تدلي المستقيم أو هبوطه عبر فتحة الشرج يسبب لك أعراض مزعجة تستدعي العلاج، يمكن إجراء عملية إصلاح هبوط المستقيم بتقنيات جراحية طفيفة التوغل في تركيا.
ما هو هبوط المستقيم؟
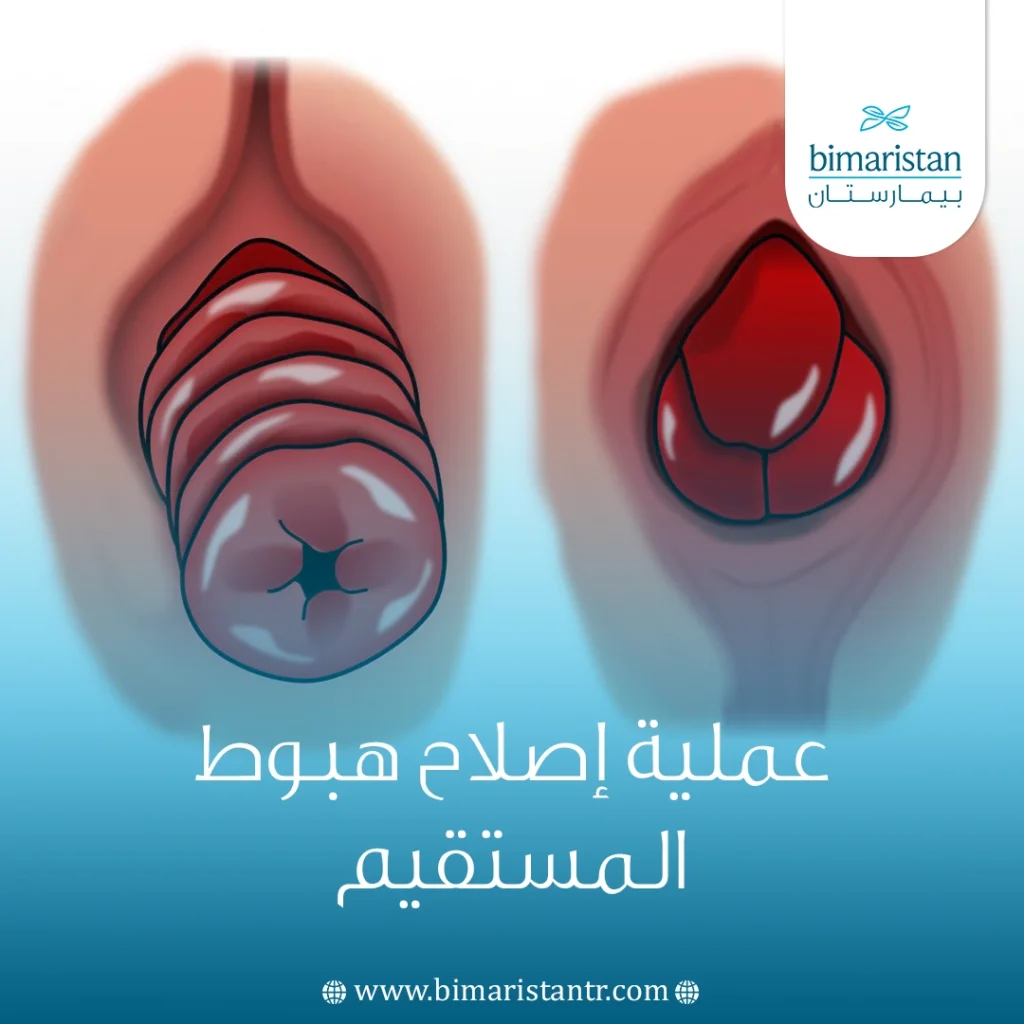
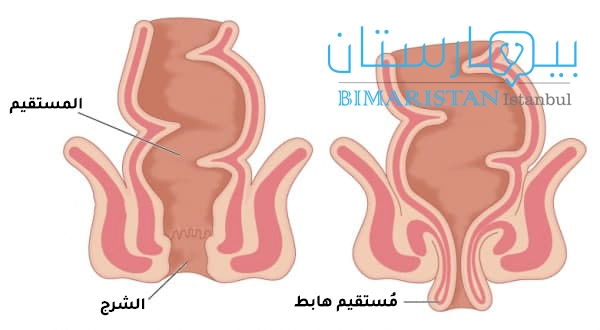
يعرف هبوط المستقيم rectal prolapse بتدلي المستقيم خارج مكانه الطبيعي نزولاً إلى الأسفل، فقد يلاحظ المريض مستقيمه المتدلي أثناء التغوط أو عند الوقوف على شكل كتلة حمراء بارزة من الشرج.
يفصل المستقيم بين آخر أجزاء القولون والشرج، ويشكل مخزناً مؤقتاً للفضلات ريثما يتم طرحها خارج الجسم، لا يمكن رؤية مستقيم الشخص الطبيعي بالعين، لكن في حالات الهبوط قد يشاهد بسهولة ككتلة حمراء هابطة تشبه لحدٍ ما البواسير.
هبوط المستقيم حالة شائعة عند كبار السن الذين يعانون من إمساك مزمن، ويحدث بشكل أكبر عند النساء بعد سن اليأس وقد يصيب الصغار أيضاً.
غالباً ما يتم إعادة المستقيم لمكانه الطبيعي بالعمل الجراحي، وحالياً يتم في تركيا إجراء الجراحة بتقنيات متطورة طفيفة التوغل قليلة الخطورة.
أعراض هبوط المستقيم
إن العرض الأشيع هو ملاحظة المستقيم الهابط ككتلة حمراء متبارزة من فتحة الشرج، تُلاحظ هذه الكتلة بشكل خاص أثناء التغوط ومع تطور الحالة تصبح مرئية عند الوقوف والمشي.
من الأعراض الأخرى لتدلي المستقيم ما يلي:
- تغوط مدمى وألم أثناء التغوط
- سلس البراز (فقدان السيطرة على عملية التبرز)
- الشعور بالرغبة بالتغوط على الرغم من عدم وجود براز
- إمساك أو إسهال
- خروج مخاط أو قيح مع البراز
أسباب هبوط المستقيم
إن السبب الرئيسي ما يزال غير مفهوم بشكل واضح، يعتقد بعض الأطباء أن سبب تدلي المستقيم هو ضعف العضلات التي تبقي المستقيم بمكانه، بينما يعتقد البعض الآخر أن هبوط المستقيم يحدث عند النساء بعد الولادة.
يتفق العلماء على وجود عدة عوامل تؤهب للإصابة بتدلي المستقيم وهي:
- الإمساك المزمن أو الإسهال
- إصابة عصبية في الأعصاب المسؤولة عن تقلص عضلات المستقيم والشرج
- الكبس الشديد المستمر خلال التغوط
- إصابة رضية سابقة في منطقة الحوض حول المستقيم
- الإنتانات على مستوى الشرج والمستقيم
- بعض الأمراض كداء التليف الكيسي أو السكري
- قد يترافق مع هبوط الرحم أو المهبل
تشخيص هبوط المستقيم
يقوم الطبيب بأخذ القصة السريرية للمريض بشكل مفصل ومعرفة التاريخ الطبي له، فوجود إمساك مزمن قد يزيد الشك باحتمال الإصابة بهبوط المستقيم.
يجب التمييز بين هبوط المستقيم والبواسير فهما حالتان طبيتان مختلفتان، قد يستعين الطبيب بأحد الفحوصات التالية للتأكد من التشخيص واستبعاد الأسباب الأخرى:
فحص المستقيم (المس الشرجي): يقوم الطبيب بارتداء قفاز وإدخال اصبعه عبر فتحة الشرج إلى المستقيم، يجري تقييم قوة المعصرة الشرجية والبحث عن كتل أو موجودات غير طبيعية أو نزف.
قياس الضغط الشرجي: تتم عبر إدخال أنبوب ضيق مرن يحوي بأسفله بالون إلى المستقيم، يتم نفخ البالون وقياس قوة تقلص مصرة الشرج.
تخطيط كهربائية العضلة الشرجية: يفيد هذا الاختبار في معرفة ما إذا كان السبب وراء هبوط المستقيم هو خلل في تعصيب عضلة المعصرة الشرجية.
تنظير القولون: يتم استخدامه لاستبعاد الأسباب الأخرى كوجود بوليبات أو تنشؤات ورمية في الأمعاء الغليظة، حيث يتم إدخال أنبوب مرن يحوي كاميرا عبر فتحة الشرج لرؤية الأمعاء الغليظة.
اقرأ أكثر عن تنظير القولون.
التصوير الشعاعي التبرزي: يقوم هذا الاختبار على تسجيل فيديو شعاعي للمستقيم والشرج خلال عملية التغوط لدراسة وجود مشاكل وظيفية أثناء التغوط في المستقيم.
عملية إصلاح هبوط المستقيم في تركيا
غالباً ما يتم اللجوء إلى العمل الجراحي لعلاج هبوط المستقيم عند البالغين، تهدف العملية لإعادة المستقيم لمكانه الطبيعي، وتتم بواسطة تقنيات جراحية تهدف إلى إصلاح أو تعزيز الحاجز المستقيمي.
تتوفر طريقتين لإجراء جراحة هبوط المستقيم وهما:
التداخل عبر البطن
يتم عبر هذه الطريقة إحداث شقوق جراحية بالبطن لتثبيت المستقيم في مكانه الطبيعي، في حال وجود تاريخ طويل للإصابة بالإمساك قد يلجأ الجراح لاسئصال جزء من القولون ومن ثم يعيد المستقيم ويثبته بمكانه الطبيعي.
يجري التداخل عبر البطن عند المرضى ذوي الصحة الجيدة الذين لا يعانون من أمراض تعيق العمل الجراحي.
التداخل عبر العجان
تستخدم هذه الطريقة عند المرضى الأكبر سناً الذين يعانون من مشاكل صحية تجعل جراحة البطن صعبة الإجراء، تتوفر طريقتين للتكنيك الجراحي وهما:
إجراء ألتميرر Altemeier procedure: يتم في هذا الإجراء استئصال الجزء الهابط من المستقيم ومن ثم يتم خياطة طرفي النهاية مع بعضهما.
إجراء ديلورمي Delorme procedure: يتم إزالة البطانة الداخلية للمستقيم الهابط فقط ومن ثم يتم خياطة طرفي البطانة الداخلية مع بعضهما، وبعد ذلك يتم طي الطبقة الخارجية للمستقيم الهابط وإعادته لمكانه الطبيعي.
ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ إصلاح هبوط المستقيم طفيفة التوغل في تركيا
تطورت الأساليب الجراحية المستخدمة في الطب الحديث، حيث ظهر مؤخراً تكنولوجيا حديثة تمتاز بكونها قليلة الخطورة وسهلة التنفيذ كاستخدام الروبوتات في العمليات الجراحية.
عملت تركيا على توفير أحدث طرق المعالجة لتصحيح تدلي المستقيم ومنها:
عملية هبوط المستقيم بالمنظار
بعد تخدير المريض يقوم الجراح بعمل شق جراحي صغير في البطن ومن ثم يتم إدخال المنظار (عبارة عن جهاز أنبوبي يحوي كاميرا بأسفله).
يقوم الطبيب بتحديد مكان القولون السيني والمستقيم لتحريره من الأنسجة المحيطة وإعادة المستقيم الهابط لمكانه الطبيعي.
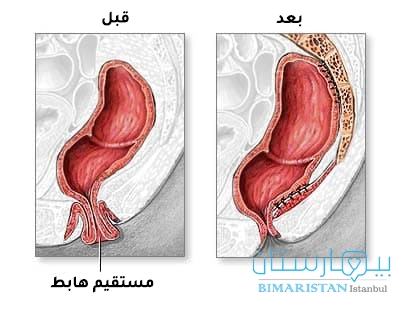
عملية هبوط المستقيم بالروبوت
يمكن بواسطة جهاز آلي يتم التحكم به من قبل الطبيب الجراح إجراء العملية بدقة بالغة وبرؤية واضحة ثلاثية الأبعاد وبأقل خطر ممكن، فبعد إجراء شقوق جراحية صغيرة جداً يتم باستخدام الروبوت تثبيت المستقيم لمكانه الطبيعي بدقة متناهية.
يُمكن مشاهدة فيديوعن العملية من هنا.
مزايا عملية إصلاح هبوط المستقيم طفيفة التوغل
تتميز عملية إصلاح هبوط المستقيم قليلة التوغل عن الجراحة التقليدية المفتوحة بما يلي:
- احتمال حدوث الاختلاطات أقل كالإنتان
- كمية الدم المفقودة أقل بكثير من الجراحة المفتوحة
- تعافي سريع بعد العملية حيثُ يعود المريض لحياته الطبيعية خلال فترة وجيزة
- غالباً تكون نتائجُها أفضل من الجراحة المفتوحة
- الندوب الجراحية تكون أقل
- الألم يكون أخف
بعد العمل الجراحي
تعتمد فترة البقاء في المستشفى بعد العملية على نوع العمل الجراحي الذي تم إجرائه، ففي عمليات المُستقيم التقليدية بالجراحة المفتوحة يبقى المريض بالمستشفى حوالي 5 إلى 8 أيام، وتكون هذه المدة أقل عند استخدام أساليب أقل توغلاً كالمنظار.
يجب الإكثار من شرب السوائل بعد العملية وقد يصف الطبيب ملينات للبراز أثناء فترة التعافي مع حمية غذائية غنية بالألياف في الأسابيع التي تلي العمل الجراحي لتجنب الإمساك الذي قد يؤدي إلى عودة تدلي المستقيم مجدداً.
يعود معظم المرضى لحياتهم الطبيعية خلال 4 إلى 6 أسابيع من العمل الجراحي، وغالباً ما تزول الأعراض بشكل كامل عند الأغلبية العظمى من المرضى.
كيفية علاج هبوط المستقيم بدون جراحة
كما ذكرنا سابقاً فإن الطريقة الأساسية في علاج الهبوط المستقيمي هي العملية الجراحية، لكن من الممكن استخدام طرق أخرى تساعد في علاج هبوط المستقيم في مراحله الخفيفة الأولية كالأعشاب والعلاج الفيزيائي.
علاج هبوط المستقيم بالأعشاب
يُنصح مرضى تدلي المستقيم بالإكثار من الطعام الغني بالألياف وخاصةً الفواكه والخضروات لتجنب الإمساك الذي يؤثر سلباً على التدلي، فمن الأعشاب التي لها دور في تدبير الإمساك وعلاج تدلي المُستقيم: أعشاب الإهليلج، الزبيب، حبة البركة، البابونج، الزنجبيل.
لم يتم بعد إثبات فعالية الأعشاب في علاج تدلي المستقيم بشكل واضح، وما تزال الدراسات قائمة على هذه النوعية للعلاج.
علاج تدلي المستقيم بالرياضة
يوجد بعض التمارين التي تفيد في تقوية عضلات قاع الحوض، حيث تعمل هذه العضلات على دعم الرحم والمثانة والمستقيم وزيادة الإستمساك لمنع تدلي الأعضاء للأسفل ومن أهم هذه التمارين:
تمارين كيغل
قم بالجلوس أو الوقوف بوضع مريح مع مباعدة الساقين ومن ثم حدد العضلات المستهدفة بشكل جيد واسحب العضلة كما لو أنك تحاول منع مرور الغازات من الأمعاء.
تخيل نفسك كما لو أنك على وشك التبول ومن ثم قم بشد العضلات التي تستخدمها للتوقف المفاجئ عن التبول، واسحب عضلات الحوض من الخلف للأمام بأفضل قدر ممكن.
استمر على حالة الشد حوالي عشر ثواني ومن ثم قم بإرخاء العضلات، استرح حوالي 5 ثواني ومن ثم كرر هذا التمرين لعدة مرات متتالية.
تمارين رفع المستقيم يدوياً
اغسل يديك جيداً وارتدي قفازك ومن ثم أدخل إصبعك لمكان المستقيم الهابط وطبق ضغطاً عليه واسحبه للأعلى بلطف، كرر هذه العملية لعدة مرات متتالية.
توقف عن أداء هذه التمارين في حال شعرت بالألم، تبقى استشارة الطبيب المختص هي الخيار الأفضل في جميع الحالات، سيعلمك الأخصائي كيفية إجراء هذه التمارين في المنزل في حال كنت بحاجة لها.
المصادر: