يُعد التهاب القولون التقرُحي من الأمراض الالتهابية التي تُصيب الأمعاء الغليظة، يسبب أعراض تؤثر على نوعية الحياة، يتم في تركيا تدبير وعلاج التهاب القولون التقرحي.
لمحة عن القولون
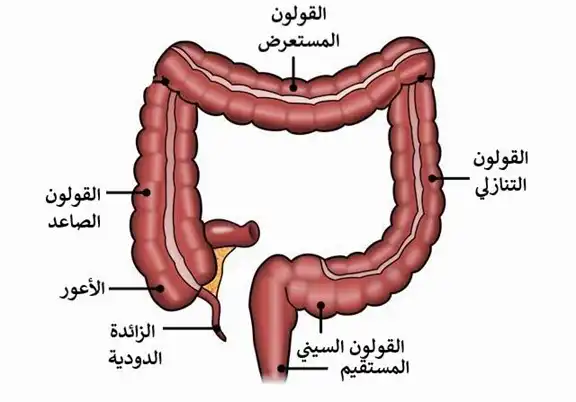
يمتد القولون من نهاية الأعور إلى بداية المُستقيم حيث يبلُغ طول القولون حوالي 150 سم.
إن الوظيفة الرئيسية للقولون هي إمتصاص الماء والأملاح من الأطعمة غير المهضومة وتحويل ما تبقى إلى فضلات (براز) ليتم طرحها إلى خارج الجسم عبر فُتحة الشرج.
يُقسم القولون تشريحياً إلى أربع أقسام :
- قولون صاعد
- قولون مُعترض
- قولون نازل
- القولون السيني
ما هو التهاب القولون التقرحي
يقتصر الالتهاب الحاصل على الأمعاء الغليظة فقط، على عكس داء كرون الذي يُسبب التهاب وتقرُحات على طول الجهاز الهضمي من الفم حتى الشرج.
وقد يتطور المرض ليُعطي مُضاعفات خطيرة مهددة للحياة تتطلب تدخُل جراحي عاجل.
أسباب التهاب القولون التقرحي
السبب الرئيسي لالتهاب القولون التقرحي غير مفهوم بشكل كامل، لكن تم إيجاد فرضيات عن الأسباب والعوامل المحتملة التي تؤدي لحدوث المرض وتفاقُم أعراضه:
فرضية الوراثة:
تٌعلل هذه الفرضية سبب التهاب القولون التقرُحي إلى خلل وراثي في عمل الخلايا المناعية, حيثُ تهاجم الخلايا المناعية الجراثيم المُتعايشة بشكل طبيعي في القولون مما يسبب التهابات وتقرُحات متكررة.
في الحقيقة, إنََ وجود قصة عائلية للإصابة بالمرض يرفع خطر الإصابة عند الأقارب حيثُ وجد أنََ حوالي 10 إلى 25% من المصابين بالتهاب القولون التقرحي يملكون قريب مُصاب إما بالتهاب الكولون التقرُحي أو داء كرون.
العوامل البيئية: ربطت بعض الدراسات العوامل البيئية بارتفاع احتمال الإصابة بالتهاب القولون التقرُحي, فاحتمال الإصابة بكون أعلى عند سُكان المدن من سكان الريف يُمكن أن يعود السبب وراء ذلك إلى تلوث الهواء في المُدن والحمية الغذائية الغنية بالدهون والمواد الضارة.
الأدوية المضادة للالتهابات اللاستيروئيدية (NSAIDS): وجدت بعض الدراسات أنََ ثُلث المرضى المُصابين بالتهاب القولون التقرُحي تتفاقم أعراضُهم عند استخدام تلك الأدوية.
العوامل النفسية: قد تلعب دور في تطور الإصابة بالمرض وتفاقُم الأعراض فبحسب دراسة أُجريت عام 2015 فإن 82% من مرضى التهاب القولون التقرُحي يعانون من مشاكل نفسية وغالباً تكون هذه المشاكل مُشخصة قبل تشخيص التهاب القولون التقرحي.
التدخين: وجدت بعض الدراسات أن المُدخنين أقل عُرضة للإصابة بالمرض (هذا لا يعني ان ننصح المريض بالتدخين للوقاية حيثُ يترافق التدخين مع مُشكلات طبية أٌخرى لا تُعد ولا تُحصى).
أعراض التهاب القولون التقرحي
- التغوط المُدمى (دم في البراز)
- الإسهال وقد يكون شديد
- ألم أسفل البطن
- غثيان وتعب
- فقر دم
- مع الزمن قد يحصل خسارة وزن
- مخاط أو قيح في البراز
- حُمى وطفح جلدي
- ألم على مستوى المفاصل
- التهاب قزحية العين
- ألم شديد بالبطن
- اضطراب بالشوارد
تشخيص التهاب القولون التقرحي في تركيا
عملية تنظير القولون
يُمكن وبواسطة التنظير أخذ خُزعة من القولون لفحصها في المخبر تحت المجهر وتحرََي وجود التغيُرات المرضية حيث يجب أخذ عدة خُزعات للتحري وتأكيد الإصابة.
يُعتبر تنظير القولون المعيار الذهبي لتشخيص التهاب القولون التقرحي.
الفحوصات الدموية
زرع البراز
الصور الشُعاعية الأٌخرى
طرق علاج التهاب القولون التقرحي في تركيا
العلاج الدوائي
في الحالات ذات الأعراض الخفيفة يتم علاج التهاب القولون التقرحي باستخدام أدوية تُقلل من الالتهابات الحاصلة في الأمعاء الغليظة ومن تلك الأدوية نذكر:
الامينوساليسيلات
من أشهر الأدوية المُستخدمة في هذه المجموعة السلفازينيل والميزالامين حيث يُعطى الميزالامين على شكل تحميلة شرجية تتميز التحميلة بتأثير جيد على المُستقيم, لكن قد يكون تأثيرُها على القولون ضعيف لذلك يلجأ للمشاركة بين التحاميل والأدوية الفموية.
الستيروئيدات
في حال عدم الاستجابة للمُعالجة السابقة أو في الحالات ذات الأعراض الأشد يتم اللجوء للستيروئيدات التي تثبط من التفاعلات الالتهابية الحاصلة، أشيع الستيروئيدات المُستخدمة البريدينوزن (prednisone) ويجب استشارة الطبيب عند أخذ الستيروئيدات فقد تُسبب اختلاطات قد تكون خطيرة في حال سحب الدواء بشكل مُفاجىء أو الإكثار من الجُرعة.
العلاج البيولوجي
في الحالات ذات الأعراض الشديدة من التهاب القولون التقرُحي والغير مُستجيبة للعلاجات السابقة يتم إعطاء الأدوية البيولوجية التي أثبتت فعاليتها كالإنفلكسيماب (infliximab), حيث يقوم هذا الدواء بكبح عامل التثبيط الورمي TNF وبالتالي يضعف الاستجابة الالتهابية في الجسم ككُل.
يتم أخذ هذا الدواء بجُرعات مُحددة فقد يرفع خطر حُدوث أمراض انتانية بالأخص عند ضعيفي المناعة.
العلاج الجراحي
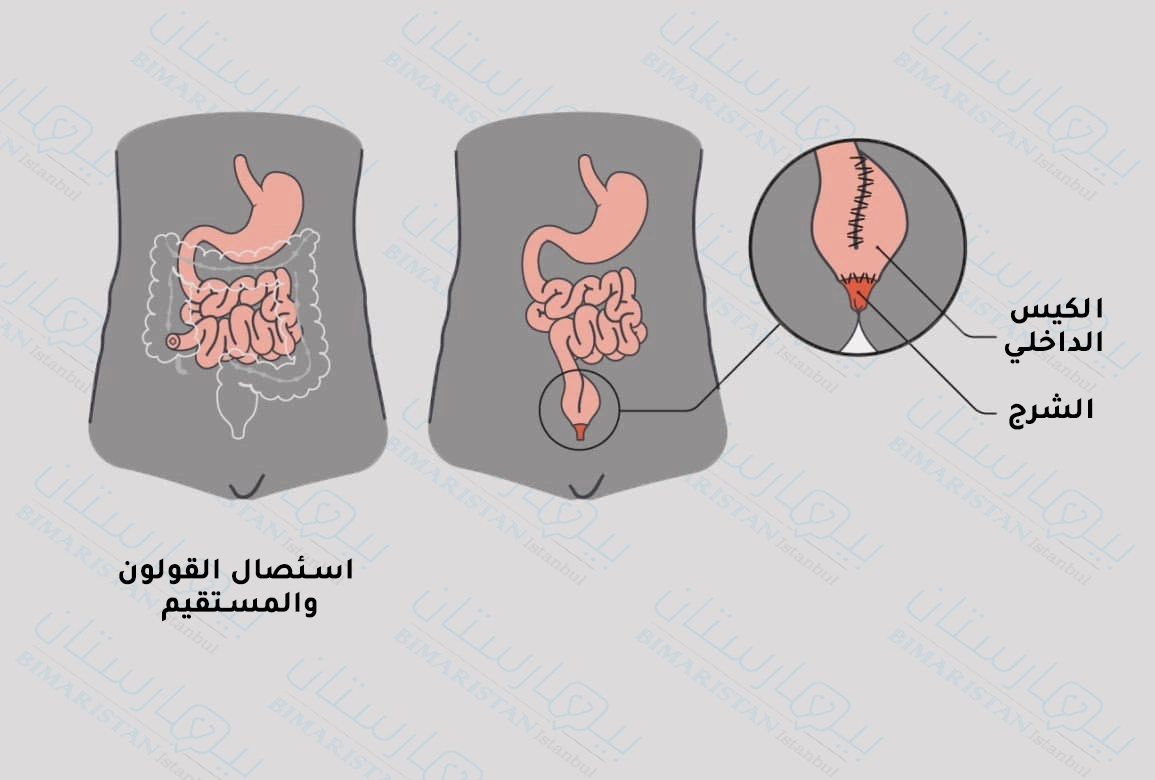
استئصال القولون والمٌستقيم مع جيب اللفائفي j-pouch procedure
يتم هذا الإجراء على عدة مراحل أي يحتاج المريض لعمليتين أو ثلاثة حسب الحالة الصحية للمريض.
العملية الأولى
إن الهدف من فغر اللفائفي هو إتاحة الفرصة للكيس بأخذ مكانه جيداً ريثما يتم إزالة الحقيبة الخارجية ويأخُذ الكيس الجديد (j pouch) وظيفته و دور الكولون المُستأصل.
العملية الثانية
بعد حوالي 8 إلى 12 أسبوع من العملية الأولى يكون الكيس الداخلي (j pouch) جاهز لأداء وظيفته فيتم بهذه العملية إغلاق فغر اللفائفي وإزالة الحقيبة الخارجية حيثُ يُصبح المريض قادر على طرح الفضلات عبر الكيس الجديد الذي يصل بين الأمعاء الدقيقة والشرج.
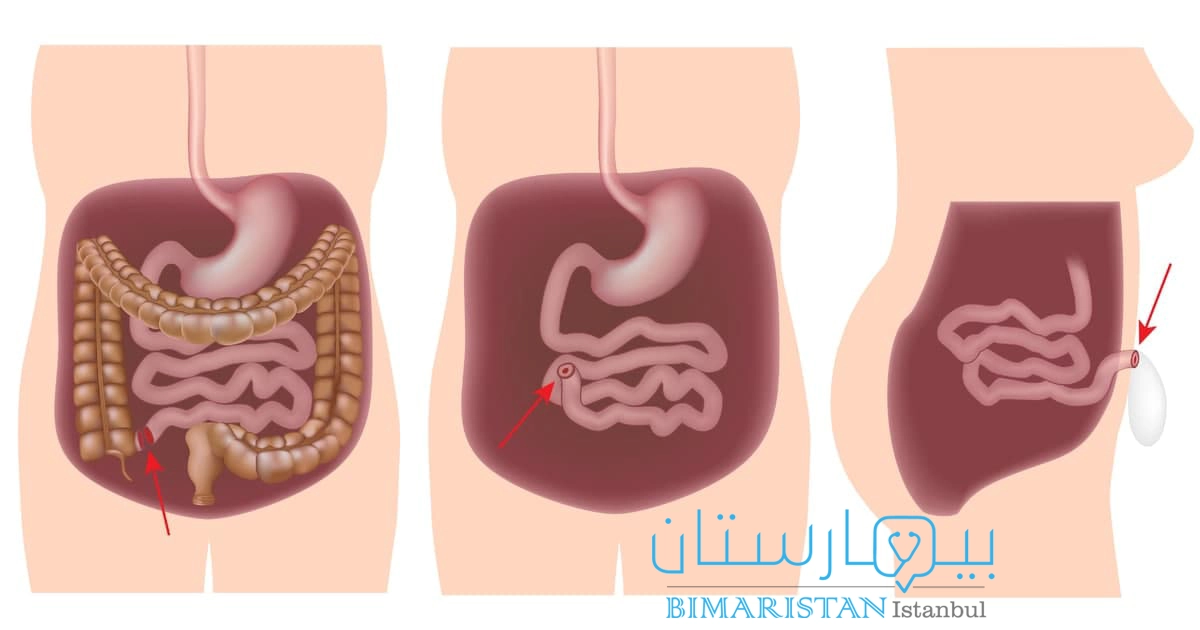
استئصال القولون والمٌستقيم والشرج مع فغر نهائي للفائفي
يتم في هذا النوع من العملية ارتداء حقيبة خارجية لبقية حياة المريض، يتم تغيير الحقيبة من فترة لاُخرى حسب تعليمات الطبيب، طبعاً هذا النمط أصعب للمريض من الجراحة الأولى التي لا تحتاج لحقيبة خارجية.
التحضير قبل العمل الجراحي
يجب الامتناع عن الأكل والشرب قبل العملية لمدة ساعات أو ليوم كامل وذلك بحسب تعليمات الطبيب.
بعد العمل الجراحي
يتم وضع المريض بعد العمل الجراحي على حمية غذائية تحوي أطعمة لينة ويجب تجنُب الأطعمة التي تُسبب غازات ويُنصح المريض بشرب كميات وافرة من الماء.
يحتاج الجسم لفترة كي يعتاد على التغيُرات الحاصلة، ففي البداية بعد عملية تركيب الكيس لا يُعطي الكيس الجديد نفس وظيفة الكولون المستأصل بل يحتاج وقت لكي يأخذ الشكل والحجم المناسب.
يصل عدد مرات التغوط لحوالي 8 مرات باليوم بعد عدة أشهُر من العملية وتختلف من شخص لآخر وقوام البراز يكون أقرب للمائي.
لماذا أختار تركيا للعلاج؟
في الآونة الأخيرة أصبحت تركيا من الدول الرائدة في مجال السياحة العلاجية على مستوى العالم يعود السبب وراء ذلك إلى توفير العلاج المُناسب بمراكز مُتطورة وتكلفة قليلة.