the scalp.
- It is a very comfortable treatment with a faster healing time.
- Incredible precision in operating, as the accuracy of the hair transplant robot exceeds that of the DHI hair transplant technique by scanning and tracking each hair about 60 times per second, allowing for the selection of the best follicles for transplantation.
Disadvantages of robotic hair transplantation in Turkey
Despite the significant advantages of robot hair transplantation in Turkey, like any other procedure, it has some drawbacks and disadvantages. The main disadvantages include:
- The patient’s hair must be smooth and dark to be able to perform the robot hair transplantation procedure.
- It is necessary to take hair follicles from the back of the scalp or the sides, as hair from other body parts cannot be used.
- There may be a risk of injuring some nerves in the scalp during robot hair transplantation, but this is very rare.
- The tool used by the robot is somewhat thick, which may damage some hair follicles, but this depends on the experience and efficiency of the surgeon in performing such procedures.
The cost of hair transplant with robots in Turkey
Recently, with medical advancements in the world, it has become possible to perform hair transplantation with robotic technology accurately and safely, especially in Turkey, which is considered the best country in this field. The cost of robotic hair transplantation in Istanbul, Turkey, starts from $2000, depending on the extent of the bald area and the number of follicles to be transplanted.
In conclusion, if you are concerned about the problem of baldness, robotic hair transplantation can treat varying degrees of hair loss. Ultimately, the primary task of the doctor is to choose the best method that suits the patient’s condition among the various hair transplantation methods.
References:
