عندما تصاب بالتهاب في اوتار ركبتك سوف تشعر بألم يزداد شدة مع الحركة، يميل التهاب أوتار الركبة لكونه أكثر شيوعاً عند الرياضيين كثيري القفز.
تكمن وظيفة الأوتار بوصل العظام مع العضلات مما يؤمن استقرار وثباتية أثناء الحركة، فلا تستطيع بسط الركبة أو الوثب بدون وجود الوتر الرضفي.
غالباً ما يحدث إلتهاب وتر الركبة knee tendinitis نتيجة الضغط المستمر على الوتر بسبب التمارين الرياضية كالقفز، لذلك سميت هذه الحالة بركبة القافز، لنتعرف أكثر عن التهاب أوتار الركبة وكيفية علاجه.
لمحة عن أوتار الركبة
تحوي ركبة الإنسان 4 أوتار رئيسية وهم: وتر العضلة رباعية الرؤوس الفخذية، الوتر المأبضي (وتر أخيل)، الوتر الرضفي، الشريط الحرقفي.
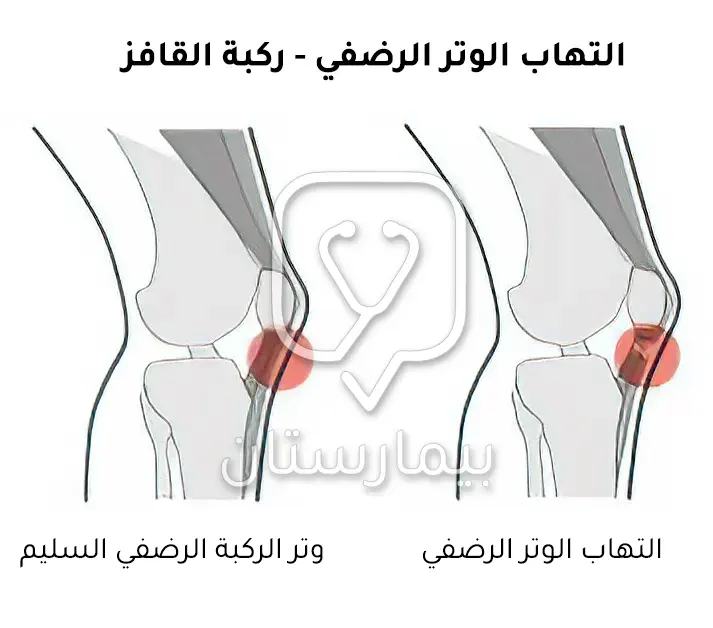
إن الوتر الرضفي patellar tendon يربط بين عظمي رضفة الركبة والظنبوب في الساق لتأمين الاستقرار والثباتية اللازمة للحركة، بالإضافة إلى دوره في دعم عضلة الفخذ مربعة الرؤوس.
بسبب الوظائف الكثيرة لهذا الوتر فهو معرض للالتهاب بِشكل أكبر من الاوتار الاخرى في مفصل الركبة، مما يجعل مصطلح “التهاب أوتار الركبة” يشير لالتهاب الوتر الرضفي في أغلب الحالات.
النشاطات الرياضية كالقفز تضع حمل على الأوتار، لذلك فإن هذه المشكلة غالباً ما تصيب لاعبي كرة السلة والطائرة.
اعراض التهاب أوتار الركبة
الألم المتوضع أسفل مفصل الركبة هو العرض الأول لالتهاب الأوتار ويشتد هذا الالم عند حركة المصاب، وقد يكون ألم التهاب الوتر غير ظاهر إلا عند الحركة وخاصةً في المراحل الأولى للإصابة.
مع مرور الوقت وتزايد شدة الإلتهاب تصبح أعراض الإصابة أكثر وضوحاً، حيث يشتد الألم لدرجة منع الشخص من ممارسة الرياضة أو صعود الدرج وبمراحل أكثر تطوراً يصبح الم الالتهاب ظاهراً حتى في أوقات راحة المريض.
قد يلاحظ أيضًا تورم بالمفصل مع تيبس وصعوبة في تحريك الركبة، قم باستشارة الطبيب عند الشعور بإحدى هذه العلامات واستمرارها لأكثر من يومين.

أسباب التهاب أوتار الركبة
التهاب وتر الركبة هو حالة من فرط التحميل على اﻟﻮﺗﺮ تؤدي مع مرور الوقت لالتهابه، تسبب الزيادة بالحمل تمزقات صغيرة بالوتر، يقوم الجسم بمحاولة إصلاح هذه التمزقات عبر عملية التهابية مما يسبب حدوث إلتهاب بالأوتار.
من عوامل الخطر التي تجهد الأوتار ما يلي:
- الجري والقفز المستمر عند الرياضيين
- التزايد المفاجئ في النشاط الرياضي (جري لمسافات طويلة عند شخص غير معتاد على ذلك)
- عضلات الساق غير متكافئة بالقوة
- الوزن الزائد
- انحراف خلقي بالقدمين
- الأمراض الوعائية المزمنة التي تضعف تدفق الدم للركبة (السكري، قصور الكلية)
تشخيص التهاب الأوتار في الركبة
سيسأل طبيب العظام والمفاصل عن تاريخ المريض الطبي ومدى ضلوعه بالأنشطة الرياضية، لينتقل بعدها للسؤال عن الاعراض بِشكل مفصل.
سيقوم بعدها بعمل فحص جسدي لتقييم إصابة المريض وشدتها، عادةً ما يكون الم التهاب الأوتار متوضع في مقدمة وأسفل الركبة، لتأكيد التشخيص ونفي الأسباب الأخرى قد يطلب أحد الفحوصات التالية:
التصوير بالأشعة السينية X-rays
تفيد هذه التقنية في استبعاد المسببات الأخرى لألم الركب كمشاكل العظام، حيث أن أوتار الركبة لا تظهر على صور الأشعة السينية.
التصوير بالأمواج فوق الصوتية Ultrasound
يستخدم هذا الاختبار أمواج فوق صوتية لتشكيل صورة عن الركبة والبنى التي تحيط بها، يمكن باستعمال الإيكو رؤية الأوتار وتحديد ظهور تمزُّق أو التهاب على امتداد الوتر، لكنه يحتاج إلى خبرة من الفاحص.
الرنين المغناطيسي MRI
من الوسائل المتقدمة في تشخيص أمراض مفصل الركبة عبر استعمال حقل مغناطيسي يسمح برؤية واضحة تظهر أية تغيرات طفيفة بالأوتار أو الغضاريف بالركبة بحيث يمكن استبعاد وجود تمزق في غضروف الركبة.

كيفية علاج التهاب أوتار الركبة
يهدف العلاج بشكل أساسي لتخفيف آلام الركبه وتقوية الأنسجة الرخوة حول المفصل لجعله أكثر صلابة وقدرة على تحمل الضغط المطبق على الأوتار.
غالباً ما يبدأ أخصائي العظام بعلاجات بسيطة قليلة التوغل ويحتفظ بالتداخلات الأكثر تعقيداً كالجراحة للمراحل المتأخرة من التهاب اﻷوﺗﺎر.
أدوية علاج التهاب أوتار الركبة
مسكنات الألم ومضادات الإلتهاب كالإيبوبروفين تريح المريض من آلامه لفترة مؤقتة، بالإضافة إلى فائدة الراحة في تخفيف أعراض الإلتهاب، كذلك فإن تطبيق الثلج على مكان الإصابة يقلل من الالتهاب والتورم بتلك المنطقة.
تمارين لعلاج التهاب أوتار الركبة
يفيد العلاج الفيزيائي في تخفيف الأعراض وتقوية الأوتار في الركبة، تعمل تمارين التمدد Stretching exercises على التقليل من التشنج العضلي وتساهم في إطالة الوتر الرضفي لجعله أكثر مقدرة على تحمل الشد والضغط.
تمارين القوة العضلية تفيد أيضاً في الوقاية من التهابات أوتار الركبة، فعضلات الفخذ الضعيفة تلعب دور مهم في زيادة القابلية لحدوث التهاب بالأوتار.
وضع حزام حول وتر الركبه الرضفيّ يعمل على توزيع الضغط بعيداً عنه مما يقلل من آلام إصابة وتر الرضفة.
علاج التهاب الأوتار في الركبة عبر حقن البلازما
أثبتت الدراسات فعالية بلازما الدم الغنية بالصفائح الدموية PRP في تسريع شفاء إلتهاب الركبة والتقليل من التورم، يمكن ايضاً استخدام البلازما لعلاج مجموعة من أمراض الركبتين كالخشونة والتهاب المفاصل، اقرأ أكثر عن فوائد البلازما للركبة.
العلاج الجراحي لالتهاب أوتار الركبة
قد تستدعي التهابات الوتر الشديدة الغير مستجيبة للعلاجات الأخرى الحاجة لإجراء عمل جراحي لإصلاح الإصابة لكن هذا الأمر نادر للغاية.
يتم إجراء عملية جراحية لإصلاح تمزقات الوتر ويمكن التداخل باستخدام منظار الركبة والذي يتميز بأنه طفيف التوغل وفترة التعافي بعد الإجراء أقل مما هي عليه في الجراحة التقليدية.
غالباً ما تتمكن من العودة لنشاطك الفيزيائي عالي المستوى بعد مضي حوالي 3 أشهر بعد العملية، قد تطول هذه المدة لسنة كاملة تبعاً لكيفية سير الجراحة وشدة إصابة الوتر.
الوقاية من التهاب أوتار الركبة
للتقليل من خطر الإصابة بالتهابات الأوتار قم باتباع الخطوات والنصائح التالية:
- لا تتجاهل ألم الركبة وتوقف عن إكمال الأنشطة الرياضية عند شعورك بالألم
- تقوية عضلات الفخذ يجعلك أكثر مقدرة على تحمل الضغط المسبب لالتهاب الاوتار
- تأكد من ارتداء الملابس والأحذية الملائمة للرياضة التي تمارسها
- الإحماء المناسب قبل البدء بالنشاط الرياضي
- العلاج الفيزيائي يساعد في إراحة العضلات وتجنب وقوع إصابات رياضية
وبالنهاية فإن السبب الأساسي لحدوث التهاب أوتار الركبة يعود للإجهاد الذي يتعرض له الرياضيين كثيري الوثب ولذلك أطلق عليها ركبة الواثب، وعلاج التهاب الأوتار يعتمد على تخفيف الإجهاد والراحة وقد يتم إجراء عمل جراحي في الحالات الشديدة، وتذكر دائماً بأن أفضل طريقة للعلاج هي الوقاية والتي تتم عبر تقوية العضلات وتجنب إجهاد الوتر.
المصادر:








