التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار هو مرض شائع لكنه أكثر مشاهدة عند الأطفال، يسبب هذا المرض عدة أعراض منها ألم الاذن ومشاكل السمع، علاج الالتهاب عند الكبار فعال غالباً.
التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار
يشير مصطلح “التهاب الاذن” في معظم الحالات إلى العدوى التي تحدث بالأذن الوسطى، يقع القسم الوسطي للأذن خلف منطقة غشاء الطبل (طبلة الاذن) ويضم عظيمات السمع التي تعمل على نقل الاهتزازت الصوتية للأذن الداخلية.
إن الإصابة بالتهاب الأذن الوسطى هي أكثر شيوعاً عند الاطفال منه عند البالغين، لكن التهاب الأذن الوسطى يمكن ان يصيب الأشخاص من مختلف الأعمار سواءً عند كبار السن أو الرضع.
الشعور بنقص السمع أو ألم بإحدى الأذنين قد تكون إحدى علامات عدوى الأذن الوسطى بالإضافة إلى ارتفاع حرارة الجسم والتعب العام.
قد يحدث في المراحل المتقدمة من التهابات الأذن الوسطى نزح سوائل من داخل الاذن لها ألوان مختلفة كاللون الأصفر أو الابيض والبني، غالباً ما يدل تصريف السائل على حدوث انثقاب في الغشاء الطبلي للأذن.
تعرف الحالة المترافقة مع انثقاب جزء من غشاء الطبل بالتهاب الأذن المزمن، وهي مرحلة متقدمة لإلتهاب الاذن الوسطى الحاد.
في الحقيقة غالباً ما يشفى التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار تلقائياً دون أية معالجة بعد مضي أسبوع إلى اسبوعين للمرض، لذا فإن كيفية علاج الإلتهاب تعتمد على شدة الأعراض.
اقرأ المزيد عن: التهاب الاذن عند الاطفال.
أسباب التهابات الاذن الوسطى عند الكبار
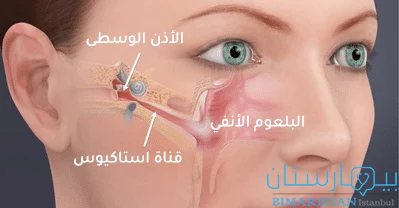
تحصل حالة التهاب الأذن الوسطى (otitis media) نتيجة عدوى بكتيرية أو فيروسية تصل القسم الأوسط للأذن عبر قناة استاكيوس (نفير أوستاش) وهي عبارة عن أنبوب عضلي يصل بين البلعوم الأنفي والاذن المتوسطة.
تكمن وظيفة هذا القناة بمعادلة ضغط الهواء على جانبي طبلة الاذن لمنع أذية الطبلة، بالإضافة إلى نزح السوائل المخاطية من الأذن المتوسطة باتجاه البلعوم منعاً لحدوث تراكم للسائل بالأذن.
يؤدي التهاب البلعوم الانفي بسبب بعض الأمراض كالزكام إلى احتقان وتورم بالقناة مما ينتج عنه انسداد بقناة إستاكيوس، ينتج عن الانسداد تجمع للسوائل داخل الأذن الوسطى وتشكيل وسط مناسب لنمو الجراثيم والفيروسات.
اقرأ المزيد: انسداد قناة استاكيوس.
أنواع عدوى الأذن الوسطى
يقسم التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الكبار إلى عدة أنماط وهي:
التهاب الاذن الوسطى الحاد
يحصل الالتهاب الحاد للأذن الوسطى بشكل مفاجئ وغالباً ما يكون تالي للإصابة بعدوى الطرق التنفسية (كالزكام)، أهم ما يميز هذا النمط هو الحمّى (الترفع الحروري) و الألم في الأذن.
التهاب الأذن الوسطى المصلي
عادةً ما يتبع هذا النوع التهاب أذن حاد، حيث نشاهد في هذا النمط تراكم للسوائل بالأذن المتوسطة بدون ظهور علامات التهاب أذن حاد كالحمى أو التعب العام.
اهم عرض لالتهاب الأذن المصلي عند الكبار هو نقص السمع.
التهاب الأذن الوسطى المزمن
يحصل بهذا النوع تجمع سائلي والتهاب متكرر بالأذن حيث ينكس مراراً وتكراراً بعد علاجه ويترافق مع انثقاب في غشاء الطبل في أغلب الحالات.
اهم ما يميزه هو نزح السائل من مجرى السمع، وقد يترافق مع مضاعفات خطيرة في حال إهمال العلاج والمراقبة كنمو ورم كولسترولي على حساب القسم الهامشي من طبلة الأذن.
أعراض التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار
تختلف أعراض التهاب الأذن من شخص لآخر بحسب شدة الالتهاب المصاب به، نذكر اهم الأعراض:
- الحمى (ارتفاع الحرارة)
- ألم بالأذن
- نقص السمع
- الطنين والإحساس بالدوخة
- نزح سائل من اذن المريض

تشخيص التهاب الأذن
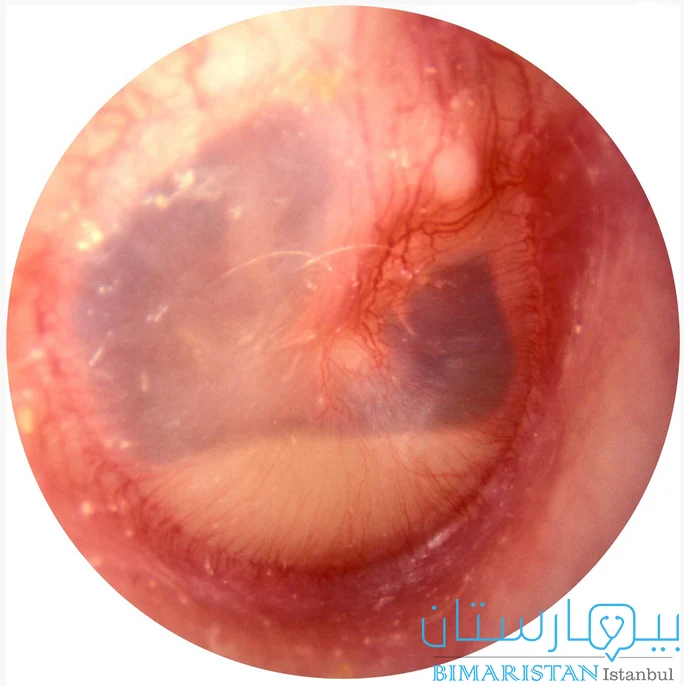
بعد أخذ القصة السريرية والسماع لأعراض المريض يقوم اخصائي أمراض الأنف والأذن والحنجرة بالفحص عبر استخدام منظار الأذن والذي يمكن الفاحص من رؤية الطبلة والبحث عن علامات الالتهاب كالاحمرار.
يمكن بواسطة المنظار ضخ هواء باتجاه الطبلة لتحديد قابليتها للحركة ففي حال تواجد تجمع سائلي بالأذن الوسطى تبقى طبلة الأذن ثابتة لا تتحرك.
قد يطلب منك الفاحص القيام بالنفخ مع إغلاق فمك حيث يؤدي ذلك لتحريك غشاء الطبل عند الأصحاء، أما عند انغلاق مجرى إستاكيوس فالغشاء يبقى ثابتاً.
طرق علاج التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الكبار
تعتمد طريقة علاج التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الكبار على عدة عوامل منها عمر المريض وشدة الالتهاب إضافةً إلى طبيعة العدوى التي تصيب الشخص.
يحدد الطبيب طريقة العلاج الأنسب وفقاً لكل حالة، فقد يكتفي بمراقبة أعراض التهاب الاذن في الحالات الخفيفة وتسكين الالم، أما في الحالات الأشد والتي لا تتحسن مع مرور الوقت يتم اللجوء لأساليب أخرى كوصف مضاد حيوي.
المضادات الحيوية Antibiotics
وفقاً للدراسات الحديثة فإن الصادات الحيوية هي حجر الأساس في علاج التهاب الأذن الوسطى عند الكبار، يتم اختيار الصاد الحيوي المناسب تبعاً لأشيع انواع البكتيريا التي تسبب التهاب الاذن.
يعتبر الأموكسيسيلين (Amoxicillin) أفضل مضاد حيوي لالتهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار، من المهم اتباع تعليمات طبيبك المختص فيما يخص جرعة الدواء والفترة اللازمة لأخذه، فمن الأخطاء الشائعة التي يفعلها بعض المرضى هي التوقف عن أخذ الدواء فور شعورهم بالتحسن.
الأدوية المسكنة للألم Pain-relieving medications
يفيد استخدام هذه الادوية التي تشمل العقاقير أو القطرات الأذنية عند المرضى الذين يعانون من أعراض تتمثل بألم الأذن وارتفاع بالحرارة.
يميل الم الأذن ليزداد شدةً أثناء الاستلقاء على الجانب المصاب ويمكن أن يؤدي إلى صعوبة في النوم، تساهم هذه الادوية بحل هذه المشكلة.
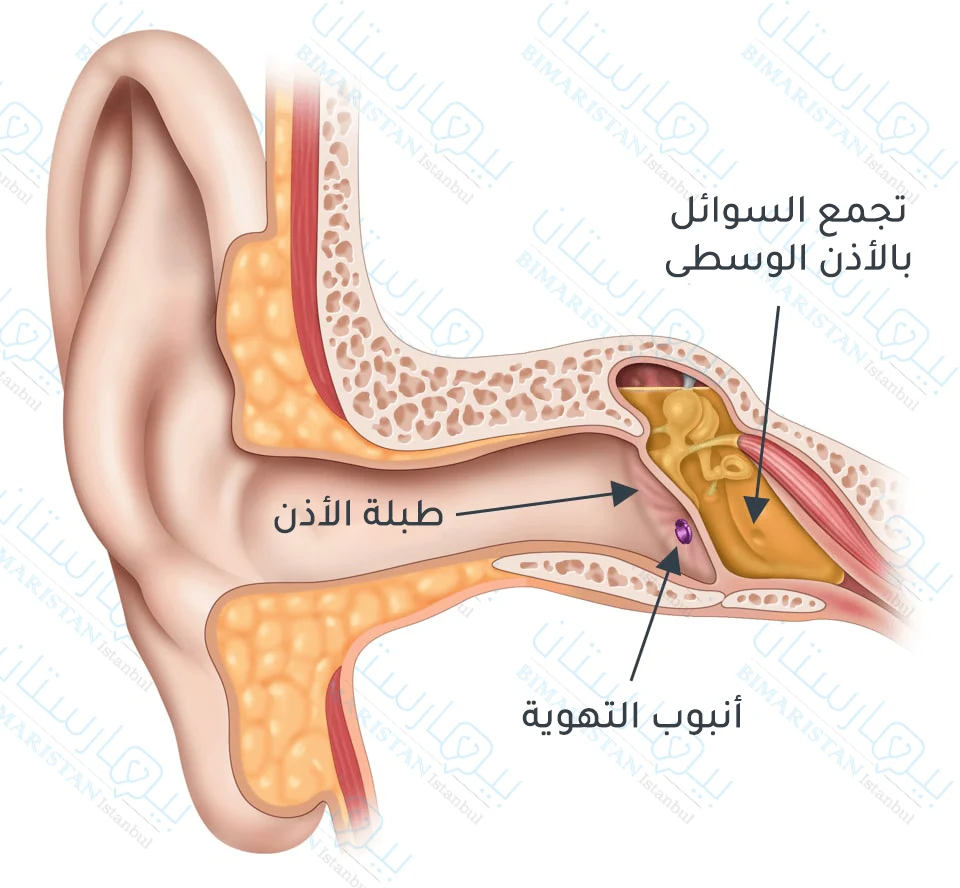
تركيب أنبوب تهوية الأذن الوسطى عبر فغر الطبلة (Tympanostomy tubes)
تستخدم هذه الوسيلة في علاج التهاب الأذن الوسطى المتكرر عند الكبار بسبب تراكم السائل بالأذن.
يقوم الجراح بعمل ثقبة صغيرة في طبلة الاذن يتمكن خلالها من شفط السوائل من أذن المريض ومن ثم يتم وضع أنبوب صغير يعمل على تهوية الأذن الوسطى ومنع عودة تراكم السائل فيها، يعتبر عمل جراحي بسيط يمكن إجرائه بالعيادة الخارجية.
مدة علاج التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار
غالباً ما تكون فترة علاج التهاب الاذن الوسطى الغير مختلط هي 5 إلى 7 أيام كورس علاجي بالصادات الحيوية، في حال لم يتحسن الشخص بعد هذه المدة يتم تغيير نوع المضاد الحيوي.
المضاعفات
لا يعتبر التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار من الأمراض الخطيرة بطبيعة الحال، لكن في حال تُرك بدون علاج قد ينتج بسببه اختلاطات ذات خطورة عالية.
من المضاعفات المحتملة والناتجة عن التهاب الاذن الوسطى عند الكبار ما يلي:
- نقص وفقدان السمع
- تمزق بغشاء الطبل
- التهاب أذن قيحي
- الورم الكوليسترولي
- التهاب الخشاء أو عظم الصخرة
- شلل العصب الوجهي
- انتشار الإنتان لمنطقة الرأس والدماغ
الوقاية من التهاب الأذن الوسطى
هنا بعض النصائح التي تساعد في الوقاية من التهاب الأذن الوسطى للكبار والأطفال:
الإقلاع عند التدخين
أثبتت الدراسات أن المدخنين هم أكثر عرضة لالتهاب الأذن، بالإضافة إلى أن الأطفال المعرضين لدخان السجائر كانوا أكثر قابلية لتطوير التهاب أذن وسطى، لذا يُنصح بتجنب التدخين بالقرب من الأطفال لكون الإلتهاب أشد انتشاراً بينهم.
السيطرة على الحساسية
في حال معاناتك من تحسس اتجاه عامل معين (كغبار الطلع، الحيوانات) فمن الأفضل الابتعاد عنهم وتجنب إثارة هجمة تحسسية لكونها تزيد من خطر الإصابة بالالتهاب.
الوقاية من نزلات البرد
احفظ نفسك من التعرض لدرجات حرارية منخفضة واحرص على غسل يديك جيداً وتجنب مخالطة الاشخاص الذين تظهر لديهم أعراض الزكام، حيث أن معظم التهابات الاذن الوسطى تكون تالية للزكام وخاصةً عند الأطفال.
تلقيح الأطفال
تلقيح الأطفال الصغار ضد الأمراض الفيروسية كالإنفلونزا يساعد في عملية الوقاية، حيث أن الوقاية من العدوى الفيروسية يقي من التهاب الاذن عند الأطفال.
الإرضاع الطبيعي
يحوي حليب الأم الطبيعي على أضداد مناعية تمرر للطفل بالإرضاع مما يزيد من مناعة الأطفال الرضع ويحميهم من التقاط عدوى بالفيروسات أو الجراثيم.
